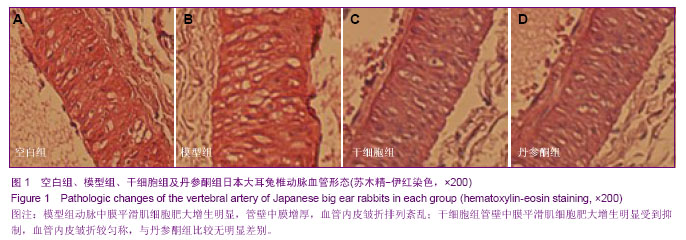
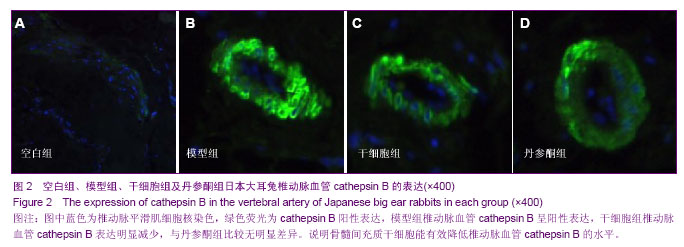
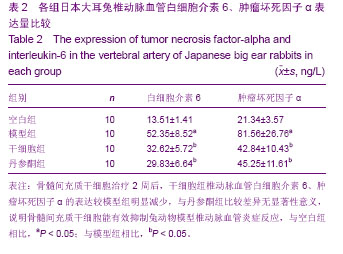
| [1] Yoon SH, Kim KJ, Chung SK,et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in the intradural extramedullary space of the lumbar spine with spondylolisthesis: case report and review of the literature.Eur Spine J. 2010;19 Suppl 2:S153-157.[2] Nagashima H, Morio Y, Yamane K,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-6 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with cervical myelopathy and lumbar radiculopathy.Eur Spine J. 2009;18(12):1946-1950. [3] Rodríguez-Mañas L, El-Assar M, Vallejo S,et al. Endothelial dysfunction in aged humans is related with oxidative stress and vascular inflammation. Aging Cell. 2009;8(3):226-238. [4] Tatenkulova SN, Mareev VIu, Zykov KA,et al.The role of inflammatory factors in pathogenesis of ischemic heart disease. Kardiologiia. 2009;49(1):4-8.[5] Lin XQ, Zhao HY, Sun Q. Acupuncture and massage therapy for 23 cases of pharyngitis caused by cervical vertebra disease。Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012;32(2):166.[6] Schmid RA, Schwenzer K, Weiss M,et al. Monostotic Paget's Disease of a cervical vertebra: differential diagnosis with F-18 FDG positron emission tomography using a coincidence technique and with Tc-99m dicarboxypropane diphosphonate. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27(7):537-538.[7] Marumo F, Nomura T, Nishikawa H.Transverse fractures of the spinous process of the 7th cervical vertebra in RDT patients: an Al related disease. Int J Artif Organs. 1987;10(2): 93-96.[8] Nowak C, Solecki J. Absence of the body of the cervical vertebra in Bechterew's disease.Wiad Lek. 1981;34(4): 325-329.[9] Dawn B, Bolli R. Adult bone marrow-derived cells: regenerative potential, plasticity, and tissue commitment. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100(6):494-503.[10] Grove JE, Bruscia E, Krause DS. Plasticity of bone marrow-derived stem cells.Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):487-500.[11] Caplan AI.Why are MSCs therapeutic? New data: new insight. J Pathol. 2009;217(2):318-324.[12] Maul TM, Chew DW, Nieponice A,et al. Mechanical stimuli differentially control stem cell behavior: morphology, proliferation, and differentiation.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10(6):939-953.[13] Patel SA, Sherman L, Munoz J,et al. Immunological properties of mesenchymal stem cells and clinical implications.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2008;56(1):1-8. [14] Parekkadan B, Milwid JM. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:87-117.[15] Yi T, Song SU. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(2):213-221.[16] Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes.Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):244-253. [17] van Laar JM, Tyndall A. Adult stem cells in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(10): 1187-1193.[18] Wu Y, Wang J, Scott PG,et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells in wound healing: a review.Wound Repair Regen. 2007; 15 Suppl 1:S18-26.[19] Ren G, Chen X, Dong F,et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells and translational medicine: emerging issues.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(1):51-58.[20] Mahmood A, Lu D, Lu M,et al.Treatment of traumatic brain injury in adult rats with intravenous administration of human bone marrow stromal cells. Neurosurgery. 2003;53(3): 697-702.[21] Shou Z, Shen L, Xiong P. Assessing the validity of a novel model of vertebral artery type of cervical syndrome induced by injecting sclerosing agent next to transverse process of cervical vertebra.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010;30(1):85-88.[22] Denis DJ, Shedid D, Shehadeh M,et al. Cervical spondylosis: a rare and curable cause of vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Eur Spine J. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][23] Rahimizadeh A, Soufiani H.Intramedullary arachnoid cyst in association with cervical spondylosis: case report.Spine J. 2013. pii: S1529-9430(13)00523-8. [24] Fujimori T, Le H, Ziewacz JE,et al. Is there a difference in range of motion, neck pain, and outcomes in patients with ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament versus those with cervical spondylosis, treated with plated laminoplasty. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;35(1):E9.[25] Ding Q, Yan M, Zhou J,et al. Clinical effects of innovative tuina manipulations on treating cervical spondylosis of vertebral artery type and changes in cerebral blood flow.J Tradit Chin Med. 2012;32(3):388-392.[26] Guo K, Li L, Zhan HS,et al. Systematic review of clinical randomized controlled trials on manipulation treatment for vertebral artery type of cervical spondylosis.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(1):9-13.[27] Liao YY, Sun DM, Zhong CP,et al. Evaluation of the immediate effect of acupuncture on cervical spondylosis of vertebral artery type based on orthogonal design.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2011;31(6):499-502.[28] Gao H, Ye YJ. Manipulative treatment of vertebral artery type of cervical spondylosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010;23(4): 257-260.[29] Chen D, Zhong J, Hong YB,et al. Influence of needle-pricking bleeding combined with pulling-rotating manipulation on blood rheology in patients with vertebral artery type cervical spondylosis.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2009;34(5):344-348.[30] Hong ES, Deng MY, Cheng LH,et al. Effect of vertebral manipulation therapy on vertebro-basilar artery blood flow in cervical spondylosis of vertebral artery type. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2005;25(8):742-744.[31] Lewis AC. Interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of posterior capsule opacification and the potential role for interleukin-6 inhibition in the future of cataract surgery. Med Hypotheses. 2013;80(4):466-474. [32] Ichikawa T, Sugiura H, Koarai A,et al. 25-hydroxycholesterol promotes fibroblast-mediated tissue remodeling through NF-κB dependent pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(8): 1176-1186.[33] Liu A, Gao X, Zhang Q,et al. Cathepsin B inhibition attenuates cardiac dysfunction and remodeling following myocardial infarction by inhibiting the NLRP3 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(2):361-366.[34] Dai C, Zhang B, Liu X,et al. Pyrimethamine sensitizes pituitary adenomas cells to temozolomide through cathepsin B-dependent and caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways.Int J Cancer. 2013;133(8):1982-1993. [35] Lin SA, Patel M, Suresch D,et al. Quantitative Longitudinal Imaging of Vascular Inflammation and Treatment by Ezetimibe in apoE Mice by FMT Using New Optical Imaging Biomarkers of Cathepsin Activity and α(v)β(3) Integrin.Int J Mol Imaging. 2012;2012:189254.[36] Zhang T, Yang ZY, Bo XP,et al. Cathepsin B promoted the apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells as induced by tumor necrosis factor-α. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011; 91(12):845-849.[37] Screen M, Dean W, Cross JC,et al. Cathepsin proteases have distinct roles in trophoblast function and vascular remodelling. Development. 2008;135(19):3311-3320. [38] González-Vela MC, Garijo MF, Fernández F,et al. Cathepsin D in host stromal cells is associated with more highly vascular and aggressive invasive breast carcinoma.Histopathology. 1999;34(1):35-42.[39] Yamaguchi T, Naruishi K, Arai H,et al. IL-6/sIL-6R enhances cathepsin B and L production via caveolin-1-mediated JNK-AP-1 pathway in human gingival fibroblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2008;217(2):423-432.[40] Sendler M, Dummer A, Weiss FU,et al.Tumour necrosis factor α secretion induces protease activation and acinar cell necrosis in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice.Gut. 2013; 62(3):430-439. [41] Boyd AS, Fairchild PJ. Approaches for immunological tolerance induction to stem cell-derived cell replacement therapies. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010;6(3):435-448.[42] Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM,et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(7):490-500.[43] Tang Q, Boden EK, Henriksen KJ,et al. Distinct roles of CTLA-4 and TGF-beta in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function.Eur J Immunol. 2004;34(11):2996-3005.[44] Kong YC, Morris GP, Brown NK,et al. Autoimmune thyroiditis: a model uniquely suited to probe regulatory T cell function.J Autoimmun. 2009;33(3-4):239-246. [45] Morris GP, Kong YC. Interference with CD4+CD25+ T-cell-mediated tolerance to experimental autoimmune thyroiditis by glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor monoclonal antibody.J Autoimmun. 2006;26(1): 24-31. [46] Maloy KJ, Salaun L, Cahill R,et al. CD4+CD25+ T(R) cells suppress innate immune pathology through cytokine-dependent mechanisms.J Exp Med. 2003;197(1): 111-119.[47] Tsai YG, Chiou YL, Chien JW,et al. Induction of IL-10+ CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells with decreased NF-κB expression during immunotherapy.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010;21(1 Pt 2):e166-73.[48] Liu Y, Wang L, Predina J,et al. Inhibition of p300 impairs Foxp3(+) T regulatory cell function and promotes antitumor immunity.Nat Med. 2013;19(9):1173-1177.[49] Yin X, Yin Y, Cao FL,et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38381.[50] Wu X, Liu L, Xie H,et al. Tanshinone IIA prevents uric acid nephropathy in rats through NF-κB inhibition.Planta Med. 2012;78(9):866-873. |