中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5749-5756.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.002
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞参与A549肺腺癌的组织修复
许 峰1,张 雷2,潘晋坤2,薛利利2,赵晓燕2,李宝平2
- 1南通市肿瘤医院胸外科,江苏省南通市 226361
2山西医科大学第二医院肿瘤生物科,山西省太原市 030001
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are involved in tissue repair of A549 lung adenocarcinoma
Xu Feng1, Zhang Lei2, Pan Jin-kun2, Xue Li-li2, Zhao Xiao-yan2, Li Bao-ping2
- 1Department of Chest Surgery, Nantong Tumor Hospital, Nantong 226361, Jiangsu Province, China
2Department of Tumor Biological Treatment, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
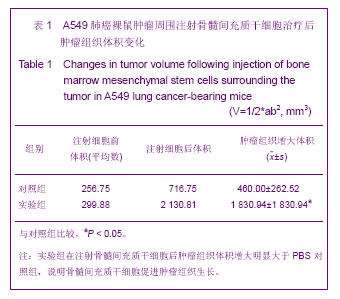
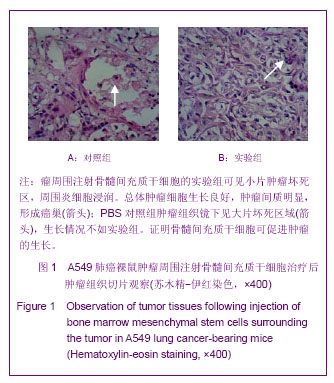
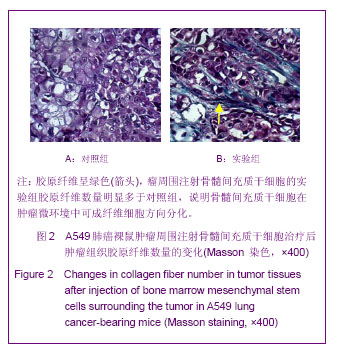
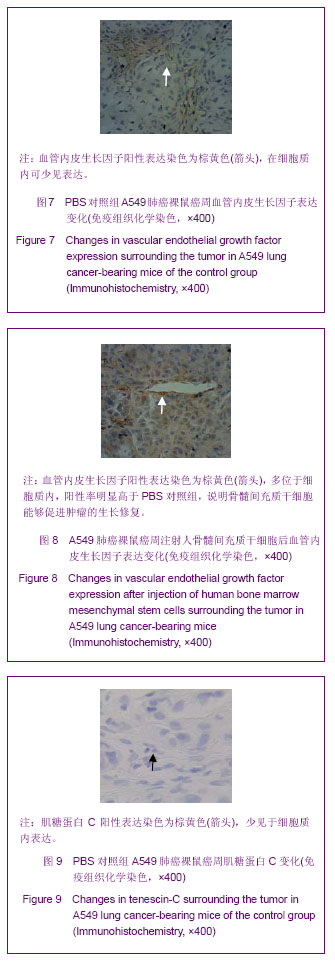
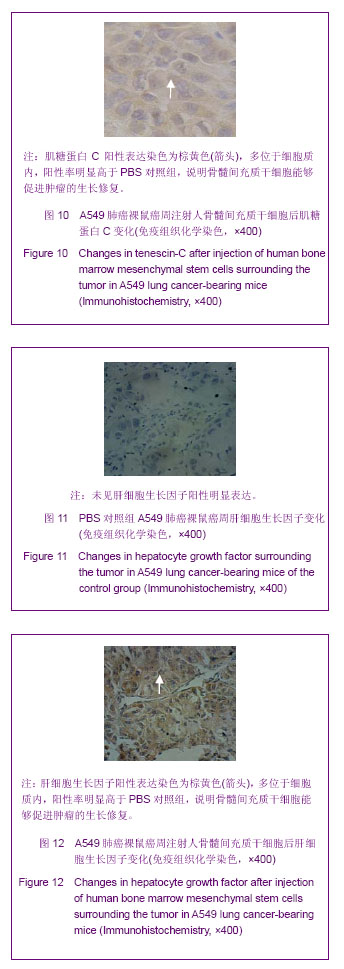
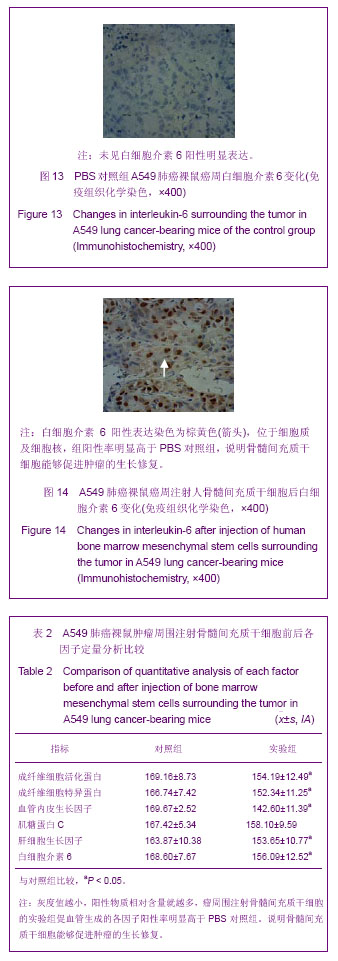
背景:肿瘤被认为是一种特殊的不愈合创伤,骨髓间充质干细胞通过向肿瘤组织归巢和向间质成分分化,参与肿瘤间质重构,从而改变肿瘤微环境,影响肿瘤的生长和转移。 目的:在A549肺癌荷瘤小鼠模型上证实骨髓间充质干细胞参与其损伤修复,探讨骨髓间充质干细胞参与肿瘤组织修复的机制。 方法:体外分离、培养人骨髓间充质干细胞,使用流式细胞术鉴定,制造A549肺癌荷瘤小鼠模型。实验组采用瘤周注射人骨髓间充质干细胞,对照组注射等量PBS,对比观察动物生活情况,肿瘤生长大小。4周后取材,苏木精-伊红染色对比观察肿瘤组织,Masson染色对比胶原纤维含量,RT-PCR检测两组α平滑肌收缩蛋白的表达,免疫组织化学检测两组成纤维细胞特异蛋白、成纤维细胞活化蛋白的表达情况,反映两组肿瘤组织的间质纤维的程度。免疫组织化学方法对比两组中血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、白细胞介素6、肌糖蛋白C的表达高低。 结果与结论:骨髓间充质干细胞促进荷瘤小鼠肿瘤的生长,实验组肿瘤组织生长速度明显快于对照组(P < 0.05)。RT-PCR检测α平滑肌收缩蛋白的表达:与对照组比较,实验组α平滑肌收缩蛋白 mRNA的表达水平显著升高。免疫组织化学方法检测实验组肿瘤组织中TAFs标志物:成纤维细胞特异蛋白、成纤维细胞活化蛋白的表达,IHC检测血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、白细胞介素6、肌糖蛋白C的表达明显高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。说明骨髓间充质干细胞在肿瘤微环境中向成纤维细胞方向分化,参与肿瘤间质的形成和构建,分泌血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、白细胞介素6、肌糖蛋白C等促进肿瘤的生长修复。
中图分类号:



.jpg)