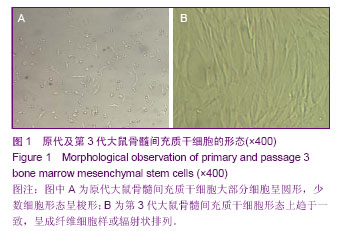
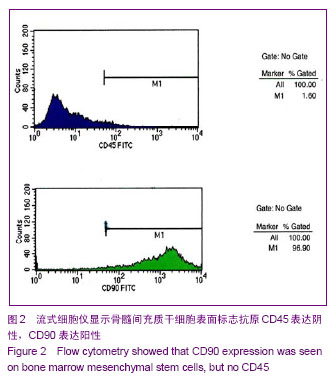
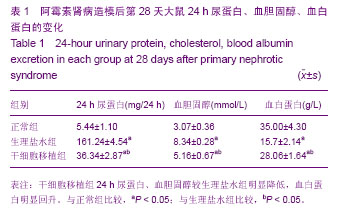
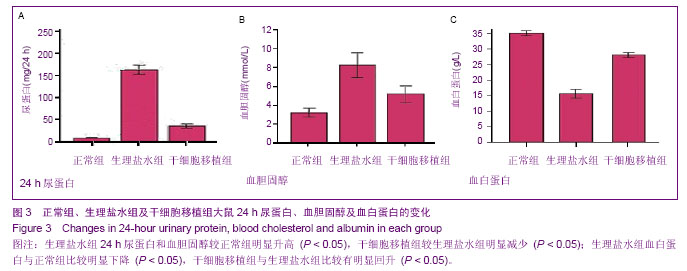
| [1] Shalhoub RJ.Pathogenesis of Lipoid nephroeis:a disorder of T-cell function.Lancet.1974;2(7880):556-560.[2] Karczewski M,Karczewski J,Kostrzewa A,et al. The role of foxp3+ regulatory T cells in kidney transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings.2009;41:1527.[3] 丰炳峰,董晨,关凤军.全骨髓法培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其生物学特性[J].徐州医学院学报,2009, 29(4):226-229.[4] 李艳菊,李宁,胡亮杉,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养方法的改进[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(1):71-74.[5] 赵科研,柳克祥,侯明晓,等.Wistar大鼠骨髓间充质于细胞的培养、鉴定和标记[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(11):1556-1558.[6] Bertani T,Poggi A,Pozzoni R,et al. Adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrom rats. LabInvest.1982;46 (1):16-23.[7] 杜宇,魏红,李海涛.阿霉素大鼠肾病模型的概述[J].中国医药指南, 2013,11(9):78-79. [8] 张勇,张蓓,宁华英,等.单次尾静脉注射法阿霉素大鼠肾病模型的建立[J].中国实验动物学报,2013,21(1):1-4,封2页.[9] 马晓红,何立群.不同剂量阿霉素致大鼠局灶节段硬化肾病模型的建立比较[J].中国比较医学杂志,2013, 23 (1):37-42,后插2-后插3页.[10] 蔺建军,杨勇,高娜,等. 阿霉素注射次数及剂量对肾病综合征模型的影响[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2011,12(8):676-678.[11] 高顺清.阿霉素肾病大鼠模型建立及泼尼松的干预作用[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2011,32(15):2397-2400. [12] 杨维娜,于琳华,郭尚温,等.改良阿霉素肾病大鼠模型的建立[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2009,30(4):445-448,452. [13] 董孟华,刘志学,孟祥辉,等.阿霉素小鼠肾病模型的建立及IL-18结合蛋白干预的实验研究[J].滨州医学院学报,2009,32(1): 13-15.[14] 李新建,刘晓城.小鼠进展性肾病模型建立的探讨及相关研究[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2005,36(2):173-177.[15] 张丽芬,黄文政,朱小棣,等. 阿霉素肾病肾小球硬化动物模型的研究[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2005,6(4):195-199.[16] 王新颖,牟兆新,王新良,等.阿霉素肾病大鼠肾脏nephrin、podocin mRNA表达[J].河北医科大学学报,2005,26(6):418-422[17] 许涛,吕磊,钱琛,等.大鼠阿霉素肾病的病理学观察[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2001,6(1):43-45. [18] 熊祖应,丁长海,张伯科,等.大鼠慢性肾功能不全模型的建立[J].安徽医科大学学报,2000,35(2):101. [19] 夏正坤,高远赋,刘光陵,等.阿霉素肾病肾组织中环孢素亲合素基因的表达[J].医学研究生学报,2000,13(S1): 35-37. [20] 毕黎琦,刘晓敏,何成彦,等.肾病综合征大鼠模型的建立及酶酚酸酯对其作用的实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2000,16(12): 681-684.[21] 董晨,卢思广,夏志强,等.双肾动脉给阿霉素制备大量蛋白尿大鼠模型[J].徐州医学院学报,1999,29(5):356-358.[22] 熊祖应,梅俏,丁长海,等. 松果腺摘除联合阿霉素肾病动物模型的建立[J].中国药理学通报,1999,15(3):283.[23] Maggi E, Cosmi L, Liotta F, et al. Thymic regulatory T cells. Autoimmun Rev.2005;4(8):579-586.[24] 高美华,薛静波,王静,等.细胞与分子免疫学[M].东营:中国石油大学出版社,2008,203-204.[25] Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N,Asano M,et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alphachains(CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune disease. J Immunol.1995;155(3): 1151-1164.[26] Nagahama K,Nishimura E,Sakaguchi S. Induction of tolerance by adoptive transfer of Treg cells.Methods Mol Biol.2007;380:431-442.[27] Marson A,Kretschmer K,Frampton GM, et al. FoxP3 occupancy and regulation of key target genes during T-cell stimulation. Nature.2007;445(7130): 931-935.[28] 黄业华,任伟,杨冰.调节性T细胞对肾脏疾病的影响[J].中国临床保健杂志,2007,10(3):236-238.[29] 杨军,李成荣,黄惠君,等. 泼尼松治疗原发性肾病综合征对患儿CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞的影响分析[J].中国实用儿科杂志, 2009, 24(5):369-371.[30] Benz K, Buttner M, Dittrich K, et al. Characterisation of renal immune cell infiltrates in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol.2010;25:1291-1298. [31] 董晨,杨焕丹,丰炳峰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对阿霉素肾病大鼠肾脏nephrin表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010; 14(32):5897-5902.[32] 杨焕丹,董晨,关凤军,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对嘌呤霉素氨基核苷肾病大鼠足细胞修复作用的研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志, 2010,12(6):483-487.[33] Aggarwal S,Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses.Blood.2005; 105(4):1815-1822.[34] Hamada A, Yoshioka S, Takuma D, et al. The Efect of Eriobotrya japonica Seed Extract on Oxidative Stress in Adriamycin-Induced Nephrepathy in Rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27(12):1961-1964.[35] Malarkodi KP, Balachandar AV, Varalakshmi P. The influence of lipoic acid On adfiamycin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;247(1/2):15-22.[36] Mansour H, Homs S,Desvaux D, et al. Intragraft levels of FoxP3 mRNA predict progression in renal transplants with borderline change.J Am Soc Nephrol.2008;19(12):2277-2281. |
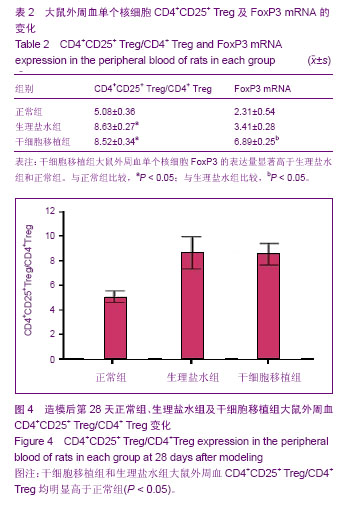
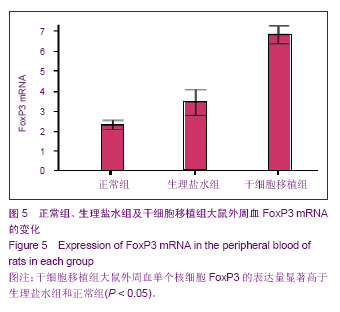
.jpg)