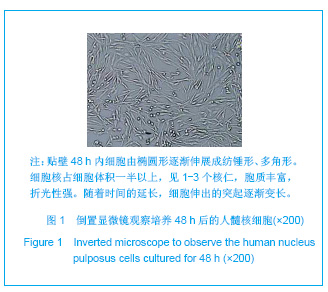
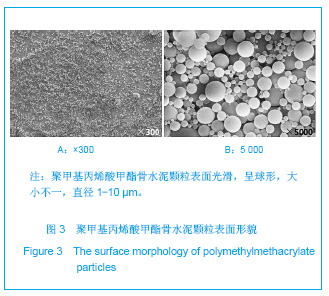
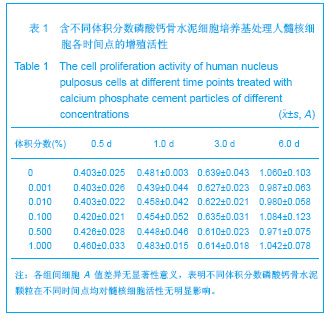
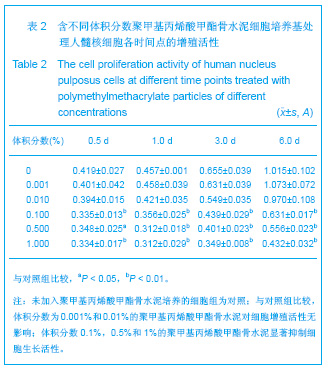
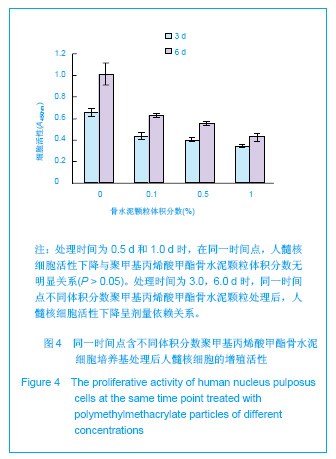
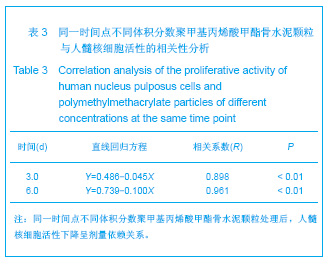
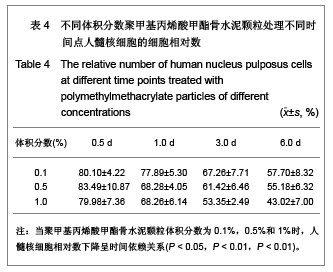
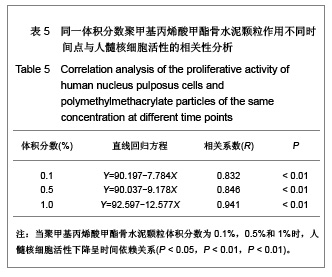
| [1] Hulme PA, Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(17): 1983-2001.[2] Lee MJ, Dumonski M, Cahill P, et al.Percutaneous treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(11): 1228-1232.[3] Gray DT, Hollingworth W,Onwudiwe N, et al.Costs and state-specific rates of thoracic and lumbar vertebroplasty, 2001-2005.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(17): 1905-1912.[4] McKiernan F,Faciszewski T,Jensen R.Quality of life following vertebroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86-A(12): 2600-2606.[5] Yeom JS, Kim WJ,Choy WS,et al.Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(1): 83-89.[6] Schmidt R, Cakir B, Mattes T,et al.Cement leakage during vertebroplasty: an underestimated problem? Eur Spine J. 2005;14(5): 466-473.[7] Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, et al.Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2004;25(2): 175-180.[8] Ahn Y, Lee JH, Lee HY, et al.Predictive factors for subsequent vertebral fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine.2008;9(2): 129-136.[9] Zhao H,Ni CF,Chen L,et al.Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2007;41(12): 1405-1408. 赵辉, 倪才方,陈珑,等.骨水泥椎间盘渗漏后组织学和细胞凋亡的实验研究[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2007,41(12): 1405-1408.[10] Zhao H,Ni CF,Chen L,et al.Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2007;23(10): 751-755. 赵辉, 倪才方,陈珑,等.犬椎体成形术中聚甲基丙烯酸甲醋渗漏对椎间盘的影响[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2007,23(10): 751-755.[11] O' Connell GD, Vresilovic EJ, Elliott DM.Comparison of animals used in disc research to human lumbar disc geometry. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(3): 328-333.[12] Elliott DM,Yerramalli CS,Beckstein JC,et al.The effect of relative needle diameter in puncture and sham injection animal models of degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(6): 588-596.[13] Kobayashi H,Fujishiro T,Belkoff SM,et al.Long-term evaluation of a calcium phosphate bone cement with carboxymethyl cellulose in a vertebral defect model. J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(4): 880-888.[14] Johnell O,Kanis JA.An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(12): 1726-1733.[15] Ling X,Cummings SR,Mingwei Q,et al.Vertebral fractures in Beijing, China: the Beijing Osteoporosis Project. J Bone Miner Res.2000;15(10): 2019-2025.[16] Ettinger B,Black DM,Nevitt MC,et al.Contribution of vertebral deformities to chronic back pain and disability. The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7(4): 449-456.[17] Silverman SL,Minshall ME,Shen W,et al.The relationship of health-related quality of life to prevalent and incident vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation Study. Arthritis Rheum.2001;44(11): 2611-2619.[18] Lindsay R,Silverman SL,Cooper C,et al.Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA.2001;285(3): 320-323.[19] Klotzbuecher CM,Ross PD,Landsman PB,et al.Patients with prior fractures have an increased risk of future fractures: a summary of the literature and statistical synthesis. J Bone Miner Res.2000;15(4): 721-739.[20] Hasserius R,Karlsson MK,Jónsson B,et al.Long-term morbidity and mortality after a clinically diagnosed vertebral fracture in the elderly--a 12- and 22-year follow-up of 257 patients. Calcif Tissue Int.2005;76(4): 235-242.[21] Kado DM,Browner WS,Palermo L,et al.Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159(11): 1215-1220.[22] Garfin SR,Yuan HA,Reiley MA.New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14): 1511-1515.[23] Lieberman IH,Dudeney S,Reinhardt MK,et al.Initial outcome and efficacy of "kyphoplasty" in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(14):1631-1638.[24] Phillips FM,Todd Wetzel F,Lieberman I,et al.An in vivo comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19): 2173-2178; discussion 2178-2179.[25] Zampini JM,White AP,McGuire KJ.Comparison of 5766 vertebral compression fractures treated with or without kyphoplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(7): 1773-1780.[26] Klazen CA,Lohle PN,de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092.[27] Mirovsky Y,Anekstein Y,Shalmon E,et al.Intradiscal cement leak following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(10): 1120-1124.[28] Komemushi A,Tanigawa N,Kariya S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2006;29(4): 580-585.[29] Syed MI, Patel NA, Jan S,et al.Intradiskal extravasation with low-volume cement filling in percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2005; 26(9): 2397-2401.[30] Pitton MB,Herber S,Bletz C,et al.CT-guided vertebroplasty in osteoprotic vertebral fractures: incidence of secondary fractures and impact of intradiscal cement leakages during follow-up.Eur Radiol.2008;18(1): 43-50.[31] Kim SH,Kang HS,Choi JA,et al.Analysis of adjacent fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: does intradiscal cement leakage really increase the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture? Skeletal Radiol.2011;40(12):1537-1542.[32] Verlaan JJ,Oner FC,Verbout AJ,et al.Temperature elevation after vertebroplasty with polymethyl-methacrylate in the goat spine. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2003;67(1): 581-585.[33] Belkoff SM, Molloy S .Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(14): 1555-1559.[34] Lai PL,Tai CL,Chen LH,et al.Cement leakage causes potential thermal injury in vertebroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12: 116.[35] Neidlinger-Wilke C,Würtz K,Urban JP,et al.Regulation of gene expression in intervertebral disc cells by low and high hydrostatic pressure. Eur Spine J.2006;15 Suppl 3: p. S372-378.[36] Setton LA,Chen J.Mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc and relevance to disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2: 52-57.[37] Baroud G, Heini P, Nemes J,et al.Biomechanical explanation of adjacent fractures following vertebroplasty. Radiology.2003; 229(2): 606-607; author reply 607-608.[38] Gruber HE,Hanley EN Jr.Human disc cells in monolayer vs 3D culture: cell shape, division and matrix formation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2000;1: 1.[39] Preradovic A,Kleinpeter G,Feichtinger H,et al.Quantitation of collagen I, collagen II and aggrecan mRNA and expression of the corresponding proteins in human nucleus pulposus cells in monolayer cultures. Cell Tissue Res.2005; 321(3): 459-464. |