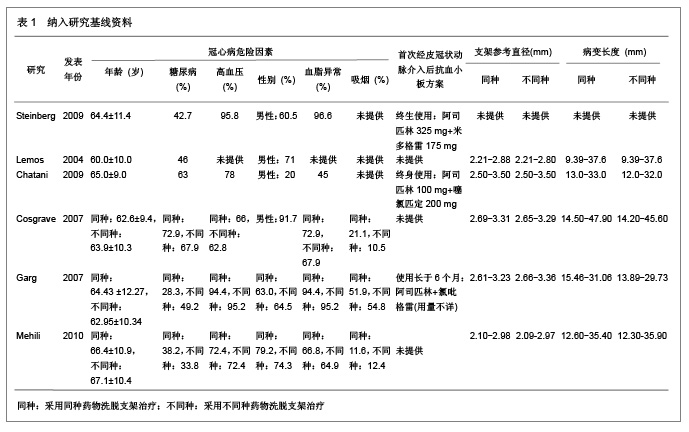
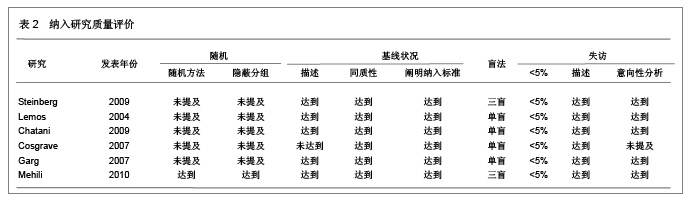
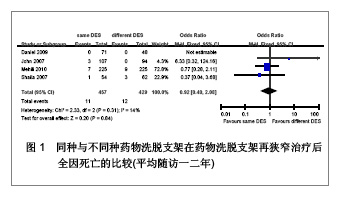
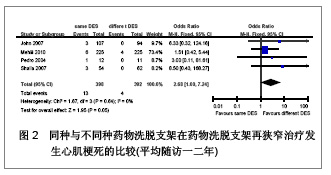
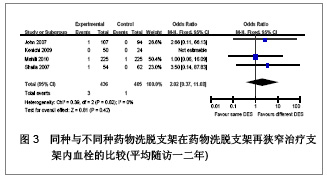
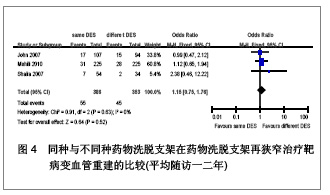
| [1] Serruys PW,Degertekin M,Tanabe K,et al. Intravascular ultrasound findings in the multicenter, randomized, double-blind RAVEL (RAndomized study with the sirolimus-eluting VElocity balloon-expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery Lesions) trial. Circulation.2002;106(7):798-803.[2] Holmes DR Jr,Leon MB,Moses JW,et al.Analysis of 1-year clinical outcomes in the SIRIUS trial: a randomized trial of a sirolimus-eluting stent versus a standard stent in patients at high risk for coronary restenosis.Circulation.2004;109(5): 634-640.[3] Schofer J,Schluter M,Gershlick AH,et al. Sirolimus-eluting stents for treatment of patients with long atherosclerotic lesions in small coronary arteries: double-blind, randomised controlled trial (E-SIRIUS). Lancet.2003;362(9390): 1093-1099.[4] Ellis SG,Colombo A,Grube E,et al. Incidence, timing, and correlates of stent thrombosis with the polymeric paclitaxel drug-eluting stent: a TAXUS II, IV, V, and VI meta-analysis of 3445 patients followed for up to 3 years.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49(10):1043-1051.[5] Kelbaek H,Helqvist S,Thuesen L,et al. Sirolimus versus bare metal stent implantation in patients with total coronary occlusions: subgroup analysis of the Stenting Coronary Arteries in Non-Stress/Benestent Disease (SCANDSTENT) trial. Am Heart J.2006;152(5):882-886.[6] Rahel BM,Laarman GJ,Kelder JC,et al.Three-year clinical outcome after primary stenting of totally occluded native coronary arteries: a randomized comparison of bare-metal stent implantation with sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for the treatment of total coronary occlusions (Primary Stenting of Totally Occluded Native Coronary Arteries [PRISON] II study). Am Heart J.2009;157(1):149-155.[7] Hong MK,Mintz GS,Lee CW,et al. Paclitaxel coating reduces in-stent intimal hyperplasia in human coronary arteries: a serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis from the Asian Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent Clinical Trial (ASPECT). Circulation.2003;107(4):517-520.[8] Silber S,Gutierrez-Chico JL,Behrens S,et al. Effect of paclitaxel elution from reservoirs with bioabsorbable polymer compared to a bare metal stent for the elective percutaneous treatment of de novo coronary stenosis: the EUROSTAR-II randomised clinical trial. EuroIntervention.2011;7(1):64-73.[9] Dibra A,Kastrati A,Mehilli J,et al.Paclitaxel-eluting or sirolimus-eluting stents to prevent restenosis in diabetic patients.N Engl J Med.2005;353(7):663-670.[10] Morice MC,Serruys PW,Barragan P,et al. Long-term clinical outcomes with sirolimus-eluting coronary stents: five-year results of the RAVEL trial. J Am Coll Cardiol.2007; 50(14):1299-1304.[11] Weisz G,Leon MB,Holmes DJ,et al. Two-year outcomes after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: results from the Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in de Novo Native Coronary Lesions (SIRIUS) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol.2006;47(7):1350-1355[12] 李浪.药物洗脱支架再狭窄后治疗方法的选择[J].中国循环杂志,2011,26(3):166-167.[13] Ko YG,Kim JS,Kim BK,et al. Efficacy of Drug-Eluting Stents for Treating In-Stent Restenosis of Drug-Eluting Stents (from the Korean DES ISR Multicenter Registry Study [KISS]). Am J Cardiol. 2012;109(5):607-613.[14] Kim YH,Lee BK,Park DW,et al. Comparison with conventional therapies of repeated sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for the treatment of drug-eluting coronary stent restenosis.Am J Cardiol.2006;98(11):1451-1454.[15] Maluenda G,Ben-Dor I,Gaglia MJ,et al. Clinical outcomes and treatment after drug-eluting stent failure: the absence of traditional risk factors for in-stent restenosis. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2012;5(1):12-19.[16] Sousa JE,Costa MA,Abizaid A,et al.Sirolimus-eluting stent for the treatment of in-stent restenosis: a quantitative coronary angiography and three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound study.Circulation.2003;107(1):24-27.[17] Steinberg DH,Gaglia MJ,Pinto ST,et al. Outcome differences with the use of drug-eluting stents for the treatment of in-stent restenosis of bare-metal stents versus drug-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol.2009;103(4):491-495.[18] Cosgrave J,Melzi G,Corbett S,et al.Repeated drug-eluting stent implantation for drug-eluting stent restenosis: the same or a different stent. Am Heart J.2007;153(3):354-359.[19] Garg S,Smith K,Torguson R,et al. Treatment of drug-eluting stent restenosis with the same versus different drug-eluting stent.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2007;70(1):9-14.[20] Mehilli J,Byrne RA,Tiroch K,et al.Randomized trial of paclitaxel- versus sirolimus-eluting stents for treatment of coronary restenosis in sirolimus-eluting stents: the ISAR-DESIRE 2 (Intracoronary Stenting and Angiographic Results: Drug Eluting Stents for In-Stent Restenosis 2) study. J Am Coll Cardiol.2010;55(24):2710-2716.[21] Lemos PA,van Mieghem CA,Arampatzis CA, et al. Post-sirolimus-eluting stent restenosis treated with repeat percutaneous intervention: late angiographic and clinical outcomes. Circulation.2004;109(21):2500-2502.[22] Chatani K,Muramatsu T,Tsukahara R,et al.Predictive factors of re-restenosis after repeated sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for SES restenosis and clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention for SES restenosis. J Interv Cardiol.2009;22(4):354-361.[23] Kang SJ,Mintz GS,Park DW,et al. Mechanisms of in-stent restenosis after drug-eluting stent implantation: intravascular ultrasound analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2011;4(1):9-14.[24] 宋莉,颜红兵.药物洗脱支架再狭窄[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2011,19(5):279-282.[25] Inoue T,Node K.Molecular basis of restenosis and novel issues of drug-eluting stents. Circ J.2009;73(4):615-621.[26] Yusuf RZ,Duan Z,Lamendola DE,et al.Paclitaxel resistance: molecular mechanisms and pharmacologic manipulation.Curr Cancer Drug Targets.2003;3(1):1-19.[27] Huang S,Houghton PJ.Mechanisms of resistance to rapamycins Drug Resist Updat.2001;4(6):378-391.[28] Huang S,Houghton PJ.Mechanisms of resistance to rapamycins. Drug Resist Updat.2001;4(6):378-391.[29] Curcio A,Torella D,Indolfi C.Mechanisms of smooth muscle cell proliferation and endothelial regeneration after vascular injury and stenting: approach to therapy. Circ J.2011; 75(6): 1287-1296.[30] Nebeker JR,Virmani R,Bennett CL,et al. Hypersensitivity cases associated with drug-eluting coronary stents: a review of available cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports (RADAR) project. J Am Coll Cardiol.2006; 47(1):175-181.[31] Balakrishnan B,Tzafriri AR,Seifert P,et al. Strut position, blood flow, and drug deposition: implications for single and overlapping drug-eluting stents. Circulation.2005;111(22): 2958-2965.[32] Dangas GD,Claessen BE,Caixeta A,et al.In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting stent era. J Am Coll Cardiol.2010; 56(23): 1897-1907.[33] Mintz GS.Features and parameters of drug-eluting stent deployment discoverable by intravascular ultrasound. Am J Cardiol.2007;100(8B):26M-35M.[34] Nayak AK,Kawamura A,Nesto RW,et al.Myocardial infarction as a presentation of clinical in-stent restenosis. Circ J.2006;70(8):1026-1029.[35] Park CB,Hong MK,Kim YH,et al. Comparison of angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis between sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stent. Int J Cardiol.2007;120(3):387-390.[36] Silber S,Colombo A,Banning AP,et al.Final 5-year results of the TAXUS II trial: a randomized study to assess the effectiveness of slow- and moderate-release polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stents for de novo coronary artery lesions. Circulation.2009;120(15):1498-1504.[37] Abizaid A,Costa JJ,Banning A,et al. The sirolimus-eluting Cypher Select coronary stent for the treatment of bare-metal and drug-eluting stent restenosis: insights from the e-SELECT (Multicenter Post-Market Surveillance) registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv.2012;5(1):64-71. |