| [1] Tecles O, Laurent P, Zygouritsas S, et al. Activation of human dental pulp progenitor/stem cells in response to odontoblast injury. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):103-108.[2] Fonfria E, Murdock PR, Cusdin FS, et al. Tissue distribution profiles of human TRPM cation channel family. J recept signal transduct re. 2006;26(3):159-178.[3] Ryazanova LV, Rondon LJ, Zierler S, et al. TRPM7 is essential for Mg2+ homeostasis in mammals. Nat Commun. 2010;1:109.[4] Penner R, Fleig A. The Mg2+ and Mg(2+)-nucleotide- regulated Channel-Kinase TRPM7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(179):313-328.[5] Cheng H, Feng JM, Beck A, et al. Transient receptor potential melastatin type 7 is critical for the survival of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell .Stem cell devel. 2011;19(9): 1393-1403.[6] Abed E, Moreau R. Importance of melastatin-like transient potential 7 and cations(magnesium, calcium)in human osteoblast-like cell proliferation. Cell Prolif. 2007;40(6): 849-865. [7] Lam DH, Grant CE, Hill CE. Differential expression of TRPM7 in rat hepatoma and embryonic and adult hepatocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 ;90(4):435-444.[8] Du J, Xie J, Zhang Z, et al. TRPM7-mediated Ca2+ signals confer fibrogenesis in human atrial fibrillation. Circ Res. 2010; 106(5):992-1003.[9] Nilius B, Owsianik G. The transient receptor potential family of ion channels. Genome Biol. 2011;12(3):218. [10] Zholos A, Johnson C, Burdyga T, et al. TRPM channels in the vasculature.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:707-729. [11] Paravicini TM, Chubanov V, Gudermann T. TRPM7: A unique channel involved in magnesium homeostasis Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(8):1381-1384. [12] Yogi A, Callera GE, Antunes TT, et al. Transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) cation channels, magnesium and the vascular system in hypertension. Circ J. 2011;75(2): 237-245 .[13] Runnels LW. TRPM6 and TRPM7: A Mul-TRP-PLIK-cation of channel functions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(1):42-53.[14] TSchlingmann KP, Waldegger S, Konrad M, et al. TRPM6 and TRPM7--Gatekeepers of human magnesium metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1772(8):813-821. [15] Scharenberg AM. TRPM2 and TRPM7: channel/enzyme fusions to generate novel intracellular sensors. Pflugers Arch. 2005;451(1):220-227.[16] Chubanov V, Mederos y, Schnitzler M, et al. Emerging roles of TRPM6/TRPM7 channel kinase signal transduction complexes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005;371(4):334-341.[17] Runnels LW, Yue L, Clapham DE. The TRPM7 channel is inactivated by PIP(2) hydrolysis. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(5):329- 336.[18] Gwanyanya A, Sipido KR, Vereecke J, Mubagwa K. ATP and PIP2 dependence of the magnesium-inhibited, TRPM7-like cation channel in cardiac myocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 ;291(4):C627-635.[19] Macianskiene R, Gwanyanya A, Vereecke J , et al. inhibition of the magnesium-sensitive TRPM7-like channel in cardiac myocytes by nonhydrolysable GTP analogs: involvement of phosphoinositide metabolism. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2008; 22(1-4):109-118. [20] Park KS, Pang B, Park SJ, et al. Identification and functional characterization of ion channels in CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells from human peripheral blood. Mol Cells. 2011;32 (2): 181-188.[21] Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Schlingmann KP. Essential role for TRPM6 in epithelial magnesium transport and body magnesium homeostasis. Pflugers Arch. 2005;451(1): 228-234.[22] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.[23] Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81(8): 531-535.[24] Zhang W, Walboomers XF, Wolke JG, et al. Differentiation ability of rat postnatal dental pulp cells in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(3-4):357-368. [25] Yang X, Zhang W, van den Dolder J, et al. Multilineage potential of STRO-1+ rat dental pulp cells in vitro. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1(2):128-135.[26] Arthur A, Rychkov G, Shi S, et al. Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(7):1787-1795.[27] Paino F, Ricci G, De Rosa A, et al. Ecto-mesenchymal stem cells from dental pulp are committed to differentiate into active melanocytes. Eur Cell Mater. 2010;7(20):295-305 .[28] Gomes JA, Geraldes Monteiro B, Melo GB, et al. Corneal reconstruction with tissue-engineered cell sheets composed of human immature dental pulp stem cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(3):1408-1414. [29] Cordeiro MM, Dong Z, Kaneko T, et al. Dental pulp tissue engineering with stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth. J Endod. 2008;34(8):962-969.[30] Sakai VT, Zhang Z, Dong Z, et al. SHED differentiate into functional odontoblasts and endothelium. J Dent Res. 2010; 89(8):791-796.[31] Bates-Withers C, Sah R, Clapham DE.TRPM7, the Mg2+ Inhibited Channel and Kinase. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704: 173-183.[32] Chokshi R, Fruasaha P, Kozak JA. 2-aminoethyl diphenyl borinate (2-APB) inhibits TRPM7 channels through an intracellular acidification mechanism. Channels. 2012;6(5): 362-369.[33] Dreyer JL. Lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer and RNA silencing technology in neuronal dysfunctions. Mol Biotechnol. 2011;47(2):169-187.[34] Manjunath N, Wu H, Subramanya S, et al. Lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(9):732- 745.[35] Nishitsuji H, Ikeda T, Miyoshi H, et al. Expression of small hairpin RNA by lentivirus-based vector confers efficient and stable gene-suppression of HIV-1 on human cells including primary non-dividing cells. Microbes Infect. 2004;6(1):76-85.[36] Jin J, Wu LJ, Clapham DE, et al.The channel kinase, TRPM7, is required for early embryonic development. PNAS. 2012; 109 (5):E225-233.[37] Schmitz C, Perraud AL, Johnson CO, et al. Regulation of vertebrate cellular Mg2+ homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell. 2003; 114(2):191-200.[38] Jiang J, Li MH, Inoue K, et al. Transient receptor potential melastatin 7-like current in human head and neck carcinoma cells:role in cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2007;67(22): 10929-10938.[39] Hanano T, Hara Y, Shi J, et al. Involvement of TRPM7 in cell growth as a spontaneously activated Ca2+ entry pathway in human retinoblastoma cell. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004;95(4): 403-419.[40] Guilbert, A, Sevestre H, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, et al. Evidence that TRPM7 is required for breast cancer cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297(3):493-502.[41] Kim BJ, Park EJ, Lee JH, et al. Suppression of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 channel induces cell death in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99(12):2502-2509.[42] Yee NS, Zhou W, Liang IC. Transient receptor potential ion channel TRPM7 regulates exocrine pancreatic epithelial proliferation by Mg2+-sensitive Socs3a signaling in development and cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4(2):240-254. |
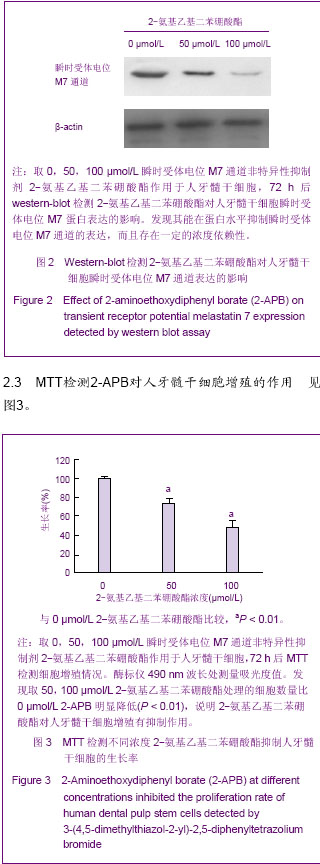
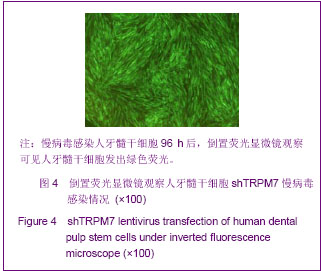

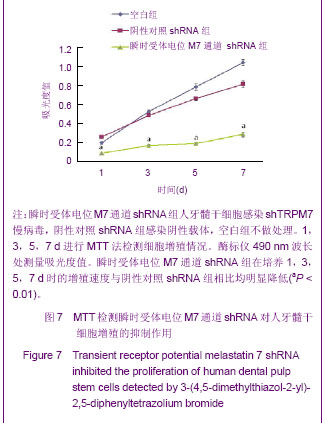
.jpg)
