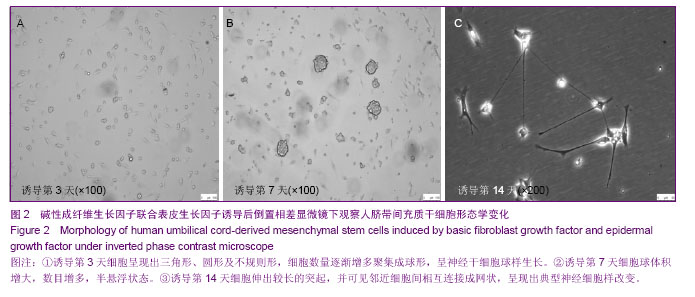
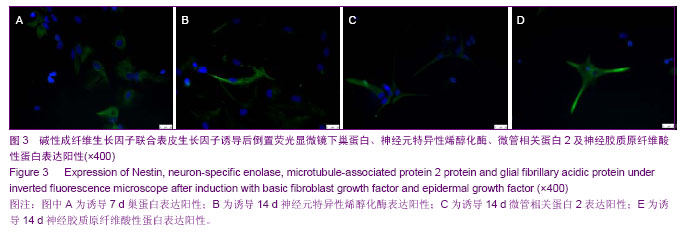
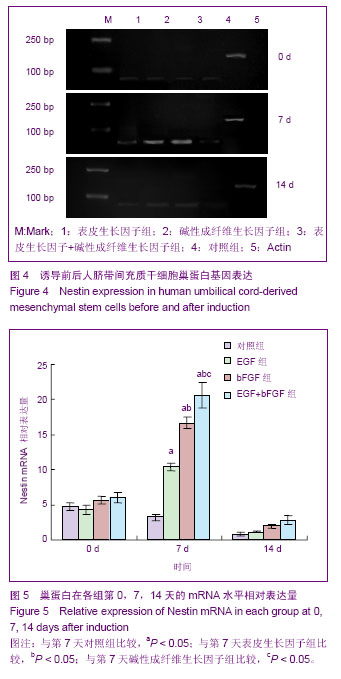
| [1] McMahon SS, Albermann S, Rooney GE, et al. Engraftment, migration and differentiation of neural stem cells in the rat spinal cord following contusion injury. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(3):313-325.[2] 姚星宇,杨丽敏,张国华.不同途径移植HUBMNCs对脑出血大鼠神经功能的影响[J].中国卒中杂志,2012,7(10):786-797.[3] Cao Q, Whittemore SR. Cell transplantation: stem cells and precursor cells. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;109:551-561.[4] Xiong N, Zhang Z, Huang J, et al. VEGF-expressing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, an improved therapy strategy for Parkinson’s diease. Gene therapy. 2011;18(4): 394-402.[5] 李志营,步星耀,张圣旭,等.自体骨髓干细胞动员移植与手术移植治疗脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中华临床医师杂志,2010,4(9): 1587-1594.[6] Chen L, Zhang ZG, Chen B, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces neuron-like cellular differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood cells in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(13):972-977.[7] in’t Anker PS, Noort WA, Scherjon SA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in human second-trimester bone marrow, liver, lung, and spleen exhibit a similar immunophenotype but a heterogeneous multilineage differentiation potential. Haematologica. 2003;88(8):845-852.[8] Zhou J, Tian GP, Wang JE, et al. In vitro differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells and bone marrow-derived stromal stem cells into neuronal-like cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011; 6(19):1467-1472.[9] Pang KM, Sung MA, Alrash-dan MS, et al. Trans-plantation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord versus human umbilical cord blood for peripheral nerve regenera-tion. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(11):838-845.[10] Nekanti U, Mohanty L, Venugopal P, et al. Optimization andScale-up of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical applications. Stem Cell Res.2010;5(3):244-254.[11] 姚星宇,杨丽敏,张国华. HUBMNCs中的神经样细胞研究[J].临床神经病学杂志,2013,26(1):41-43.[12] Ma K, Fox L, Shi G, et al. Generation of neural stem cell-like cellsFrom bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Neurol Res. 2011;33(10):1083-1093.[13] 张建富,孟庆海,金澎,等.全骨髓贴壁法获得纯化骨髓间充质干细胞向神经干细胞的诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12):2240-2244.[14] Scuteri A, Miloso M, Foudah D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells neuronal differentiation ability: a real perspective for nervous system repair. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;6(2):82-92.[15] Rismanchi N, Floyd CL, Berman RF, et al. Cell death and long-term maintenance of neuron-like state after differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells: a comparison of protocols. Brain Res. 2003;991(1-2):46-55.[16] Goldberg JL, Barres BA. The relationship between neuronal survival and regeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2000;23: 579-612.[17] 张毅敏,唐纯志,程少冰,等.针刺对创伤性脑损伤大鼠脑组织EGF和bFGF表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(6): 1132-1134.[18] 吴晓娟,魏明发,柴成伟,等.胶质细胞源神经营养因子在大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞神经分化中的表达[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2009, 24(23):1806-1808.[19] 王丰,屠冠军,朱悦. bFGF对神经干细胞分化为星形胶质细胞的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2012,41(3):193-197.[20] Brewer GJ. Regeneration and proliferation of embryonic and adult rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Exp Neurol. 1999; 159(1):237-247.[21] Liu Y, Dulchavsky DS, Gao X, et al.Wound repair by bone marrow stromal cells through growth factor production. J Surg Res.2006:136(2):336-341.[22] Fuse K, Tinner B. Zoli M, et al. Computer assisted mapping of basic fibroblast growth factor immunore active nerve cell population in the rat brain. J Chem Neuroanal. 1996; 11(1): 13-35.[23] Li JS, Zhou YL, Liu K, et al. angiogenesis of brain after ischemia/reperfusion injury of brain in aged rats and changes in expressions of basic fibroblast growth factor factor and transformation growth factor-β1. Chin crit care med. 2010; 22(10):583-586. [24] 石旺清,郑关毅,陈晓东,等.大鼠脑缺血/再灌注后bFGF和GAP-43的表达与神经再生[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2013,29(1): 63-67.[25] Sanalkumar R, Vidyanand S, Lalitha Indulekha C, et al. Neuronal vs. glial fate of embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors(ES-NPs)is determined by FGF2/EGF during proliferation. J Mol Neurosci. 2010;42(1):17-27.[26] Ciccolini F, Svendsen CN. Fibroblast growth factor2(FGF-2) promotes acquisition of epidermal growth factor (EGF) responsiveness in mouse striatal precursor cells: identification of neural precursors responding to both EGF and FGF-2. J Neurosci. 1998;18(19):7869-7880.[27] 何丁文,殷嫦嫦,顾玉荣. bFGF和EGF诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化成神经样细胞[J].基础医学与临床,2013,33(4):444-449.[28] Mckay R. Stem cells in the central nervous system. Science. 1997;276(5309):66-71.[29] Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB, McKay RD. CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell. 1990;60(4):585-595.[30] Chen N, Kamath S, Newcumb J, et al. Trophic factor induction of human umbilical cord blood cells in vitro and in vivo. J Neural Eng. 2007;4(2):130-145.[31] Maslov AY, Barone TA Plunkett RJ. et al. Neural stem cell detection, characterization. and age-related changes in the subventricular zone of mice. J Neurosci.2004;24(7): 1726-1733.[32] Zulewski H, Abraham EJ, Gerlach MJ, et al. Multipotential nestin-positive stem cells isolated from adult pancreatic islets differentiate ex vivo into pancreatic endocrine, exocrine, and hepatic phenotypes. Diabetes. 2001;50(3):521-533.[33] Piras F, Ionta MT, Lai S, et al. Nestin expression associates with poor prognosis and triple negative phenotype in locally advanced (T4) breast cancer. Eur J Histochem. 2011;55(4): e39. |
.jpg)