| [1] Ramón-Cueto A, Muñoz-Quiles C. Clinical application of adult olfactory bulb ensheathing glia for nervous system repair. Exp Neurol. 2011;229(1):181-194. [2] Li Y, Field PM, Raisman G. Regeneration of adult rat corticospinal axons induced by transplanted olfactory ensheathing cells. J Neurosci.1998;18:10514-10524. [3] Lu J, Feron F, Ho SM,et al.Transplantation of nasal olfactory tissue promotes partial recovery in paraplegic adult rats. Brain. 2001;889:344-357. [4] Ito D, Fujita N,Ibanez C,et al. Serum-free medium provides a clinically relevant method to increase olfactory ensheathing cell numbers in olfactory mucosa cell culture.Cell Transplant. 2008;16(10):1021-1027. [5] Wu M,Fan D,Tadmori I,et al.Death of axotomized retinal ganglion cells delayed after intraoptisc nerve transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells in adult rats. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(2):159-166. [6] Shen Y,Qian Y,Zhang H,et al. Guidance of olfactory ensheathing cell growth and migration on electrospun silkfibroin scaffolds. Cell Transplant. 2010; 19:147-157.[7] Ma Y,Zhang Y,Cao L,et al.Effect of neurotrophin-3 genetically modifiedolfactory ensheathing cells transplantation on spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant. 2010;19:167-177. [8] Ramón-Cueto A, Nieto Sampedro M. Regeneration into the spinal cord of transected dorsal root axons is promoted by ensheathing glia transplants. Exp Neurol.1994;127(2): 232-244.[9] Mie M,Ohgushi H,Yanaqida Y,et al.Osteogenesis coordinated in C3H10T1/2 cells by adipogenesis-dependent BMP-2 expression system.Tissue Enq.2000;6(1):9-18.[10] Ramer LM, Au E, Richter MW, et al. Peripheral olfactory ensheathing cells reduce scar and cavity formation and promote regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2004;473(1):1-15.[11] Huang H,Chen L,Wang H,et al.Influence of patients’ age on functional recovery after transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells into injured spinal cord injury. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003;116:1488-1491. [12] Huang H, Wang H, Chen L, et al. Influence factors for functional improvement after olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation for chronic spinal cord injury. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006;20:434-438. [13] Huang H,Chen L,Xi H,et al. Long-Term Outcome of Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Therapyfor Patients With Complete Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplantation.2012;21:S23–S31. [14] 孙天胜,任继鑫,吴军,等.嗅鞘细胞移植促进脊髓损伤修复的长期实验和临床观察[J].中国临床康复.2005;9(2):122-124.[15] Wu J,Sun T,Ye C,et al.Clinical Observation of Fetal Olfactory Ensheathing Glia Transplantation(OEGT) in Patients With Complete Chronic Spinal Cord Injury.Cell Transplantation. 2012;21: S33-S37. [16] 郑遵成,刘超,张振兴,等.嗅鞘细胞移植治疗陈旧性脊髓损伤48例[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(9):170-172.[17] 郑遵成,魏开斌,刘峰,等. 嗅鞘细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的临床验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(27):5119-5122.[18] Dobkin BH, Curt A, Guest J. Cellular Transplants in China:Observational Study from the Largest Human Experiment in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.2006;20(1):5-13.[19] Lima C,Pratas-Vital J, Escada P,et al.Olfactory mucosa autografts in human spinal cord injury: a pilot clinical study.Spinal Cord Med. 2006;29: 191-203. discussion 204-206.[20] Lima C, Escada P, Pratas-Vital J, et al.Olfactory mucosal autografts and rehabilitation for chronic traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair.2010; 24:10-22.[21] Chhabra HS, Lima C, Sachdeva S, et al.Autologous olfactory [corrected] mucosal transplant in chronic spinal cord injury:an Indian Pilot Study. Spinal Cord. 2009;47: 887-895. [22] Mackay-Sim A, St John JA. Olfactory ensheathing cells from the nose: Clinical application in human spinal cord injuries. Exp Neurol.2011;229: 174-180.[23] Dobkin BH. Recommendations for publishing case studies of cell transplantation for spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2010;24(8):687-691. [24] Mackay-Sim A. An olfactory ensheathing cells and spinal cord repair. Keio J Med. 2005;54(1):8-14. [25] Mackay-Sim A, Féron F, Cochrane J, et al. Autologous olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation in human paraplegia: a 3 year clinical trial. Brain.2008;131(Pt 9): 2376-2386. [26] Feron F, Perry C, Cochrane J, et al.Autologous olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation in human spinal cord injury. Brain.2005;128:2951-2960.[27] Lu J,Feron F,Ho SM,et al.Transplantation of nasal olfactory tissue promotes partial recovery in paraplegic adult rats.Brain Res.2001;889(1-2):344-357.[28] Lu J,Feron F,Mackay-Sim A,et al.Olfactory ensheathing cells promote locomotor recovery after delayed transplantation into transected spinal cord.Brain.2002;125(Pt 1):14-21.[29] Bohbot A. Olfactory ensheathing glia transplantation combined with LASERPONCTURE in human spinal cord injury: Results measured by electromyography monitoring. Cell Transplantation. 2010;19:179-184.[30] Chen L, Chen D, Xi H,et al.Olfactory ensheathing cell neurorestorotherapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: Benefits from multiple transplantations.Cell Transplant.2012; 21Suppl 1:S65-77. [31] Zhang SX,Huang F,Gates M,et al.Tail nerve electrical stimulation combined with scar ablation and neural transplantation promotes locomotor recovery in rats with chronically contused spinal cord.Brain Res. 2012;1456:22-35.[32] Li BC,Xu C,Zhang JY,et al.Differing Schwann Cells and Olfactory Ensheathing Cells Behaviors, from Interacting with Astrocyte, Produce Similar Improvements in Contused Rat Spinal Cord's Motor Function.J Mol Neurosci.2012; 48(1): 35-44.[33] Silva NA, Sousa RA, Pires AO,et al.Interactions between Schwann and olfactory ensheathing cells with a starch/polycaprolactone scaffold aimed at spinal cord injury repair. J Biomed Mater Res A.2012; 100A:470-476.[34] Liu X,Sun J,Cui X,et al.Protective effect of olfactory ensheathing cells in combination with intrathecal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor on injured spinal cord in rats.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2011; 25(6): 699-704. |
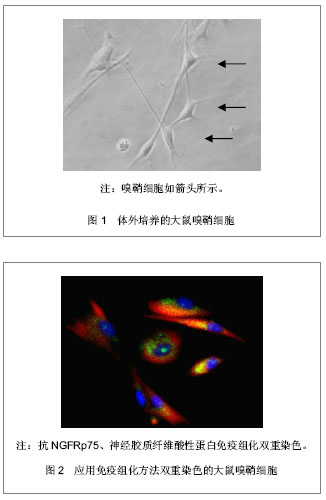
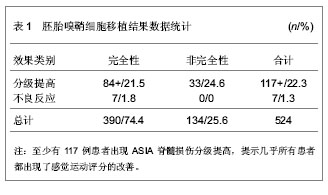
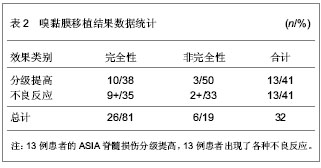

.jpg)