| [1] Yang XH, Zhang L, Chen DY, et al. Taishan Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2008;29(12):945-948.杨兴华,张僚,陈岱运,等.兔骨髓基质干细胞的培养及成骨诱导研究[J].泰山医学院学报,2008,29(12):945-948. [2] Vinardell T, Sheehy EJ, Buckley CT, et al. A comparison of the functionality and in vivo phenotypic stability of cartilaginous tissues engineered from different stem cell sources. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(11-12):1161-1170. [3] Zhang L, Li YQ, Zhang Y, et al. Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2008;31(1): 8-10.张林,李玉泉,张炎,等.骨髓间质细胞中组织定向干细胞的鉴定[J].解剖学杂志,2008,31(1):8-10.[4] Boyd SK, Müller R, Leonard T, et al. Long-term periarticular bone adaptation in a feline knee injury model for post-traumatic experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(3):235-242.[5] An BL, Ren QJ, Jiao K, et al. Guoji Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2010;37(5):552-554.安佰利,任青杰,焦凯,等.软骨下骨改变与骨关节病[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010,9,37(5):552-554. [6] Yu Q, Li HP, Guo X, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2012;25(6): 530-534.余强,李浩鹏,郭雄. MicroRNA在软骨损伤退变中作用机制的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(6):530-534. [7] Qiang YW, Heuck CJ, Shaughnessy JD Jr, et al. Proteasome inhibitors and bone disease. Semin Hematol. 2012;49(3): 243-248.[8] Blaney Davidson EN, Vitters EL, van Beuningen HM, et al. Resemblance of osteophytes in experimental osteoarthritis to transforming growth factor beta-induced osteophytes: limited role of bone morphogenetic protein in early osteoarthritic osteophyte formation. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(12): 4065-4073.[9] Dejica VM, Mort JS, Laverty S, et al. Cleavage of typeⅡ collagen by cathepsin K in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2008;173(1):161-169.[10] Yu JB. Shandong Daxue. 2011.于舰斌. 颌骨骨纤维异常增殖症骨髓基质干细胞的分离培养及Gsα基因突变分析[D]. 山东大学,2011.[11] Yang L, Wang DM, Hong X, et al. Ziran Kexue Jinzhan. 2001; 10(1):1062-1067.杨莉,王冬梅,洪欣,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增和定向诱导分化为骨和软骨细胞的研究[J].自然科学进展,2001,10(1): 1062-1067.[12] Ito S, Sato M, Yamato M, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect with layered chondrocyte sheets and cultured synovial cells. Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5278-5286. [13] Dai BB, Lu J, Chen SS. Shengming Kexue. 2000;12(4): 152-154.戴冰冰,卢健,陈诗书.骨髓基质细胞的特征及其在细胞和基因治疗中的应用[J].生命科学,2000,12(4):152-154.[14] Khanmohammadi M, Khanjani S, Bakhtyari MS, et al. Proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation potential of menstrual blood- and bone marrow-derived stem cells in two-dimensional culture. Int J Hematol. 2012;95(5):484-493.[15] Liu J, Liu X, Zhou G, et al. Conditioned medium from chondrocyte/scaffold constructs induced chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012;295(7):1109-1116.[16] Ahdjoudj S,Lasmoles F,Oyajobi BO,et al.Reciprocal control of osteo-blast/chondroblast and osteoblast/adipocyte differentiation ofmultipotential clonal humanmarrowstromal F/STRO-1(+) cells.J Cell Biochem.2001;81(1):23-38.[17] Delgado M, Toscano MG, Benabdellah K, et al. In vivodelivery of lentiviral vectors expressing vasoactive intestinalpeptide complementary DNA as gene therapy for collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(4):1026-1037.[18] Wang QY, Xu YC, Cai DZ.Zhonguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(46):9037-9040.王其友,徐义春,蔡道章,等.犬骨髓基质干细胞体外定向分化为软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46): 9037-9040.[19] Han SH, Kim YH, Park MS. Histological and biomechanical properties of regenerated articular cartilage using chondrogenic bone marrow stromal cells with a PLGA scaffold in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A JT. 2008;87(4):850-861.[20] Zhou JJ, Yu GR, Cao CF, et al. Zhonguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010,14(33):6194-6197.周军杰,俞光荣,曹成福,等.组织工程化软骨细胞的定向诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(33):6194-6197.[21] Yu SF. Beijing: The Publishing House of People’s Health. 2001:188.于世凤.口腔组织病理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001:188.[22] Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Altman RD, et al. Collagenolytic activity and collagen matrix breakdown of the articular cartilage in the Pond-Nuki dog model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983;26(7):866-874.[23] Chen G, Hu B, Wang DZ, et al. Shiyong Kouqiang Yixie Zazhi. 2003;117(6):5-7.陈刚,胡波,王大章,等.颞下颌关节骨关节病动物模型的建立及组织病理学观察[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2003,117(6):5-7.[24] Yang B, Zhang ZG. Guoji Gouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2010;37(5): 608-612.杨彬,张志光.颞下颌关节骨关节病基因治疗的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010;37(5):608-612.[25] Tominaga K, Yamada Y, Fukuda J. Changes in chewing pattern after surgically induced disc displacement in the rabbit temporomandibular joint. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(4): 400-405.[26] Man C, Ma B, Ma YQ, et al. Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2009;25(12):714-716.满城,张碧,马永清,等. 关节腔注射TGF-1 治疗兔颞下颌关节骨关节炎的实验研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(12): 714-716.[27] Jeong CG, Zhang H, Hollister SJ.Three-dimensional polycaprolactone caffold-conjugated bone morphogenetic protein-2 promotes cartilage regeneration from primary hondrocytes in vitro and in vivo without accelerated endochondral ossification. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100 (8): 2088-2096.[28] Pritzker KP,Gay S,Jimenez SA,et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology:grading and staging. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2006,14(1):13-29.[29] Shang W, Dong G, Li NY, et al. ZHongguo Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi. 2005;3(3):227-230.尚伟,董刚,李宁毅,等.羧甲基壳聚糖对兔颞下颌关节软骨修复的作用[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2005,3(3):227-230.[30] Shi J, Zhang X, Zeng X, et al.One-step articular cartilage repair: combination of in situ bone marrow stem cells with cell-free poly(L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold in a rabbit model. Orthopedics. 2012;35(5):e665-671. |
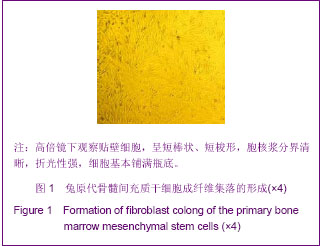

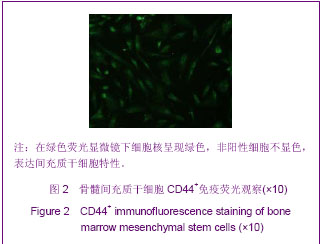
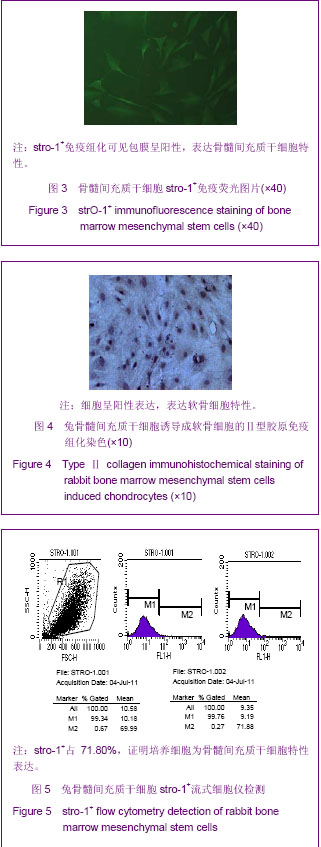

.jpg)