| [1] Testa M, Yeh M, Lee P, et al. Circulating levels of cytokines and their endogenous modulators in patients with mild to severe congestive heart failure due to coronary artery disease or hypertension. J Am Coil Cardiol. 1996;28:964-971.
[2] Torre-Amione G, Kapadia S, Benedict C, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine levels in patients with depressed left ventricular ejection fraction a report from the Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction. J Am Coil Cardiol. 1996;27:1201-1206.
[3] Ono K, Matsumori A, Shioi T,et al. Cytokine gene expression after myocardial infarction in rat hearts:possible implication in left ventricular remodeling. Circulation. 1998;98:149-156.
[4] Kinugawa S ,Tsutsui H, Hayashidani S, et al. Treatment with dimethylthiourea prevents left veruldcular remodeling and failure after experimental myocardial infarction in mice:role of oxidative stress. Circ Res. 2000;87:392-398.
[5] Kumar D, Lou H, Singal PK. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in heart dysfunction. Herz. 2002;27:662-668.
[6] Dhalla NS, Eimoselhi AB, Hata T,et al. Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia--reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;7:46-56.
[7] Chattopadhyay A, Choudhury TD, Bandyopadhyay D, et al. Protective effect of erythropoietin on the oxidative damage of erythrocyte membrane by hydroxyl radical. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;59:419-425.
[8] Testa M, Yeh M, Lee P, et al. Circulating levels of cytokines and their endogenous modulators in patients with mild to severe congestive heart failure due to coronary artery disease or hypertension. J Am Coil Cardiol. 1996;28:964-971.
[9] Kumar D, Lou H, Singal PK. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in heart dysfunction. Herz. 2002;27:662-668.
[10] Chattopadhyay A, Choudhury TD, Bandyopadhyay D, et al. Protective effect of erythropoietin on the oxidative damage of erythrocyte membrane by hydroxyl radical. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;59:419-425.
[11] Rafiee P, Shi Y, Su J, et al. Erythropoietin protects the infant heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by triggering multiple signaling pathways. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100(3): 187-197.
[12] Li F, Chong ZZ, Maiese K. Erythropoietin on a tightrope: Balancing neuronal and vascular protection between intrins and cxtrinsic pathways. Neurosignals. 2004;13(6):265-289.
[13] Wright GL, Hanlon P, Amin K, et al. Erythropoietin receptor expression in adult rat cardiomyocytes is associated with an acute cardioprotective effect for recombinant erythropoietin during ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 2004;18: 1031-1033.
[14] Parsa CJ, Matsumoto A, Kim J, et al. A novel protective effect of erythropoietinin the infarcted heart. J Clin Invest. 2003;112: 999-1007.
[15] Siren AL, Fratelli M, Brines M, et al. Erythropoietin prevents neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia and metabolic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:4044-4049.
[16] Tada H, Kagaya Y, Takeda M, et al. Endogenous erythropoietin system in Non-hematopoietic lineage cells plays protective role in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion Cardivasc Res. 2006;71(3):466-477.
[17] Burger D, lei M, Geoghegan-Morphet N, et al. Erythropoietin protects cardiomyocytes from apoptosis viaupregulation of endothelia nitric oxide symthase. Cardiovasc Res. 2006; 72(1):51-59.
[18] Sezgin Y, Ersin A, Cigdem T,et al. The protective effect of erythropoietin on ischaemia-reperfusion injury of liver. J Int Hepatol Pancreat Biliary Assoc. 2004;6(3):169-173.
[19] Li Y,Takemura G,Okada H, et al. Reduction of inflammatory cyrokine expression and oxidative damage by erythropoitin in chronic heart failure. Cardivasc Res. 2006;7(4):684-694.
[20] Young PR, McLaughlin MM, Kumar S, et al. Pyridiny l imidazole inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase bind in the ATP site. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(18):12116-12121.
[21] 张新金, 马业新, 文渊, 等.促红细胞生成素抑制血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的大鼠心脏成纤维细胞中转化生长因子β1和胶原的表达[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2008, 36(7):636-640.
[22] 张炜, 汪虹, 邓悦,等. 促红细胞生成素促进组织器官血管新生的理论研究与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(37): 7020-7024.
[23] OliVetti G, Capasso JM, Meggs LG,et al.Cellular basis of chronic ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction inrats.Cirs Res. 1991;68:856-859.
[24] Rogers TB. Angiotension signal transduction pathway in the cardiovascular system. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1994;38(4): 110-113.
[25] 田风石, 李晒, 胡大一, 等. 急性心肌梗死和不稳定性心绞痛患者黏附分子及相关因素的研究[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2001, 3(5):301-303.
[26] Gui T, Feng Q, Lei M, et al. Erythropoietin prevents the acute myocardial inflammatory response induced by ischemia-reperfusion via induction of AP-1. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:71 9-727.
[27] Brines ML, Ghezzi P, Keenan S, et al. Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:10526-10531.
[28] Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves Cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;412:641-647.
[29] Villa P,Bigini P,Mennini T,et al. Erythropoietin selectively attenuates cytokine production and inflammation in cerebral ischemia by targeting neuronal apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2003; 198:971-975.
[30] Zhang W, Lü SY, Yu ZY, et al. Effects of erythropoietin on the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Bax after facial nerve axotomy in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(6):444-449.
[31] Kawakami M, Sekiguc MM, Sato K, et al. Erythropoietin receptor-mediated inhibition of exocytotic glutamate release confers neuroprotection during chemical ischemia. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39469-39475.
[32] Villa P, Bigini P, Mennini T, et al. Erythropoietin selectively attenuates cytokine production and inflammation in cerebral ischemia by targeting neuronal apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2003; 198(6):971-975.
[33] Liu X, Xie W, Liu P, et al. Mechanism of the cardio protection of rhEPO pretreatment on suppressing the inflammatory response in ischemia-reperfusion. Life Sci. 2006;78(19): 2255-2264.
[34] Dong WB, Hou HM, Wang Q, et al. NF-kappaB-mediated protective effect of erythropoitin on neuron against glutamate-induced damage. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;24(6):584-585.
[35] Li Y, Takemura G, Okada H,et al. Reduction of inflammatory cytokine expression and oxidative damage by erythropoietin in chronic heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71:684-694. |
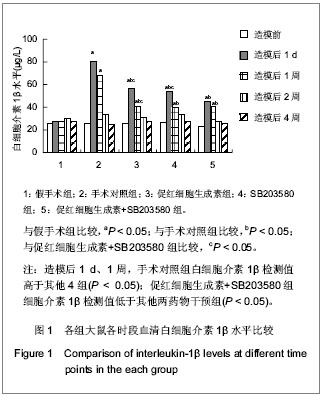
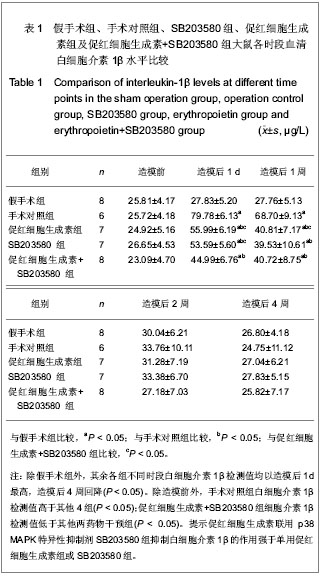
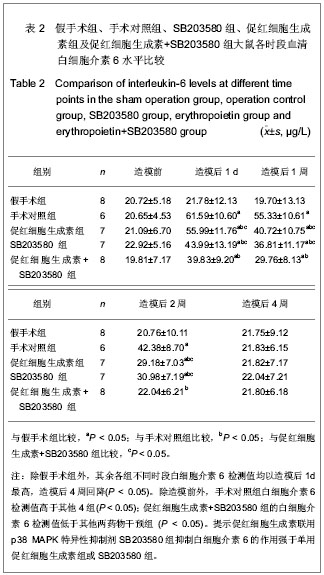
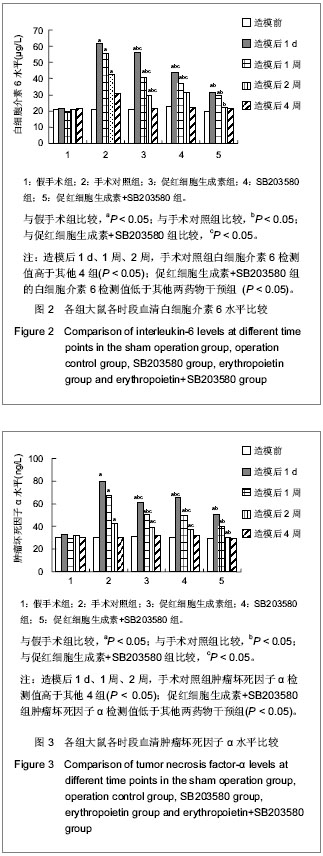
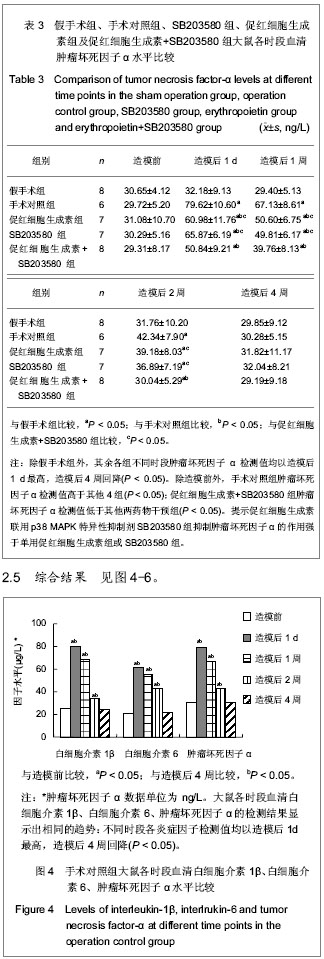
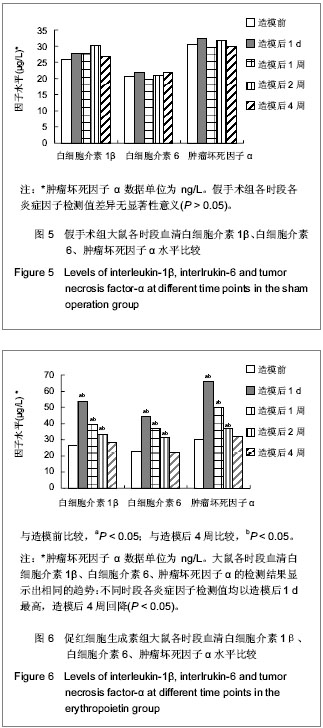
.jpg)