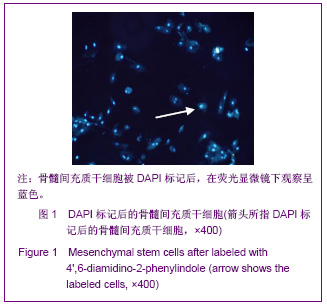
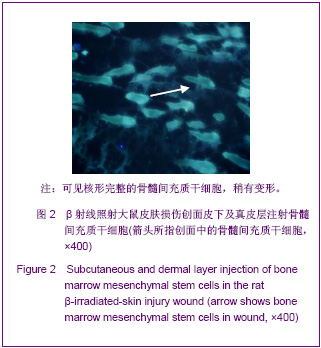
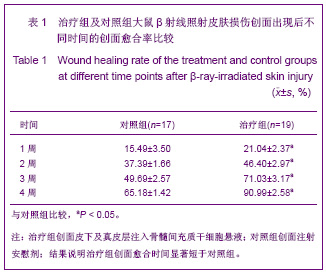
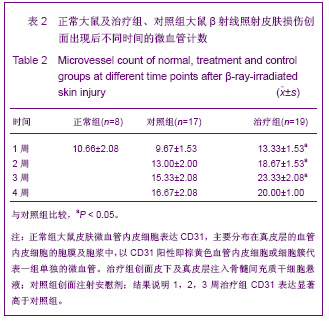
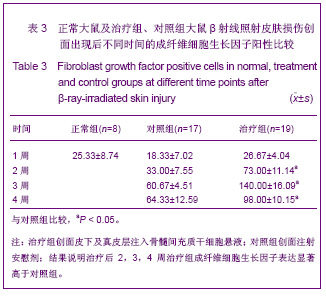
| [1] Elizabeth M, Kedge. A systematic review to investigate the effectiveness and acceptability of intervention for moist desquamation in radiotherapy patients.Radiography. 2009; 15(3):147-257.[2] FitzGerald TJ, Jodoin MB, Tillman G, et al.Radiation Therapy Toxicity to the skin.Dematol Clin. 2008;26(1):161-172.[3] Differ A,mkmansu M,Bora H,et al.The effect of vitamin E On acute skin reaction caused by radiotherapy.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32(5):571-573.[4] Chen JM,Yao WR,Li Y, et al.Jiangsu Yiyao.2010;36(19): 2306-2308. 陈建梅,姚荣伟,李勇,等.骨髓间充质干细胞的分离、培养及生物学特性[J].江苏医药,2010,36(19):2306-2308.[5] Wang YT,Zheng QX,Guo XD,et al.Huazhong Keji Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2003;32(5):526-529. 王运涛,郑启新,郭晓东,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的优化获取及生物学鉴定[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2003;32 (5):526-529.[6] Hu JB,Zhou Y,Jiang DD,et al. Xibao Yu Fenzhi Mianyixue Zazhi. 2006;22(1):7-10. 胡静波,周燕,蒋丹丹,等.体外扩增过程中人骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖与分化规律[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2006,22(1):7-10.[7] De Ugaae DA,Alfonso Z,Zuk PA,et a1.Diferential expression of stem cell mobilization-associated molecules on multi-lineage cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow. Immunol lett.2003;89(23):267-270.[8] Shen GL,Lu XA,Tang J,et al.Zhonghua Fangshe Yixue Yu Fanghu Zazhi. 2006; 26(6):577-579. 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤动物模型的建立与应用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2006, 26(6):577-579.[9] Hu KX, Sun QY,Guo M,et al. The radiation protection and therapy effects of mesenchymal stem cells in mice with acute radiation injury. The British Journal of Radiology. 2010; 83 (985) :52-58.[10] Kuo YR, Wang CT, Cheng JT, et al.Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhanced Diabetic Wound Healing through Recruitment of Tissue Regeneration in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128(4):872-880.[11] Cai Q,Dong F,Liu Y.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(36):6733-6737. 蔡黔,董方,刘毅.异体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠糖尿病足溃疡及血管内皮生长因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(36):6733-6737.[12] Mansilla E,Matin GH,Sturla F,et al.Hum an mesenchymal stem cells ale tolerized by mice and improve skin and spine cord injuries.Transplant Proc.2005;37(1):292-294.[13] Zhu HY,Zhang H,Fu JX,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(32):6303-6308. 朱红燕,张宏,傅晋翔,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与急性放射性皮肤损伤的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与组织康复,2009,13(32): 6303-6308.[14] Satoh H, Kishi K,Tanaka Y,et al.Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells are elective for skin regeneration in actue cutaneous wounds.Cell Transplant.2004;13(4):405-412.[15] Shumakov VI,Onishchcnko YA,Rasulov MF,et al. Mesenchymal bone marrow stem cells more efectively stimulate regeneration of deep bum woHn ds than em bryonic fibroblasts.Bull ExpBiol Med.2003;136(2):192-195.[16] Zhong XH, Wang MG, Zhao LP, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(6): 1019-1022. 钟晓红,王明刚,赵李平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在糖尿病创面中向皮肤腺上皮的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(6): 1019-1022.[17] Yang ZC.Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House. 2006:92. 杨宗城.烧伤治疗学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2006: 92.[18] Shen GL,Lu XA,Tang J,et al.Jiangsu Yiyao. 2006;32(11): 1031-1033. 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤创面愈合过程中基质金属蛋白酶-2的表达[J].江苏医药, 2006,32(11): 1031-1033.[19] Zhou YH,Wu SL,Wang XZ,et al.Fushe Fangfu.2005; 25(6): 257-261. 周迎会,吴士良,王秀珍,等.β和γ射线放射性皮肤损伤动物模型的初步研究[J].辐射防护.2005, 25(6):257-261.[20] Shen GL,Lu XA,Tang J,et al.Zhonghua Shaoshang Zazhi. 2007;23(5):374-375. 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠皮肤β射线损伤创面愈合过程中基质金属蛋白酶9的表达[J].中华烧伤杂志,2007,23(5):374-375.[21] Shen GL,Sun F,Lu XA ,et al.Jiangsu Yiyao. 2010;36(17): 2045-2047. 沈国良,孙峰,陆兴安,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤创面愈合过程中PDGF及其受体的表达[J].江苏医药, 2010,36(17):2045- 2047. |