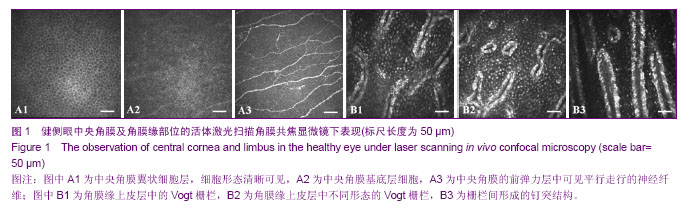
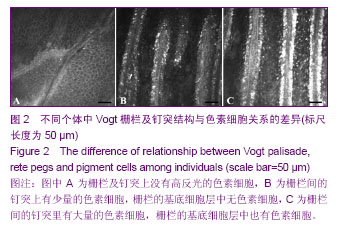
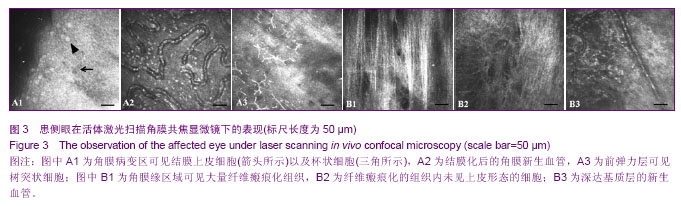
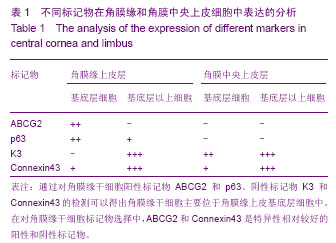
| [1] Davanger M, Evensen A. Role of the pericorneal papillary structure in renewal of corneal epithelium. Nature. 1971; 229(5286):560-561.[2] Schermer A, Galvin S, Sun TT. Differentiation-related expression of a major 64K corneal keratin in vivo and in culture suggests limbal location of corneal epithelial stem cells. J Cell Biol. 1986;103(1):49-62.[3] Chen Z, de Paiva CS, Luo L,et al. Characterization of putative stem cell phenotype in human limbal epithelia.Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):355-366.[4] Majo F, Rochat A, Nicolas M,et al. Oligopotent stem cells are distributed throughout the mammalian ocular surface.Nature. 2008;456(7219):250-254. [5] Sindt CW, Lay B, Bouchard H, et al. Rapid image evaluation system for corneal in vivo confocal microscopy.Cornea. 2013; 32(4):460-465. [6] Hamrah P, Cruzat A, Dastjerdi MH,et al. Unilateral herpes zoster ophthalmicus results in bilateral corneal nerve alteration: an in vivo confocal microscopy study. Ophthalmology. 2013;120(1):40-47.[7] Ledbetter EC, Scarlett JM.In vivo confocal microscopy of the normal equine cornea and limbus.Vet Ophthalmol. 2009;12 Suppl 1:57-64.[8] Priya CG, Prasad T, Prajna NV,et al.Identification of human corneal epithelial stem cells on the basis of high ABCG2 expression combined with a large N/C ratio.Microsc Res Tech. 2013;76(3):242-248.[9] Lim MN, Umapathy T, Baharuddin PJ,et al. Characterization and safety assessment of bioengineered limbal epithelium. Med J Malaysia. 2011;66(4):335-341.[10] Dobrowolski D, Wylega?a E, Orzechowska-Wylega?a B,et al. Culture morphology of the autologous cultivated corneal epithelium.Klin Oczna. 2011;113(7-9):249-253.[11] Turuwhenua JT, Patel DV, McGhee CN. Fully automated montaging of laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy images of the human corneal subbasal nerve plexus.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(4):2235-2242. [12] Misra S, Craig JP, McGhee CN,et al. Interocular comparison by in vivo confocal microscopy of the 2-dimensional architecture of the normal human corneal subbasal nerve plexus.Cornea. 2012;31(12):1376-1380.[13] Patel DV, Sherwin T, McGhee CN. Laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy of the normal human corneoscleral limbus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(7):2823- 2827.[14] Zarei-Ghanavati S, Ramirez-Miranda A, Deng SX. Limbal lacuna: a novel limbal structure detected by in vivo laser scanning confocal microscopy. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2011;42 Online:e129-131.[15] Petroll WM, Weaver M, Vaidya S,et al. Quantitative 3-dimensional corneal imaging in vivo using a modified HRT-RCM confocal microscope.Cornea. 2013;32(4):e36-43.[16] Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Miani F, et al. Comparison between laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy and noncontact specular microscopy in assessing corneal endothelial cell density and central corneal thickness.Cornea. 2011;30(7): 754-759.[17] Bochert R, Zhivov A, Kraak R,et al. Contribution to comprehension of image formation in confocal microscopy of cornea with Rostock cornea module.Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89(10):1351-1355.[18] Shortt AJ, Secker GA, Munro PM,et al. Characterization of the limbal epithelial stem cell niche: novel imaging techniques permit in vivo observation and targeted biopsy of limbal epithelial stem cells.Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1402-1409.[19] Falke K, Prakasam RK, Guthoff RF,et al. In vivo imaging of limbal epithelium and palisades of Vogt. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2012;229(12):1185-1190.[20] Zhu WQ, Xu JJ, Sun XH,et al. The ocular surface of severe alkali burns patients on confocal microscopy. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2010;46(1):18-24.[21] Miri A, Alomar T, Nubile M,et al. In vivo confocal microscopic findings in patients with limbal stem cell deficiency.Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96(4):523-529.[22] Sejpal K, Bakhtiari P, Deng SX. Presentation, diagnosis and management of limbal stem cell deficiency. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2013;20(1):5-10.[23] Nubile M, Lanzini M, Miri A,et al. In vivo confocal microscopy in diagnosis of limbal stem cell deficiency. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;155(2):220-232. [24] Lagali N, Edén U, Utheim TP,et al. In vivo morphology of the limbal palisades of vogt correlates with progressive stem cell deficiency in aniridia-related keratopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54(8):5333-5342.[25] Ledbetter EC, Scarlett JM. In vivo confocal microscopy of the normal equine cornea and limbus.Vet Ophthalmol. 2009;12 Suppl 1:57-64. [26] Zarei-Ghanavati S, Ramirez-Miranda A, Deng SX. Limbal lacuna: a novel limbal structure detected by in vivo laser scanning confocal microscopy. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2011;42 Online:e129-131.[27] Fatima S, Zhou S, Sorrentino BP. Abcg2 expression marks tissue-specific stem cells in multiple organs in a mouse progeny tracking model.Stem Cells. 2012;30(2):210-221.[28] de Paiva CS, Chen Z, Corrales RM,et al. ABCG2 transporter identifies a population of clonogenic human limbal epithelial cells.Stem Cells. 2005;23(1):63-73.[29] Budak MT, Alpdogan OS, Zhou M,et al. Ocular surface epithelia contain ABCG2-dependent side population cells exhibiting features associated with stem cells.J Cell Sci. 2005; 118(Pt 8):1715-1724.[30] Chen W, Hara K, Tian Q,et al. Existence of small slow-cycling Langerhans cells in the limbal basal epithelium that express ABCG2. Exp Eye Res. 2007;84(4):626-634.[31] Cancino GI, Yiu AP, Fatt MP,et al. p63 Regulates adult neural precursor and newly born neuron survival to control hippocampal-dependent Behavior. J Neurosci. 2013;33(31): 12569-12585. [32] Pignon JC, Grisanzio C, Geng Y,et al. p63-expressing cells are the stem cells of developing prostate, bladder, and colorectal epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(20): 8105-8110.[33] Nubile M, Curcio C, Dua HS,et al. Pathological changes of the anatomical structure and markers of the limbal stem cell niche due to inflammation. Mol Vis. 2013;19:516-525.[34] Loureiro RR, Cristovam PC, Martins CM,et al. Comparison of culture media for ex vivo cultivation of limbal epithelial progenitor cells. Mol Vis. 2013;19:69-77.[35] Ueno H, Ferrari G, Hattori T,et al. Dependence of corneal stem/progenitor cells on ocular surface innervation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(2):867-872.[36] Shahdadfar A, Haug K, Pathak M, et al. Ex vivo expanded autologous limbal epithelial cells on amniotic membrane using a culture medium with human serum as single supplement. Exp Eye Res. 2012;97(1):1-9. [37] Márquez-Rosado L, Solan JL, Dunn CA,et al. Connexin43 phosphorylation in brain, cardiac, endothelial and epithelial tissues.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1818(8):1985-1992.[38] Kameritsch P, Pogoda K, Pohl U.Channel-independent influence of connexin 43 on cell migration.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1818(8):1993-2001. [39] Matic M, Evans WH, Brink PR,et al. Epidermal stem cells do not communicate through gap junctions.J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118(1):110-116.[40] Grueterich M, Espana E, Tseng SC. Connexin 43 expression and proliferation of human limbal epithelium on intact and denuded amniotic membrane. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43(1):63-71.[41] Chen Z, Evans WH, Pflugfelder SC,et al. Gap junction protein connexin 43 serves as a negative marker for a stem cell-containing population of human limbal epithelial cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1265-1273. |