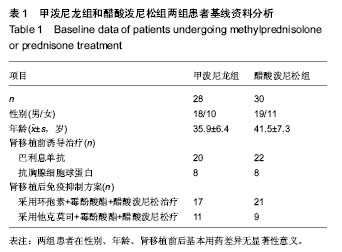
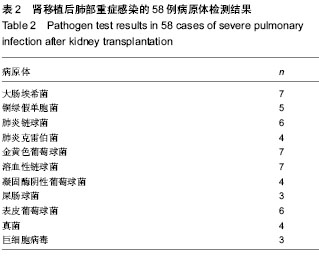
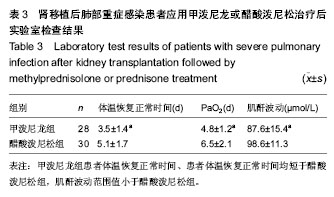
| [1] San Juan R, Aguado JM, Lumbreras C, et al. clinical characteristics and risk factors of late infection in solid-organ transplant recipients: data from the RESITRA study group. Am J Transplant.2007;7(4):964-971.[2] Jha R, Narayan G, Jalel M, et al. Pulmonary infections after kidney transplantation. J Asoc Physicians lndia.1999;47(8): 779-783.[3] Kupeli E, UlubayG, Colak T, et al. Pulmonary complications in renal recipients after transplantation. Transplant Proc.2011; 43(2):551-553.[4] 中华医学会重症医学分会.急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊断和治疗指南(2006)[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2007,16(4): 343-349.[5] Fishman JA.Infection in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(25): 601-614.[6] 曾力,刘鹏,张雷,等.肾移植患者术后重症肺部感染的诊治经验[J].器官移植杂志,2011,3(2):152-156.[7] 郭君其,谭建明,吴守法,等.肾移植术后并发感染的病原体监测及菌群分布特点[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2003,13(4):386-388.[8] Hoyo I, Linares L, Cervera C, et al. Epidemiology of pneumonia in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc.2010;42(8):2938-2940.[9] Schwerk N, Hartmann C, Baumann U, et al. Chronic Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in a child after renal transplantation.Pediatr Transplant. 2010;14(3):E26-29.[10] 邵晓丽,刘淑梅,楼文勇,等.甲泼尼龙辅助治疗难治性支原体肺炎疗效观察[J].中国全科医学,2011,14(01):186-187.[11] Camara B, Mouzin M, Ribes D, et al. Perihepatitis and perinephric abscess due to Mycoplasma hominis in a kidney transplant patient.Exp Clin Transplant. 2007; 5(2):708-709.[12] Paran Y, Shalev V, Steinvil A, et al. Thrombosis following acute cytomegalovirus infection: a community prospective study.Ann Hematol. 2013;92:969-974. [13] Schimanski S, Linnemann B, Luxembourg B, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection is associated with venous thromboembolism of immunocompetent adults--a case-control study. Ann Hematol. 2012;91:597-604. [14] Kazory A, Ducloux D, Coaquette A, et al. Cytomegalovirus-associated venous thromboembolism in renal transplant recipients: a report of 7 cases. Transplantation. 2004;77:597-599.[15] 张勇.肾移植术后合并真菌性肺炎的X线分析[J].山西中医学院学报,2006,7(6):32-32.[16] Einolahi B, Lesan-Pezeshki M, Pourfarziani V, et al. Invasive fungal infections following renal transplantation: a review of 2410 recipients.Ann Transplant.2008;13(4):55-58. [17] 李利佳,全昌斌.肾移植术后以多脏器结节病灶为特点侵蚀性曲霉菌感染一例[J].中华临床医学杂志,2010,4(11):2333-2334. [18] Mathema B, Kurepina NE, Bifani PJ, et al. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis: current insights. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006t;19(4):658-685.[19] de Beer JL, van Ingen J, de Vries G, et al. “Comparative study of IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism and variable-number tandem-repeat typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in the Netherlands, based on a 5-year nationwide study. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(4):1193-198.[20] 金蕊,马雪梅,曾毅.EB病毒感染和自身免疫病的相关性研究[J].医学综述,2010,16(10):1465-146[21] 罗求本,胡遵德.甲泼尼龙联合抗生素治疗重症肺炎的临床研究[J].当代医学,2010,16(14):77.[22] 朱有华,闵志廉,齐隽,等.广义降阶梯治疗方案在肾移植后重症肺部感染患者中的应用[J].中华国际医学杂志,2002,2(6): 497-499.[23] Laurent J, Stanicki D, Huang TL, et al. Bisbenzamidines as antifungal agents. Are both amidine functions required to observe an anti-Pneumocystis carinii activity? Molecules. 2010;15:4283-4293.[24] 张琼.甲泼尼龙治疗肺炎支原体性大叶肺炎的临床效果分析[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(8):104-105[25] 许霞,郭述良.肾移植术后肺部感染的研究进展[J].重庆医学, 2013,42(1):82-84.[26] 黎东伟,刘龙山,李军,等. 国产重组抗CD25人源化单克隆抗体在肾移植免疫诱导中的应用研究[J]. 器官移植,2013,4(5):274- 278,298.[27] 杨其顺,张琳,杨广庭,等. 肾上腺皮质激素在肾移植术后肺部感染治疗中的应用研究[J]. 器官移植,2012,3(6):334-337. [28] 杨其顺,杨广庭,姜伟,等. 肾移植术后肺炎48例诊治分析[J]. 器官移植,2012,3(1):40-44. [29] 周洪澜,王远涛,王刚,等. 肾移植术后患者合并甲型H1N1流行性感冒的诊治(附3例报告)[J]. 器官移植,2011,2(3):165-167. [30] 杨广庭,姜伟,刘彦斌,等. 国产他克莫司胶囊对肾移植患者的疗效观察[J]. 中国药师,2011,14(4):534-535.[31] 朱云松,邱晓拂,王尉,等. 肾移植术后机会感染的预防[J]. 器官移植,2010,1(4):211-215. [32] 俞波,魏晓阳,杨渝,等. 两种方法治疗肾移植术后肺囊虫肺炎的临床研究[J].人民军医,2010,53(7):491-492.[33] 胡红星,邓素雄,郑克立,等. 肾移植术后巨细胞病毒肺炎的治疗探讨——附35例报告[J].新医学,2007,38(10):643-644. [34] 赵永伟,梅如冰,刘志峰,等. 肾移植术后巨细胞病毒肺炎22例临床分析[J].山东医药,2007,47(18): 59-60. [35] 卫红涛,史丽敏,程晟,等. 2004年我院肾移植患者免疫抑制剂应用分析[J].中国药房,2006,17(9):675-677.[36] 费继光,陈立中,王长希,等.糖皮质激素在治疗肾移植术后巨细胞病毒性重症肺炎中的作用[J].中华器官移植杂志,2005, 26(12): 748-750.[37] 沙国柱,尹广,季大玺,等.免疫吸附和他克莫司、霉酚酸酯及甲泼尼龙联合治疗移植肾加速性排斥反应[J].医学研究生学报,2004, 17(3):251-255. |