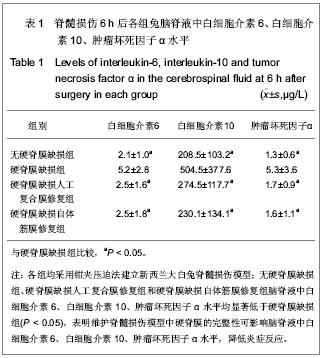
| [1] Garbossa D,Fontanella M,Fronda C,et al. New strategies for repairing the injured spinal cord:the role of stem cells. Neurol Res.2006;28(5):500-504.[2] Streit WJ,Semple-Rowland SL,Hurley SD,et al.Cytokine mRNA profiles in contused spinal cord and axotomiazed facial mucleus suggest a beneficial role for inflammation and gliosis. Exp Neurol.1998;152(1):74-87. [3] 孙为增.电针对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后白介素-1β表达及其作用的影响[G].汕头大学硕士论文, 2009.[4] 谭永红.罗哌卡因对大鼠脊髓穿刺损伤后脊髓神经毒性的影响[D].南方医科大学博士论文,2011. [5] 孙为增,王新家.脊髓损伤后细胞因子的变化及作用[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(8): 1337-1338.[6] Sufium S,Lahav R,Han J,et al. Leukaemia inhibitory factor is required for normal inflammatory responses to injury in the peripheral and central nervous systems in vivo and is chemotactic for macrophages in vitro. Eur J Neurosci.2000; 12(2):457-466.[7] Mukaino M,Nakamura M,Okada S,et al. Role of IL-6 in regulation of inflammation and stem cell differentiation in CNS trauma.Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi.2008;31(2): 93-98.[8] Kang MK,Kang SK. Interleukin-6 induces proliferation in adult spinal cord derived neural progenitors via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway with EGf-indued MAPK phosphorylation. Cell Prolif. 2008;41(3):377-392.[9] Milligan ED,Soderquist RG,Malone SM,et al.Intrathecal polymer-based interleukin-10 gene delivery for neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2006;2(4):239-308.[10] Bethea JR,Dietrich WD,Targeting the host inflammatory response in traumatic spinal cord injury. J Curr Opin Neurol. 2002;15(3):355-360.[11] Plukett JA,Yu CG,Easton JM,et al. Effects of interleukin-10 (IL-10) on pain behavior and gene expression following excitotoxic spinal cord injury in the rat. J Exp Neurol.2001; 168(1):144-154.[12] 周华,刘华,黄坚,等.IL-10对脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡和CD95作用的初步探讨[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2005,25(3):395-397.[13] Wang CX,Reece C,Wrathall JR,et al.Expressing of tumor necrosis factor alpha and its mRNA in the spinal cord injury. Neuroreport.2002;13(11):1391-1393.[14] Basu A,Krady JK,O'Malley M,et al.The type 1 Interleukin-1 receptor is essential for the effient activation of microglia and the induction of multiple proinflammatory medators in response to brain injury. J Neurosci.2002; 22(14):6071-6082.[15] Baeuerle PA,Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system.Annu Rev Immunol.1994;12:141-179.[16] Kim GM,Xu J,Xu J,et al.Tumor necrosis factor receptor deletion reduces nuclear factor-kappa B activation, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 expression, and functional recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosci.2001; 21(17):6617-6625. |