| [1] Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK,et al. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50(2):197-263.[2] Vega-Warner V, Ransom RF, Vincent AM, et al. Induction of antioxidant enzymes in murine podocytes precedes injury by puromycin aminonucleoside. Kidney Int. 2004;66(5): 1881-1889.[3] Bost F, Aouadi M, Caron L,et al. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase isoform ERK1 is specifically required for in vitro and in vivo adipogenesis. Diabetes. 2005;54(2): 402-411.[4] Jaiswal RK, Jaiswal N, Bruder SP,et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic or adipogenic lineage is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(13):9645-9652.[5] Xiao G, Jiang D, Thomas P, et al. MAPK pathways activate and phosphorylate the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, Cbfa1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(6):4453-4459.[6] Lin YP, Zhou RX,Zhang AP, et al.Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2001;24(6): 521-526.林燕萍,周瑞祥,张爱平,等.健骨颗粒对去卵巢骨质疏松模鼠骨组织结构的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2001,24(6):521-526.[7] Lin YP, Zhou RX, Li YL, et al. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2006;26(5):435-438.林燕萍,周瑞祥,李异龙,等. 健骨颗粒对去卵巢骨质疏松模型鼠尿脱氧吡啶酚及骨组织整合素β1 mRNA表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2006,26(5):435-438.[8] Lin Y, Lin YP, Lu TX, et al. Fujian Zhongyi Xueyuanh Xuebao. 2008; 18(5):48-50. 林煜,林燕萍,卢天祥,等. 健骨颗粒对大鼠成骨细胞OCN、Cbfal的影响[J].福建中医学院学报,2008,18(5):48-50.[9] Lin Y, Lu TX, Wu YS , et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangufu. 2010;14(46):8625-8630.林煜,卢天祥,吴银生,等. 健骨颗粒含药血清培养成骨细胞整合素/黏着斑激酶信号通路相关因子的表达[J]].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(46):8625-8630.[10] Lin Y, Wu YS, Lu TX, et al. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2012; 27(1):162-165.林煜,吴银生,卢天祥,等. 健骨颗粒对成骨细胞分化的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(1):162-165.[11] Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, et al. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation.Cell. 2002; 108(1): 17-29.[12] Zhou MM, Yang K, Jiang YP, et al. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1999;15(1):44-45.周明眉,杨奎,姜远平,等.中药血清药理学的方法学研究-采血时间的确定及时效关系研究[J].中药药理与临床, 1999, 15(1): 44-45.[13] Yang K, Zhou MM, Jiang YP, et al.Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1999;15(3):43-44.杨奎,周明眉,姜远平,等. 中药血清药理学的方法学研究——给药方案的研究[J].中药药理与临床,1999, 15(3):43-44.[14] Situ ZQ, Wu JZ. Xi'an:World Book Publishing Company. 2004: 160-164, 250-255.司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].西安:世界图书出版公司,2004: 160-164, 250-255.[15] Lavoie JN, L'Allemain G, Brunet A, et al. Cyclin D1 expression is regulated positively by the p42/p44MAPK and negatively by the p38/HOGMAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(34): 20608-20616.[16] Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 2002;298(5600):1911-1912. [17] Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E,et al. Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell. 2007;130(3): 456-469.[18] Song B, Estrada KD, Lyons KM. Smad signaling in skeletal development and regeneration. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):379-388.[19] Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S,et al.Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 1997;89(5):755-764.[20] Ge C, Xiao G, Jiang D, et al. Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. J Cell Biol. 2007; 176(5):709-718.[21] Cheng Q,Zhu HM,Gan JM,et al. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2008; 14(12): 845-848.程群,朱汉民,甘洁民,等. ERK5调节成骨细胞功能的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(12):845-848.[22] Rodionova NV, Oganov VS, Zolotova NV. Ultrastructural changes in osteocytes in microgravity conditions. Adv Space Res. 2002;30(4):765-770.[23] Viguet-Carrin S, Garnero P, Delmas PD. The role of collagen in bone strength. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(3):319-336.[24] Boskey AL, Wright TM, Blank RD. Collagen and bone strength. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(3):330-335.[25] Ducy P, Starbuck M, Priemel M,et al. A Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev. 1999;13(8):1025-1036.[26] Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, et al. Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation.Cell. 1997;89(5):747-754.[27] Tai G, Christodoulou I, Bishop AE, et al. Use of green fluorescent fusion protein to track activation of the transcription factor osterix during early osteoblast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333 (4):1116-1122. [28] Sengupta TK, Talbot ES, Scherle PA,et al. Rapid inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling and Stat3 activation mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(19):11107-11112.[29] Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Fibrogenesis of parenchymal organs. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008;5(3):338-342.[30] Forte A, Della Corte A, De Feo M, et al. Role of myofibroblasts in vascular remodelling: focus on restenosis and aneurysm. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;88(3):395-405. [31] Pannu J, Nakerakanti S, Smith E, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I-dependent fibrogenic gene program is mediated via activation of Smad1 and ERK1/2 pathways. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(14):10405-10413. |
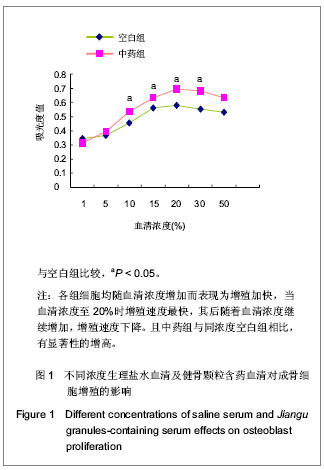
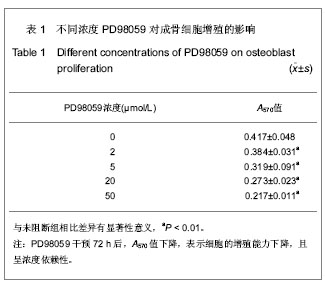
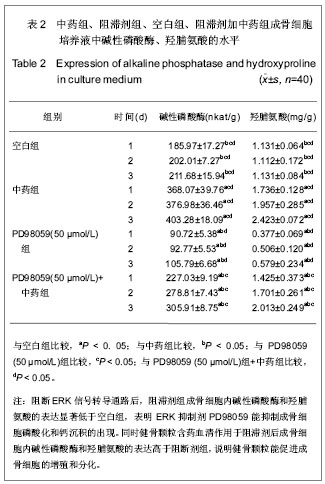
.jpg)
.jpg)