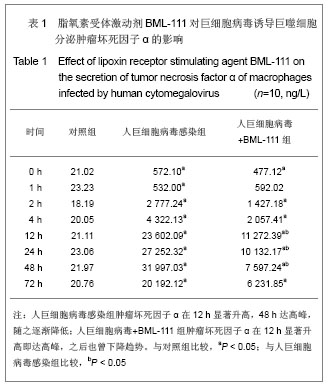
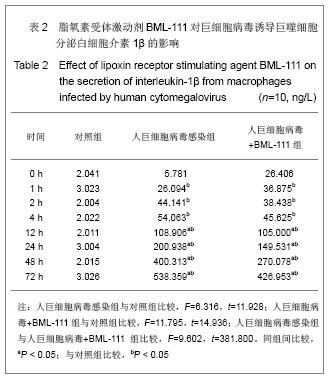
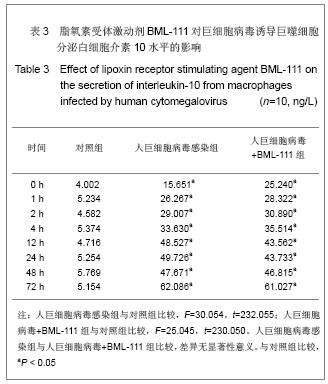
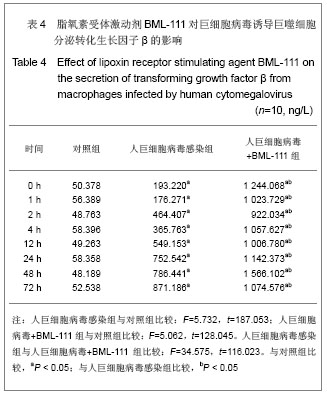
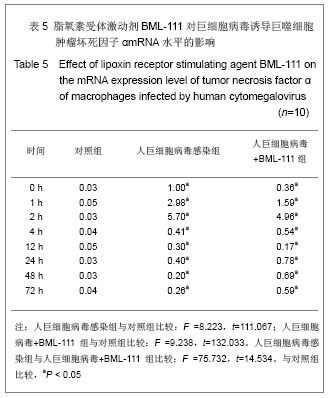
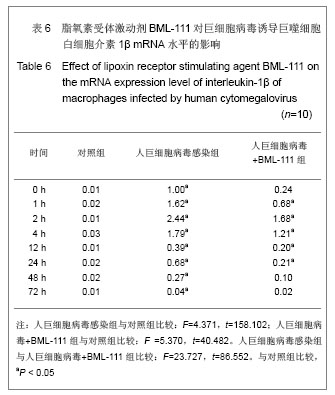
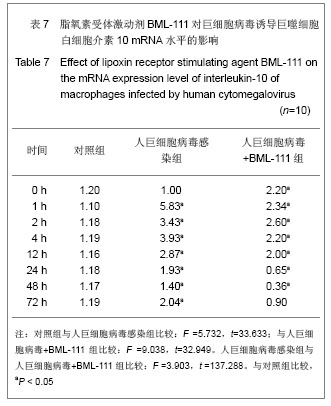
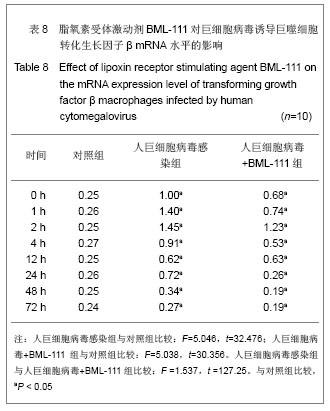
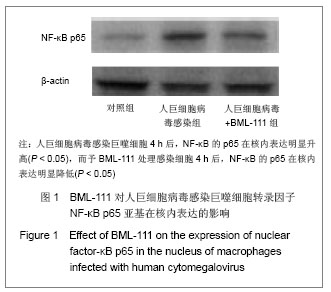
| [1] Fang F.Shiyong Erke Linchuang Zazhi.2010;25(10):701-703.方峰.儿童巨细胞病毒性疾病的诊断与防治[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2010,25(10):701-703.[2] Chen XF, Zhang WZ. Zhengjiang Yixue. 2011;33(12): 1819-1820.陈筱凡, 张伟珍.巨细胞病毒感染检测在骨髓和外周血干细胞移植中的意义[J].浙江医学,2011,33(12):1819-1820.[3] Xiao YM, Hu ZH. Zhongguo dangdai Erke Zazhi. 2010;12(1): 21-23.肖咏梅,胡志红. 不同年龄阶段儿童巨细胞病毒感染的临床表现差异[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2010,12(1):21-23.[4] Fiorentini S, Luganini A, Dell'Oste V, et al. Human cytomegalovirus productively infects lymphatic endothelial cells and induces a secretome that promotes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis through interleukin-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Gen Virol. 2011;92(Pt 3):650-660.[5] Streblow DN, Dumortier J, Moses AV, et al. Mechanisms of cytomegalovirus-accelerated vascular disease: induction of paracrine factors that promote angiogenesis and wound healing. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008; 325:397-415.[6] Penner MJ. Empirical tests demonstrating two coexisting sources of tinnitus: a case study. J Speech Hear Res. 1989; 32(2):458-454.[7] Yacoubian S, Serhan CN. New endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators: implications for rheumatic diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3(10):570-579.[8] Schäfer H, Struck B, Feldmann EM, et al. TGF-β1-dependent L1CAM expression has an essential role in macrophage-induced apoptosis resistance and cell migration of human intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2012 Feb 20.[9] Kim MR, Park DW, Lee JH, et al. Progesterone-dependent release of transforming growth factor-beta1 from epithelial cells enhances the endometrial decidualization by turning on the Smad signalling in stromal cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005; 11(11):801-808.[10] Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, di Sciacca R, et al. Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(33):3574-3589.[11] Baker N, O'Meara SJ, Scannell M, et al. Lipoxin A4: anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic impact on endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2009;182(6):3819-3826.[12] Su JB, Wang XQ, Ma XH, et al. Jiangsu Yiyao. 2012;38(6): 631-634. 苏建彬,王雪琴,马向华,等. 脂联素干预TNF-α作用后的巨噬细胞脂联素受体mRNA表达水平及其吞噬脂质变化[J]. 江苏医药, 2012,38(6):631-634. [13] Ng YH, Zhu H, Pallen CJ, et al. Differential effects of interleukin-1beta and transforming growth factor-beta1 on the expression of the inflammation-associated protein, ADAMTS-1, in human decidual stromal cells in vitro. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(8):1990-1999.[14] Vural P, De?irmencio?lu S, Saral NY, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (-308), interleukin-6 (-174) and interleukin-10 (-1082) gene polymorphisms in polycystic ovary syndrome.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2010;150(1): 61-65.[15] Balkwill F. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(5):361-371.[16] Martinon F, Tschopp J. Inflammatory caspases: linking an intracellular innate immune system to autoinflammatory diseases. Cell. 2004;117(5):561-574.[17] Li MO, Flavell RA. Contextual regulation of inflammation: a duet by transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10. Immunity. 2008;28(4):468-476.[18] Radnai B, Tucsek Z, Bognar Z, et al. Ferulaldehyde, a water-soluble degradation product of polyphenols, inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in mice. J Nutr. 2009;139(2):291-297. [19] Caron PL, Fréchette-Frigon G, Shooner C, et al. Transforming growth factor beta isoforms regulation of Akt activity and XIAP levels in rat endometrium during estrous cycle, in a model of pseudopregnancy and in cultured decidual cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009;7:80.[20] Arici A, MacDonald PC, Casey ML. Modulation of the levels of transforming growth factor beta messenger ribonucleic acids in human endometrial stromal cells. Biol Reprod. 1996;54(2): 463-469.[21] Chen BC, Bai YH, Pan XD, et al. Zhonghua Yiyuan Ganran Zazhi. 2012;22(4):753-755.陈必成,白永恒,潘晓东,等.移植患者免疫抑制剂治疗后感染多瘤病毒及巨细胞病毒的现状[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2012,22(4): 753-755.[22] Xiang HL, Xue WJ, Tian PX, et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2011;32(10):592-595.项和立,薛武军,田普训,等.肾移植术后并发巨细胞病毒肺炎患者的细胞免疫状态[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(10): 592-595.[23] Jing K, Sun M. Zhongguo Dangdai Erke Zazhi. 2010;13(8): 661-664.荆科,孙梅.谷氨酰胺对肠组织NF-κB及肿瘤坏死因子α的调节与肠损伤保护作用的关系[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2010,13(8): 661-664.[24] Liu YS, Chen JQ, Zhu BX. Xuzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2009; 29(8):553-556.刘元山,陈剑群,朱炳喜.细胞因子表达与NF-κB活化在溃疡性结肠炎发病中的意义[J].徐州医学院学报,2009,29(8):553-556.[25] Zhang Y, Wang LN. Guoji Jianyan Yixue Zazhi. 2012;33(4): 436-438.张园,王露楠.巨细胞病毒与自身免疫病关联的研究进展[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2012,33(4):436-438.[26] Ren WY, Zhu L, Hua F, et al. ZHonghua Jiehe he Huxi Zazhi. 2010,33(5):367-371.任卫英,朱蕾,华峰,等. 脂多糖对大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞Toll样受体4和髓样分化蛋白-2基因表达及炎性因子分泌的影响[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2010,33(5):367-371 |