中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1272-1279.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1965
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
多种特殊状态下关节软骨缺损修复的组织工程技术
陈劲松1,王中汉2,常 非2,刘 贺2
- 1贵州省黔东南州人民医院骨二科,贵州省凯里市 556000;2吉林大学第二医院骨科医学中心,吉林省长春市 130041
-
收稿日期:2019-03-26修回日期:2019-04-02接受日期:2019-05-08出版日期:2020-03-18发布日期:2020-01-23 -
通讯作者:刘贺,主治医师,吉林大学第二医院骨科医学中心,吉林省长春市 130041 -
作者简介:陈劲松,男,贵州省凯里市人,侗族,2005年贵州医科大学毕业,硕士,副主任医师,主要从事骨肿瘤、骨病、创伤研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81171681,81701811);国家自然科学基金(81772456)
Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions
Chen Jinsong1, Wang Zhonghan2, Chang Fei2, Liu He2
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Qiandongnan People’s Hospital, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Orthopedic Medical Center, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-26Revised:2019-04-02Accepted:2019-05-08Online:2020-03-18Published:2020-01-23 -
Contact:Liu He, Attending physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Qiandongnan People's Hospital, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Chen Jinsong, Master, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Qiandongnan People's Hospital, Kaili 556000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171681, 81701811, and 81772456
摘要:
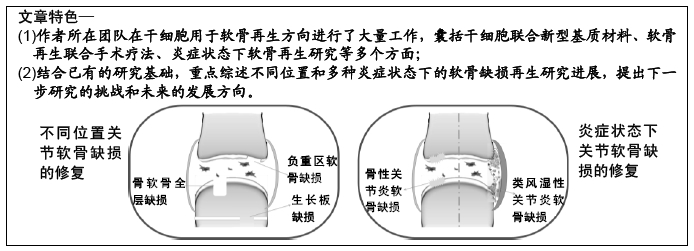
文题释义:
生长板:是位于儿童长骨末端的软骨组织结构,生长板中的软骨细胞可不断增生、成熟、肥大并发生骨化过程,使长骨增长。当长骨生长至一定程度,生长板软骨逐渐被成熟骨组织取代,长骨至此也停止生长。
特殊状态:文章提及的特殊状态即指关节软骨缺损的临床治疗中常见的阻碍因素,即全层软骨缺损及骨软骨缺损、生长板缺损、负重区软骨缺损、炎症状态下(骨性关节炎、风湿性关节炎)的软骨缺损。
背景:应用组织工程学技术可获得良好的关节软骨再生,但多为生理状态下小面积缺损的单纯修复。然而临床上的软骨缺损常伴随骨性关节炎、类风湿性关节炎等基础疾病,且缺损的位置、范围、深度均不确定,给软骨组织修复带来了很大挑战。
目的:总结不同位置和炎症状态下软骨缺损的修复方式。
方法:检索PubMed数据库和CNKI数据库,英文检索词为“cartilage defect regeneration,osteochondral,growth plate,weight-bearing area,inflammatory”,中文检索词为“关节软骨缺损,骨软骨,生长板,负重区,炎症”,检索建库至2019年3月发表的相关文献。共检索到相关文献209篇,按照纳入与排除标准,最终纳入86篇文献进行总结。
结果与结论:针对各种特殊状态下的关节软骨缺损,其修复目标和策略是不同的:全层软骨和骨软骨结构缺损多采用具有多层结构的支架,旨在修复软骨特有的分层结构及软骨下骨结构,同时避免新生软骨内异位骨化的问题;生长板缺损的修复关键在于避免长骨成熟后发生畸形,因此在修复支架内应添加胰岛素样生长因子、骨发生形态蛋白7等生长因子,以持续刺激生长板的修复并发挥骨生长的生理功能;负重区软骨修复则需要修复支架具有良好的力学性能,负重时不会发生严重形变及结构破坏,同时新生的软骨组织具有足够的力学强度以支撑持续的纵向压力和磨损;炎症状态下的软骨缺损则要同时治疗炎症与软骨缺损,间充质干细胞的引入可同时发挥免疫调节及组织再生功能,以使疾病达到彻底治疗的目标。ORCID: 0000-0001-9443-8158(陈劲松)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈劲松, 王中汉, 常 非, 刘 贺. 多种特殊状态下关节软骨缺损修复的组织工程技术[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279.
Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279.
2.1 软骨缺损修复的组织工程技术
2.1.1 种子细胞 通常认为软骨细胞是作为软骨组织修复的最佳细胞来源,但事实上,软骨细胞的局限性限制了它的使用:软骨细胞数量有限,细胞移植数量不足;软骨细胞从基质分离的过程复杂且不易控制。在胶原酶消化过程中可能引起不可逆的细胞损伤,导致软骨再生效果较差[15-16]。由于软骨细胞的局限性,研究者发现间充质干细胞是一种理想的替代细胞源。间充质干细胞广泛存在于骨髓、脂肪组织、滑膜和脐带等组织中,虽然这些组织中间充质干细胞的总含量相对较低,但由于其增殖能力较强,通过体外扩增可获得足够的细胞数量。间充质干细胞具有强大的分化功能,在接受各种类型的理化刺激后可向不同方向分化。在接受刺激后,间充质干细胞主要通过以下通路发挥成软骨分化作用:①生物信号通路:骨发生蛋白、Hedgehog、Notch通路等;②化学物质促进分化:地塞米松、成纤维细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子I、钙离子等;③生物力学信号:剪切应力、基底硬度均可调控其呈软骨分化[17]。
骨髓间充质干细胞来源于骨髓组织,其在软骨向分化潜能的研究最多。通过全骨髓贴壁筛选法和密度梯度离心法可以获得高纯度的骨髓间充质干细胞[18]。通过将骨髓间充质干细胞与软骨细胞在模拟体内环境中共同培养1周后发现,周围基质中Ⅱ型胶原与蛋白聚糖分泌均增加[19]。另外,有大量研究证实了骨髓间充质干细胞具有向软骨细胞分化并分泌相应基质形成软骨组织的能力[20-22]。但有些研究应用骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化能力以修复软骨缺损时,发现修复处有软骨下骨异常增生及骨赘形成的现象。因此,骨髓间充质干细胞定向定位诱导仍是值得关注的问题[23]。
脂肪源性间充质干细胞是另一种常见的间充质干细胞种类,并有大量针对其成骨、成软骨、成肌潜能的基础研究。相比于骨髓间充质干细胞,脂肪源性间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中有2点突出优势:脂肪源性间充质干细胞来源于脂肪,其来源相比于骨髓间充质干细胞更丰富且更易于获得;脂肪源性间充质干细胞的增殖效率相比骨髓间充质干细胞更高,原代脂肪源性间充质干细胞的增殖速度为骨髓间充质干细胞的2倍左右[24-25]。但由于脂肪源性间充质干细胞成软骨分化相关的研究起步较晚,关于其分化能力、分化条件与环境等仍需要进一步研究。
另外,脐带间充质干细胞也是常见的间充质干细胞来源,脐带间充质干细胞的增殖、定向分化能力均较强,且免疫原性低,具有较强的免疫调节能力[26-28]。
2.1.2 支架 支架是除了种子细胞外用于软骨组织工程重建的另一要素。引入组织工程支架的3点重要原因包括:①为种子细胞提供稳定而充足的三维微环境来黏附与生长。支架中复杂的网状结构可以维持其间细胞的基本形态,也利于细胞营养交换和废物代谢;②细胞可以受到支架的一定物理刺激,使得细胞增殖、分化得到正向调控;③组织工程支架可以为缺损部位的重建提供一定的力学支撑强度,维持重建组织的形态,这在负重区组织重建中尤为重要[29-30]。
用于组织工程支架构造的原材料分为2种,包括天然材料和合成材料,前者包括透明质酸、壳聚糖、天然胶原、藻酸盐等[31-33],后者则包括聚乳酸-羟基乙酸聚合物、聚乳酸、聚己内酯等[34-35]。上述的各类支架材料在软骨组织重建中各有优劣势,亦有大量研究对比他们在成软骨能力方面的能力。JIANG等[36]以透明质酸作为原料合成一种光敏性水凝胶,并将其用于软骨缺损修复中取得了满意效果。SOLCHAGA等[37]比较了透明质酸基和聚酯基支架用于骨软骨缺损重建的效果,发现聚酯基支架骨软骨缺损修复效果更好,他们解释为在2种材料生物相容性均好的情况下,聚酯材料的降解速度更快,为新生组织的早期生长提供了更多的空间。
除了不同的支架材料,支架的形态也是调控细胞行为的重要因素,尤其在骨软骨缺损修复当中,多相结构支架可以模拟各层组织形态,如细密定向结构利于软骨层的修复,多孔隙的材料则利于骨层的重建[38]。因此,针对这种情况各种,各种类型的双层支架如胶原/羟基磷灰石支架、硫酸软骨素-透明质酸钠/陶瓷支架等材料被用以大量研究[4,36,39]。
2.2 特殊状态下软骨修复
2.2.1 全层软骨缺损与骨软骨缺损的修复 严重的创伤性关节疾病及一些自身疾病如剥脱性骨软骨炎,经常性地导致全层软骨缺损乃至更深层的骨软骨缺损。因为此类组织缺损结构复杂、深度及范围均大,因此对其良好的修复仍是的一大挑战。近年来世界范围各实验室针对该方向进行了大量的研究,并有了可观的研究成果。
最初,关节内注射是软骨全层缺损的治疗选择之一。通过关节内注射乙酰氨基葡糖等可以使全层缺损的软骨组织得到一定修复,新生组织内的氨基葡聚糖和转移生长因子β2等软骨向分化的基质物质和细胞因子均呈高表达,但通过此方式修复的软骨结构不平整,不能满足临床治疗的需求[40]。之后,组织工程技术用以治疗全层软骨缺损,作者所在团队于10年前即开展了此类研究,将骨髓间充质干细胞混合骨髓源性单核细胞包载于水凝胶材料中,植入家兔膝关节软骨全层缺损中12周后,发现新生的软骨组织在生化学和组织学检测中均明显优于对照组[41]。随之开展了多种不同组成的细胞支架搭载间充质干细胞用于全层缺损软骨修复的研究,使用壳聚糖、透明质酸作为细胞支架均可获得良好的软骨再生效果[42]。
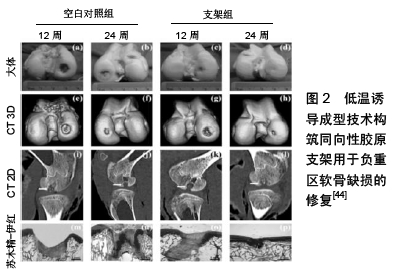
类似的,应用脐带间充质干细胞包载于羟基磷灰石基水凝胶中用于全层软骨缺损修复也得到了积极的结果[43]。随着对软骨组织结构的深入了解,研究中构建了一种模拟软骨内天然胶原纤维排布的定向结构支架。应用温度逐层多相诱导技术调控天然软骨基质材料定向排列,垂直于关节面方向,这种定向排列后的软骨基质材料抗压强度明显高于温度多相诱导前随机排列的结构,负载骨髓间充质干细胞后可以在负重区域全层软骨缺损的修复中收获良好结果[44],见图2。
骨软骨缺损修复则涉及更复杂的过程,该治疗过程需要对骨、软骨2个层面进行修复,同时也需要关注骨-软骨界面的重建。初期的一些对于骨软骨缺损修复的研究仅关注关节层面的重建而忽略了软骨下骨层,这样造成了关节整体结构的不稳定。近年来用于骨软骨缺损修复的分层结构支架被发明并进行了广泛研究,这种层状梯度形态的支架具有仿生结构,模拟了关节软骨-骨层的解剖形态。作者所在团队也一直致力于开发这种具有仿生结构、利于骨软骨全层修复的多层材料。位于上层的支架通常采用一些利于软骨生长的材料,如胶原、透明质酸以及聚乳酸等材料;而下层的支架则需要利于骨组织生长,因此羟基磷灰石、脱基质骨等具有骨诱导作用的材料多被使用[45]。随着对分层结构支架研究的加深,双层支架结构的缺陷逐渐体现:骨和软骨再生的微环境是有差异的,2个层面支架的直接连接导致微环境互相影响,易导致再生软骨组织的骨化。在生理结构中,骨与软骨之间有一钙化层面,可将两者进行分隔。ZHANG等[44]对于此结构进行模拟,于2层支架中间构造一个极薄的致密层形成“三明治”结构,在动物实验中,骨与软骨均生长良好,避免了软骨骨化的问题。另外,DA等[46]、LEVINSTON等[47]均构造了类似结构的支架并取得了良好骨软骨缺损修复效果,为获得软骨下骨层足够的力学性能,WEI等[48]应用了孔隙钽金属作为软骨下骨修复层,并于其上黏附上胶原膜层作为软骨修复材料,在植入山羊骨软骨缺损16周后,软骨层缺损和软骨下骨缺损均得到良好的修复。
文内涉及软骨修复所需材料、措施和结果见表1。

2.2.2 生长板缺损的修复 生长板是位于儿童长骨末端的软骨组织结构,生长板中的软骨细胞可不断增生、成熟、肥大并发生骨化过程,使长骨增长。当长骨生长至一定程度,生长板软骨逐渐被成熟骨组织取代,长骨至此也停止生长。超过20%的儿童长骨骨折合并生长板的损伤,这会导致长骨发育不良甚至发育停滞等严重不良后果[49-50]。寻求一种合适的生长板损伤修复方式可在早期预防长骨畸形、缩短的发生,避免成年后大型的畸形矫正术。
Salter-Harris分型是用于生长板损伤的常用分型系统,首先由Salter和Harris在1963年首次提出,此分型对生长板损伤的相关治疗和预后情况均有重要的指导意义。Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型的损伤由于易于复位,未造成干骺端损伤,通常预后良好;其余4型损伤均易造成损伤生长板后骨性修复,从而导致生长停滞和长骨成交畸形[51]。传统的治疗方式包括将脂肪或肌肉组织填充生长板缺损处以组织骨性修复,但此方法疗效仍然存有争议且软骨修复效果欠佳[52]。
组织工程技术和干细胞技术被认为是修复生长板损伤的有效方法。首先,依据上文内容,植入生长板损伤部位的间充质干细胞可以对损伤部位进行修复,恢复软骨组织的平整和完整性。同时,间充质干细胞可以模拟缺损生长板的生理功能,由间充质干细胞分化的软骨组织可随年龄增加发生软骨内骨化过程,促进长骨的生理性生长。AZARPIRA等[53]在4周龄兔的股骨远端生长板组织构造圆形缺损,分别植入不同浓度的骨髓间充质干细胞,3个月后获取股骨远端,发现间充质干细胞组股骨畸形角度均小于对照组,且大浓度骨髓间充质干细胞(1.5×109 L-1)组收获了更好的预防畸形的效果。
用于生长板修复的组织工程技术有2点特殊需求:组织工程支架需要一定的力学强度和结构稳定性,以阻止异常骨桥的生长;支架通常是利于软骨组织修复的生物降解材料,包括聚乳酸-羟基乙酸聚合物、琼脂糖、壳聚糖、纤维蛋白胶和透明质酸等[54]。
生长板的功能特点为其可以促进长骨生长,此过程为软骨祖细胞在静止区成熟,并逐渐转移至增殖区。然后在增殖区和肥大区,细胞开始分泌软骨基质并进行软骨内成骨[55]。这个复杂的过程是由多种生物因子和信号通路调节,因此有必要在生长板板损伤修复过程中利用特殊支架和特定生长因子对此微环境进行模拟。起初,生长因子(胰岛素样生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子2和骨形成蛋白7)被直接加入支架中发挥功能调控作用[56-57]。该方法获得了一定的效果,但不能保证生长因子的长期稳定释放直至软骨缺损完全修复。之后,基因技术被选用来解决该问题。通过转染技术将靶基因转移到干细胞遗传因子内使生长因子在胞中持续表达,发挥促进其成骨分化功能[55]。另外,LIU等[58]直接在生长板增殖区内提取软骨细胞,进行异体软骨细胞局部移植治疗生长板缺损,其治疗效果优于从成熟关节软骨组织分离的软骨细胞移植。
2.2.3 负重区关节软骨缺损的修复 关节软骨表面区域根据应力分布可分为负重区和非负重区。以膝关节股骨远端侧为例,与半月板接触的内、外侧髁为负重区,而髁间窝和髁上区域属于非负重区[59]。当人处于站立位时,下肢力线穿过关节的负重区,因此负重区的软骨起到了缓冲、吸收应力的作用。由于长期的力学刺激,负重区和非负重区软骨组织学形态存在一定差异:负重区的软骨更厚,软骨组织基质更加丰富。另外,负重区软骨内的软骨细胞体积更大且形态更不规则,这种可能反映了细胞的高代谢和濒临凋亡的状态,这也是导致骨性关节炎的危险因素[60]。
据数据统计,超过75%的关节软骨缺损均发生于负重区域[61],因此在动物实验中在负重区软骨构造缺损也更具有临床意义。此领域中大部分研究使用豚鼠或家兔作为实验动物,但这些动物体型过小,造模时不能完全模拟临床上负重区软骨缺损的情况。为了构造更拟合临床情况的负重区关节软骨缺损,现在的研究更偏好选择如猪、羊等更大型的动物。GONG等[62]在猪股骨滑车处负重区软骨制造缺损,并植入包载脂肪源性间充质干细胞的聚酯支架进行缺损修复,6个月后可见负重区软骨形态已趋于正常。另一些研究表明,负重区软骨缺损修复速度也快于非负重区处,这可能归因于负重区处的更强力学刺激利于此处细胞的增殖与分化。LIN等[63]则利用生物素-亲和素系统接合CD44抗体并负载于壳聚糖支架中用于负重区软骨缺损的修复,也获得了良好的修复效果。
负重区缺损修复使用的支架也有着相当的力学强度要求,在高强度压力下能够保持结构的完整性。另外,负重区的软骨缺损修复面临另一严峻问题,缺损修复处将持续受到摩擦、挤压等力学刺激,可能造成初期组织修复不稳定,导致缺损处纤维修复等不良结果[64]。作者的研究建议在负重区软骨缺损修复过程中使用关节牵引器,以避免关节面接触,从而有利于软骨层的修复[65]。HARADA等[66]亦建议在负重区软骨缺损修复后使用关节牵引器,以避免关节面接触,其亦比较了使用负重区软骨缺损修复使用关节牵引器和未使用组的软骨修复效果,发现行8周关节牵引组较未使用组软骨再生效果更佳。
2.2.4 骨性关节炎状态下关节软骨缺损的修复 骨性关节炎是目前临床最常见的关节疾病之一,可引起关节疼痛、畸形,甚至致残。剧WTO统计,世界范围内超过27%的60岁以上人群均患有骨性关节炎,且疾病严重程度与年龄呈正比[67]。由于承受大部分体质量,膝关节是骨性关节炎最常受累的关节。由于劳损造成的如腕、肘关节骨性关节也是一大常见原因。骨性关节炎病理特征为进展性地软骨组织退化、软骨下骨重建,后期发生关节间隙变窄、骨赘生成。
关节腔内玻璃酸钠注射是治疗早期骨性关节炎的常用选择,玻璃酸钠可以润滑关节面,减小摩擦以缓解症状,但这只是暂时控制症状的对症治疗,无法达到长期有效治疗的目的[68]。而后,使用关节镜修补不平整或缺失的关节面也常被使用。但关节镜手术只在物理层面恢复了关节面的光滑,忽略了骨性关节炎软骨组织的病理状态[69]。目前干细胞技术也被应用于骨性关节炎的治疗。相比于上述疗法,干细胞治疗属于重建性治疗方法,间充质干细胞有着分化和免疫调节双重作用,在修复软骨缺损的同时可以调节关节的炎症状态。
绝大多数的动物骨性关节炎模型是用手术方式构造的,通过切除半月板或交叉韧带组织造成关节的不稳定,并逐渐发生骨性关节炎。MURPHY等[70]应用半月板切除联合交叉韧带切除构造了山羊的骨性关节炎模型。在骨性关节炎关节内注射同种异体间充质干细胞后,关节软骨组织退化、骨赘生成、软骨下骨硬化等骨性关节炎特征性病理变化均得到控制。DESONDO等[71]进一步测定间充质干细胞关节内注射后相关炎症因子表达,发现干细胞治疗可降低关节滑膜和半月板中基质金属蛋白酶1和肿瘤坏死因子α含量。另有大量类似研究均证实干细胞治疗对骨性关节炎有正向治疗效果。基于这些研究,BLACK等[72]报道了首例随机双盲安慰剂对照试验,发现关节内注射间充质干细胞可有效缓解狗髋关节骨性关节炎跛行、疼痛和活动度。
为取得更好的治疗效果,目前前沿研究方向为转染技术与干细胞治疗相结合。编码骨性关节炎治疗相关蛋白的基因被转染导入间充质干细胞中,构成基因修饰间充质干细胞。通常转染的基因分为2大类,其一是骨性关节炎相关基因,MATSUMOTO等[73]报道,将骨形成蛋白4基因导入间充质干细胞,联合血管内皮生长因子拮抗剂和可溶性Flt-1注射入大鼠骨性关节炎的关节内,取得了良好的软骨修复效果;另一类基因为炎症抑制基因,如转移生长因子抑制蛋白基因、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂基因等,将其转染入间充质干细胞后可以起到控制免疫异常的作用[74]。
2.2.5 类风湿性关节炎状态下关节软骨缺损的修复 类风湿是一类系统性累及全身器官的免疫性疾病,关节则为类风湿最主要的累及靶组织,称为类风湿性关节炎,其主要症状为关节的僵硬、肿胀,并可以造成长期的关节畸形,严重损害了患者生活质量[75]。
类风湿性关节炎病例过程十分复杂,其机制目前尚未完全清楚。简要来说,类风湿性关节炎初期发生关节水肿和滑膜炎症细胞浸润,同时多种炎症细胞如淋巴细胞、单核细胞、巨噬细胞和纤维样滑膜细胞大量分泌浆液,造成关节积液。其中,T淋巴细胞被认为是类风湿性关节炎发病过程中的关键因子之一,关节内的T淋巴细胞持续刺激单核及巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、基质金属蛋白酶等致病因子。这些炎症因子刺激滑膜增生并形成血管翳,逐步侵蚀关节软骨和软骨下骨等组织,造成关节结构破损[76]。药物治疗对于早期类风湿性关节炎的效果是确切的,非类固醇类抗炎药可以有效缓解关节疼痛的症状;肿瘤坏死因子α阻滞剂(英夫利昔单抗、阿达木单抗、依那西普等)等进一步提高了类风湿性关节炎药物治疗的疗效[77]。但这些药物仅可以缓解症状,并不能改善类风关晚期关节软骨和软骨下骨的损伤状态。
已有大量研究证明间充质干细胞具有抗炎和免疫调节功能,它可以抑制T淋巴细胞增殖和单核细胞成熟,同时通过树突状细胞抗原提呈避免细胞毒性淋巴细胞的产生[78]。另外,间充质干细胞还可以抑制树突状细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素10,降低辅助性T-1淋巴细胞和自然杀伤细胞分泌干扰素γ,同时刺激辅助性T-2淋巴细胞分泌白细胞介素4[79]。
关节内注射Ⅱ型胶原和弗氏完全佐剂是类风湿性关节炎动物造模的常见方法,应用间充质干细胞的免疫抑制作用治疗类风湿的研究亦被广泛研究。单纯的间充质干细胞注射可以预防并改善类风湿的免疫异常状态,白细胞介素10、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子的表达均得到抑制。类风湿性关节炎末期软骨和软骨下骨组织均严重受损,由于间充质干细胞疗法具有组织再生修复和免疫调节作用,其被视为对于终末期类风湿性关节炎的理想治疗方式[80]。作者将骨髓间充质干细胞干细胞疗法和微骨折技术相结合用于兔类风湿性关节炎的治疗,在修复了受损的关节软骨的同时,外周血中CD4+和CD8+ T淋巴细胞以及炎症因子均明显下调[81]。随后,作者所在团队使用纤维凝胶和温敏性水凝胶作为细胞支架搭载骨髓间充质干细胞,在类风湿性关节炎模型上得到了更好的组织修复效果[82-83]。另外,物理疗法辅助干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎也是研究热点之一,ROSS等[84]使用脉冲电磁场在体外诱导间充质干细胞,促进类风关模型软骨缺损中植入的间充质干细胞具有更强的免疫调节和软骨修复作用。
干细胞治疗结合基因技术是类风湿性关节炎治疗的未来方向。特种蛋白与短链RNA通过受体抑制作用阻止信号传递(单克隆抗体、可溶性受体、小分子靶向转导蛋白等),还可以通过阻断转录因子或上游因子等方式从根源性阻断炎症因子表达。利用基因技术构造具有抗类风湿性关节炎因子表达的基因修饰干细胞可,以更加高效、靶向地作用于类风湿性关节炎的治疗[85-86]。

| [1] BUCKWALTER JA, MANKIN HJ.Articular cartilage: degeneration and osteoarthritis, repair, regeneration, and transplantation. Instr Course Lect. 1998;47:487. [2] HUNZIKER EB.Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(6):432-463. [3] MORT JS, BILLINGTON CJ.Articular cartilage and changes in Arthritis: Matrix degradation.Arthritis Res.2001;3(6):337. [4] NUKAVARAPU SP, DORCEMUS DL.Osteochondral tissue engineering: current strategies and challenges .Biotechnol Adv.2013;31(5):706. [5] 沈梓维,林子洪,郑秋坚.膝关节骨关节炎的非手术治疗现状[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(7):774-780. [6] UPMEIER H, BRUEGGENJUERGEN B, WEILER A, et al.Follow-up costs up to 5 years after conventional treatments in patients with cartilage lesions of the knee.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2007;15(3):249. [7] STEADMAN JR, RODKEY WG, RODRIGO JJ.Microfracture: surgical technique and rehabilitationto treat chondral defects.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;391(391 Suppl):S362. [8] HORAS U, PELINKOVIC D, HERR G, et al.Autologous chondrocyte implantation and osteochondral cylinder transplantation in cartilage repair of the knee joint. A prospective, comparative trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(12):2487. [9] MCNICKLE AG,PROVENCHER MT,COLE BJ. Overview of existing cartilage repair technology.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2008;16(4):196-201. [10] 高祎,杨柳.骨髓间充质干细胞移植应用于骨科的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(2):121-128. [11] HIRAOKA K, GROGAN S, OLEE T, et al.Mesenchymal progenitor cells in adult human articular cartilage.Biorheology. 2006;43(3-4):447-454. [12] WAKITANI S, GOTO T, PINEDA SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4):579. [13] JONES E, FIELD S, ENGLISH A, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell repair capabilities are defective in rheumatoid arthritis in relation with in vivo exposure to inflammation.Arthritis Res Ther.2007; 9(S3):1-2. [14] SWART JF, DE RS, HOFHUIS FM, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in proteoglycan induced arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(4):769. [15] VAN DER KRAAN PM, BUMA P, VAN KUPPEVELT T, et al.Interaction of chondrocytes, extracellular matrix and growth factors: relevance for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(8):631-637. [16] MELGAREJO-RAMÍREZ Y, SÁNCHEZ-SÁNCHEZ R, GARCÍA-LÓPEZ J.Characterization of pediatric microtia cartilage: a reservoir of chondrocytes for auricular reconstruction using tissue engineering strategies.Cell Tissue Bank.2016;17(3):481-489. [17] ZHOU S, CHEN S, JIANG Q, et al.Determinants of stem cell lineage differentiation toward chondrogenesis versus adipogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci.2019;76(9):1653-1680. [18] OTSURU S, HOFMANN T,RAMAN P.Equivalent MSC preparations using two isolation methods.Cytotherapy. 2014;16(4):S75-S75. [19] COOKE ME, ALLON AA, CHENG T, et al.Structured three-dimensional co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells with chondrocytes promotes chondrogenic differentiation without hypertrophy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(10):1210-1218. [20] WEI B, JIN C, XU Y, et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of marrow clots after microfracture with BMSC-derived ECM scaffold in vitro.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(19-20):2646-2655. [21] 刘广涛,高峰,徐军,等.可注射性纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合支架与骨髓间充质干细胞、骨形态发生蛋白2修复骨缺损的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(2):228-233. [22] BA R, WEI J, LI M, et al.Cell-bricks based injectable niche guided persistent ectopic chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and enabled nasal augmentation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):16. [23] RANGANATHAN K, LODER S, AGARWAL S.Heterotopic Ossification: Basic-Science Principles and Clinical Correlates.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(13):1101-1111. [24] PAK J, LEE JH, KARTOLO WA,et al.Cartilage Regeneration in Human with Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Current Status in Clinical Implications. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016(1):4702674. [25] IM GI.Regeneration of articular cartilage using adipose stem cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(7):1830. [26] LIU S, YUAN M, HOU K, et al.Immune characterization of mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and derived cartilage cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;278(1-2):35-44. [27] LEE OK,KUO TK,CHEN WM,et al.Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood.Blood. 2004;103(5):1669. [28] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Zhou JR.Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord.Stem Cell Rev. 2011; 7(1):195-207. [29] LI WJ, TULI R, OKAFOR C, et al.A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials.2005;26(6):599. [30] CHUNG CA, YANG CW, CHEN CW.Analysis of cell growth and diffusion in a scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;94(6):1138. [31] WANG CC, YANG KC, LIN KH, et al.A highly organized three-dimensional alginate scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering prepared by microfluidic technology.Biomaterials.2011;32(29):7118-26. [32] 张弩,吴宇.温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶复合细胞因子修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(34):6298-6302. [33] WU G,WANG YJ,LU HD,et al.Application of Multilayer Collagen/HA Scaffold in Cartilage Tissue Engineering.Key Eng Mat.2007;336-338: 1549-1552. [34] FAN H, HU Y, ZHANG C, et al.Cartilage regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and a PLGA-gelatin/chondroitin/hyaluronate hybrid scaffold. Biomaterials.2006;27(26):4573-4580. [35] ALVES ML, MARTINS A, COSTAPINTOAR, et al.Cartilage tissue engineering using electrospun PCL nanofiber meshes and MSCs. Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(12):3228-3236. [36] JIANG J, TANG AG, GUO XE, et al.Bioactive stratified polymer ceramic-hydrogel scaffold for integrative osteochondral repair.Ann Biomed Eng.2010;38(6):2183. [37] SOLCHAGA LA, TEMENOFF JS, GAO J, et al.Repair of osteochondral defects with hyaluronan-and polyester-based scaffolds.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(4):297-309. [38] ZHANG ZZ, JIANG D, DING JX.Role of scaffold mean pore size in meniscus regeneration.Acta Biomater.2016;43:314-326. [39] GETGOOD AMJ, KEW SJ, BROOKS R, et al. Evaluation of early-stage osteochondral defect repair using a biphasic scaffold based on a collagen-glycosaminoglycan biopolymer in a caprine model. Knee. 2012;19(4):422-430. [40] CHANG NJ, LIN YT, LIN CC, et al.The repair of full-thickness articular cartilage defect using intra-articular administration of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine in the rabbit knee: randomized controlled trial. Biomed Eng Online. 2015;14(1):10. [41] CHANG F, ISHII T, YANAI T, et al.Repair of large full-thickness articular cartilage defects by transplantation of autologous uncultured bone- marrow-derived mononuclear cells.J Orthop Res.2008;15(1):18-26. [42] LI X, DING J, ZHUANG X, et al.Chitosan-Based Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Chitosan: A Promising Substrate for Regenerative Medicine in Drug Formulation,2015:61-82 [43] HA CW, PARK YB, CHUNG JY, et al.Cartilage Repair Using Composites of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel in a Minipig Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(9):1044. [44] ZHANG T, ZHANG H, ZHANG L,et al.Biomimetic design and fabrication of multilayered osteochondral scaffolds by low-temperature deposition manufacturing and thermal-induced phase-separation techniques. Biofabrication. 2017;9(2):025021. [45] LI X, DING J, WANG J, et al.Biomimetic biphasic scaffolds for osteochondral defect repair. Regen Biomater. 2015;2(3):221. [46] Da H, Jia SJ, Meng GL,et al.The impact of compact layer in biphasic scaffold on osteochondral tissue engineering.PloS One. 2013;8(1): e54838. [47] LEVINGSTONE TJ, RAMESH A, Brady RT, et al.Cell-free multi-layered collagen-based scaffolds demonstrate layer specific regeneration of functional osteochondral tissue in caprine joints. Biomaterials.2016;87:69. [48] WEI X, LIU B, LIU G, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell-loaded porous tantalum integrated with biomimetic 3D collagen-based scaffold to repair large osteochondral defects in goats. Stem Cell Res Ther.2019;10(1):72. [49] KRONENBERG HM.Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature. 2003;423(6937):332-336. [50] CARTER SR, ALDRIDGE MJ.Stress injury of the distal radial growth plate.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1988;70(5):834-836. [51] BROWN JH, DELUCA SA.Growth plate injuries: Salter-Harris classification.Am Fam Physician.1992;46(4):1180-1184. [52] ROSA C, FOSTER BK, XIAN CJ.Preclinical Studies on Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Growth Plate Cartilage Injury Repair. Stem Cells Int.2011;2011(1):570125. [53] AZARPIRA MR, SHAHCHERAGHI GH, AYATOLLAHI M.Tissue engineering strategy using mesenchymal stem cell-based chitosan scafolds in growth plate surgery: A preliminary study in rabbits. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2015;101(5):601. [54] TEIXEIRA CC, NEMELIVSKY Y, KARKIA C.Biphasic calcium phosphate: a scaffold for growth plate chondrocyte maturation.Tissue Eng Part A. 2006;12(8):2283-2289. [55] XIAN CJ, FOSTER BK.Repair of injured articular and growth plate cartilage using mesenchymal stem cells and chondrogenic gene therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2006;1(2):213-229. [56] CLARK A, HILT JZ, MILBRANDT TA, et al.Treating Proximal Tibial Growth Plate Injuries Using Poly (Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffolds. Bioresearch OA. 2015;4(1):65-74. [57] SUNDARARAJ SK,CIEPLY RD,GUPTA G,et al.Treatment of growth plate injury using IGF-I-loaded PLGA scaffolds.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;9(12):E202-E209. [58] LIU ZM, CHEN PC, LU CC, et al.Characterization, of the proliferating layer chondrocytes of growth plate for cartilage regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A.2019;25(5-6):364-378. [59] SANFRIDSSON J, SVAHN G, JONSSON K, et al.Computed radiography for characterisation of the weight-bearing knee.Acta Radiol. 1997;38(1):514-519. [60] EGGLI PS, HUNZIKER EB,SCHENK RK.Quantitation of structural features characterizing weight- and less-weight-bearing regions in articular cartilage: a stereological analysis of medial femoral condyles in young adult rabbits.Anat Rec.1988;222(3):217. [61] BUCKLANDWRIGHT JC, MACFARLANE DG, JASANI MK, et al. Quantitative microfocal radiographic assessment of osteoarthritis of the knee from weight bearing tunnel and semiflexed standing views.J Rheumatol. 1994;21(9):1734. [62] GONG L, ZHOU X, WU Y, et al.Proteomic Analysis Profile of Engineered Articular Cartilage with Chondrogenic Differentiated Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Loaded Polyglycolic Acid Mesh for Weight-Bearing Area Defect Repair.Tissue Eng Part A.2014;20(4):575-587. [63] LIN H, ZHOU J, CAO L, et al.Tissue-engineered cartilage constructed by a biotin-conjugated anti-CD44 avidin binding technique for the repairing of cartilage defects in the weight-bearing area of knee joints in pigs.Bone Joint Res.2017;6(5):284-295. [64] NISHINO T, ISHII T, CHANG F, et al.Effect of gradual weight-bearing on regenerated articular cartilage after joint distraction and motion in a rabbit model.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5):600. [65] NISHINO T, CHANG FT, YANAI T, et al.Joint distraction and movement for repair of articular cartilage in a rabbit model with subsequent weight-bearing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):1033-1040. [66] HARADA Y, NAKASA T, MAHMOUD EE, et al.Combination Therapy With Intra-Articular Injection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Articulated Joint Distraction for Repair of a Chronic Osteochondral Defect in the Rabbit.J Orthop Res. 2015;33(10):1466. [67] LI M, XIAO R, LI JB, et al.Regenerative approaches for cartilage repair in the treatment of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10): 1577-1587. [68] RIVERA F, BERTIGNONE L, GRANDI G, et al.Effectiveness of intra-articular injections of sodium hyaluronate-chondroitin sulfate in knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter prospective study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2016;17(1):27-33. [69] 王少杰,夏春,石磊,等.膝关节脱位的治疗策略及疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志, 2012,32(6):545-550. [70] MURPHY JM, FINK DJ, HUNZIKER EB, et al.Stem cell therapy in a caprine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:3464-3474. [71] DESANDO G, CAVALLO C, SARTONI F.Intra-articular delivery of adipose derived stromal cells attenuates osteoarthritis progression in an experimental rabbit model.Arthritis Res Ther.2013;15(1):R22. [72] BLACK LL, GAYNOR J, GAHRING D, et al.Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem and regenerative cells on lameness in dogs with chronic osteoarthritis of the coxofemoral joints: a randomized, double-blinded, multicenter, controlled trial.Vet Ther.2007;8(4):272-284. [73] MATSUMOTO T, COOPER GM, GHARAIBEH B.Cartilage repair in a rat model of osteoarthritis through intraarticular transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells expressing bone morphogenetic protein 4 and soluble Flt-1.Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(5):1390-1405. [74] AFIZAH H, HUI JHP.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016;7(3):177. [75] KLARESKOG L,CATRINA AI, PAGET S.Rheumatoid arthritis.Lancet. 2009;373(9664):659-672. [76] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G.The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med.2011;365(23):2205. [77] NGUYEN DX, EHRENSTEIN MR.Anti-TNF drives regulatory T cell expansion by paradoxically promoting membrane TNF–TNF-RII binding in rheumatoid arthritis.J Esp Med.2016;213(7):1241. [78] ANSBORO S, ROELOFS AJ, DE BC.Mesenchymal stem cells for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: immune modulation, repair or both? Curr Opin Rheumatol.2017;29(2):201. [79] BOUFFI C, DJOUAD F, MATHIEU M, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and rheumatoid arthritis: risk or benefit? Rheumatology. 2009;48(10):1185-1189. [80] SNOWDEN JA, PASSWEG J, MOORE JJ, et al.Autologous hemopoietic stem cell transplantation in severe rheumatoid arthritis: a report from the EBMT and ABMTR.J Rheumatol. 2004;31(3):482. [81] LIU H, DING J, WANG J, et al.Remission of collagen-induced arthritis through combination therapy of microfracture and transplantation of thermogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. PloS One.2015;10(3):e0120596. [82] LIU H, DING J, LI C, et al. Hydrogel is Superior to Fibrin Gel as Matrix of Stem Cells in Alleviating Antigen-Induced Arthritis. Polymers. 2016; 8(5): 182. [83] LIU H, DING J, WANG C, et al.Intra-Articular Transplantation of Allogeneic BMMSCs Rehabilitates Cartilage Injury of Antigen-Induced Arthritis.Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(21-22):2733. [84] ROSS CL, ANG DC, ALMEIDA-PORADA G.Extremely-low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Modulate Inflammation and Restore Homeostasis in Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA). Front Immunol.2019. [85] GIBBONS LJ, HYRICH KL.Biologic Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioDrugs. 2009;23(2):111. [86] VAN DE LOO FA, VAN DEN BERG WB.Gene therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Lessons from animal models, including studies on interleukin-4, interleukin-10, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist as potential disease modulators.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2002;28(1):127-149. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [7] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
关节软骨是一种具有弹性的光滑组织,它包绕着关节骨表面以形成关节结构。因为其特有的物理性质,它可以在负重区域起到力量缓冲作用,同时它也极大地减少了关节运动中的摩擦[1-2]。多种疾病包括骨性关节炎、类风湿性关节炎、运动损伤等均可导致关节软骨的损害,这些疾病致病的病理生理学因素均有差异:在骨性关节炎主要为关节软骨退行性变,在类风湿性关节炎中为炎症侵蚀,在运动损伤中则为机械性磨损为主[3]。另外,关节软骨缺损的不同部位和范围也是值得注意的问题,诸如骨软骨全层缺损、儿童生长板缺损和关节面负重区缺损等不同部位范围的缺损会造成不同的症状和预后。然而,由于关节软骨自身修复能力有限,使得其治疗仍是一项巨大的挑战。
目前临床上用于关节软骨缺损的治疗方法可分为3大类,即姑息性治疗、修复性治疗和重建性治疗[4-5]。姑息性治疗主要为关节镜下清理术和软骨成形术等,其主要目的为清理关节表面不平整的软骨面及移除软骨碎片等,以恢复关节面的光滑平整,这种治疗方法有创性较小且可以一定程度缓解患者的症状,但其疗效有限,不能有效阻止关节炎的发展进程[6]。修复性治疗包括微骨折治疗、骨软骨移植等,虽然相比于姑息性治疗具有更高的有创侵入性,但可使得局灶性关节软骨缺损得到一定的修复。同时,骨软骨移植的缺点也很明显,自体移植需要多次手术取自体软骨,导致供区并发症,而同种异体移植则具有免疫排除反应、组织整合较慢等问题[7]。自体软骨细胞移植是现有唯一投入临床应用的软骨缺损重建性治疗方法,它是通过分离自身软骨细胞并富集于基质材料中移植到软骨缺损部位[8]。自体软骨细胞移植技术已出现27年,大量研究和随访对其有效性和安全性进行了证实。但自体软骨细胞移植仍存在一定的局限性:植入的软骨细胞成熟周期较长,且自体软骨细胞移植不适用于类风湿性关节炎等存在自身免疫异常的病例中[9]。
间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能、自我复制和免疫调控功能,以间充质干细胞为中心的细胞治疗技术包括组织工程技术等,被认为是一种用于关节软骨缺损的理想治疗方式。将间充质干细胞植入软骨缺损部位后,其自我复制和多向分化能力使得间充质干细胞在损伤部位大量扩增,并在内源、外源性刺激后成软骨向分化,以重建破坏的关节表面[10-12]。同时近年来的研究发现,间充质干细胞能够调节类风湿性关节炎患者的全身免疫状态,抑制系统性炎症反应,使得间充质干细胞在治疗类风湿性关节炎患者软骨缺损时即对软骨组织进行了修复重建,又可以缓解全身炎症状态[13-14]。
作者所在团队在干细胞用于软骨再生方向进行了大量工作,囊括干细胞联合新型基质材料、软骨再生联合手术疗法、炎症状态下软骨再生研究等多个方面。此文章将结合已有的研究基础,重点对于不同位置和多种炎症状态下的软骨缺损再生研究进展进行综述,并提出下一步研究的挑战和未来的发展方向。
1.1 资料来源 检索PubMed数据库中国知网数据库(CNKI),英文检索词为“cartilage defect regeneration,osteochondral,growth plate,weight-bearing area,inflammatory”,中文检索词为“关节软骨缺损,骨软骨,生长板,负重区,炎症”。检索建库至2019年3月发表的相关文献。
1.2 资料筛选
纳入标准:①软骨组织工程领域原创性文章;②与该文主题相关程度高;③关于软骨缺损的较新的细胞、动物实验和临床试验研究论文;④具有时效性、权威性的综述文章。
排除标准:①研究目的与文章无关;②质量低,证据等级不够的文章;③非时效性文章。
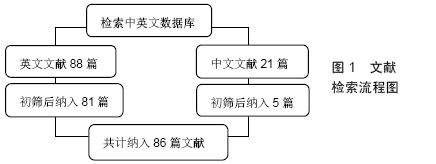
1.3 资料提取 首先根据检索策略初检共得到209篇文章。阅读所有检索文献,并根据筛选标准进行纳入与排除,得到符合标准的论文共计86篇。文献检索流程见图1。
初期关于软骨组织再生的研究多数集中于单纯的软骨组织再生,即在实验室条件下可再生出软骨组织。但临床上面临的软骨缺损情况常常十分复杂,骨软骨缺损、生长板缺损、负重股关节面缺损、伴随骨性关节炎、类风湿性关节炎的软骨缺损均是临床常见的、且在治疗上存在争议。而这些不同状态下软骨缺损也面临着不同的问题:骨软骨全层缺损造成的软骨内骨化;生长板缺损造成的长骨畸形成角;负重区软骨缺损因微动造成的愈合效果不佳;多种炎症状态下软骨修复效果不佳。
随着医工结合的深入,软骨组织工程学研究也逐渐意识到这些解决这些问题的必要性,并研究设计出针对不同情况下软骨修复策略。利用多层支架修复骨软骨全层缺损的研究为目前的研究热点之一,软骨层修复材料通常为凝胶类软性材料,而骨层修复材料则为羟基磷灰石、硬性水凝胶、金属支架等弹性模量于骨组织更接近的材料。并在支架不同层间根据其修复目的添加相应的细胞或生长因子,以调控各层中组织修复分化方向。在此基础上,另有研究在软骨层和骨层间添加高密度薄层结构,以避免两层组织修复的互相干扰,避免异位骨化等问题。生长板缺损的修复策略为应用软质水凝胶材料包载各型生长因子以模拟生长板生化微环境,来促进其再生。但针对生长板修复的大部分研究时程较短,在短期研究中观察到缺损的生长板得到修复即止,仅有极少量研究来观察修复的生长板对肢体生长的影响情况,在未来的研究中设计长期实验以验证生长板功能的修复效果是必要的。负重区软骨缺损造模要求需在如羊、猪等大动物上操作。与大鼠、兔等啮齿类动物后肢形态不同,大动物后肢力线与人更接近,且关节软骨面积大,适合于负重区软骨面缺损的制造。但与生长板修复遇到的问题相同,负重区软骨缺损修复实验设计时长通常不超过3个月。而在临床治疗后,负重区软骨则要经历数年或数十年的生理性挤压、磨损。这也为后续研究提供了方向,即着重研究长期生理性挤压、磨损后,负重区软骨缺损的修复效果。炎症条件下的软骨缺损是临床中最常见的软骨缺损情况,而治疗策略为通过各类炎症抑制药物和间充质干细胞进行免疫调节发挥炎症抑制作用的同时,来进行软骨缺损的修复。目前骨性关节炎的造模方法为通过切除半月板、交叉韧带诱导造成骨性关节炎,但这只模拟了骨性关节炎关节不稳定这一治病因素,而如遗传、炎症因子侵袭、性别等因素在此模型中均未体现。如能构建出模拟骨性关节炎天然发病机制的动物模型进行研究,则可进一步验证治疗的效果。针对类风湿性关节炎条件下的软骨缺损,各类单克隆抗体类药物为目前的治疗与研究热点,但这类药物存在不良反应大、价格昂贵的问题,故通过组织工程手段控制药物缓释,使其可以安全、高效的发挥治疗作用,具有巨大的医疗和社会效益。
组织工程及再生医学研究是伴随着生物材料科学的发展而进步的,而新型医学治疗手段也可以引入再生医学研究领域。已有少量关于软骨再生的研究中涉及了干细胞修饰及转染、生长因子级联放大、辅助物理治疗等手段增强了软骨修复的效果。这是软骨组织再生的新兴方向,且这些治疗手段已发展的较为成熟,有利于治疗方案后续的临床转化道路。另外,用于软骨组织修复的组织工程技术临床推广工作仍需进一步进行,积累更多的临床研究资料,加速临床转化速度,使得此技术实现真正的突破和临床应用。

文题释义:
生长板:是位于儿童长骨末端的软骨组织结构,生长板中的软骨细胞可不断增生、成熟、肥大并发生骨化过程,使长骨增长。当长骨生长至一定程度,生长板软骨逐渐被成熟骨组织取代,长骨至此也停止生长。
特殊状态:文章提及的特殊状态即指关节软骨缺损的临床治疗中常见的阻碍因素,即全层软骨缺损及骨软骨缺损、生长板缺损、负重区软骨缺损、炎症状态下(骨性关节炎、风湿性关节炎)的软骨缺损。
此篇文章不同于以往的研究单纯分析总结软骨缺损的组织工程学修复方法,而是着重于真实的临床情况下的软骨缺损修复。根据缺损位置及是否复合炎症,将软骨缺损分为:软骨全层缺损及骨软骨缺损、生长板缺损、负重区软骨缺损、软骨缺损伴骨性关节炎和类风湿性关节炎5大类,并依次总结出针对不同软骨缺损类型的软骨修复策略,以期在软骨再生的同时,修复材料亦可发挥防止异位骨化、刺激组织生长、负重、抗炎等额外功能。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||