| [1]Anwar MA, Al Shehabi TS, Eid AH. Inflammogenesis of Secondary Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:98.[2]Kasuya Y, Umezawa H, Hatano M. Stress-Activated Protein Kinases in Spinal Cord Injury: Focus on Roles of p38. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3): E867.[3]He FY, Feng WZ, Zhong J, et al. Effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine anesthesia on Th1/Th2 of rat spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(6):1355-1361.[4]Yang J, Zhang X, Chen X, et al. Exosome Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Promotes Neurogenesis after Ischemia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;7:278-287.[5]Qi J, Zhou Y, Jiao Z, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Tumor Growth Through Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(6):2242-2254.[6]Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59.[7]Guo ZY, Sun X, Xu XL, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve repair via paracrine mechanisms. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(4):651-658. [8]Li Z, Qin H, Feng Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-loaded amniotic membrane for the repair of radial nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(36):3441-3448.[9]Xin H, Li Y, Buller B, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells. 2012;30(7): 1556-1564.[10]Sun L, Li M, Ma X, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 reduces rat spinal cord astrocytic swelling and AQP4 expression after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation via TLR4 and NF-κB signaling in an IL-6-dependent manner. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):231.[11]Wang YF, Fan ZK, Cao Y, et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol inhibits the up-regulation of AQP4 and AQP1 expression after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2011;1370:220-226.[12]Zheng Y, Wang L, Chen M, et al. Upregulation of miR-130b protects against cerebral ischemic injury by targeting water channel protein aquaporin 4 (AQP4). Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(7):3452-3461.[13]Zeng Z, Leng T, Feng X, et al. Silencing TRPM7 in mouse cortical astrocytes impairs cell proliferation and migration via ERK and JNK signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119912.[14]李浩阳,陈旭,李强,等.人脐带华通胶间充质干细胞对白细胞介素1β诱导髓核细胞退变的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(25): 3943-3948.[15]Caradec J, Kharmate G, Hosseini-Beheshti E, et al. Reproducibility and efficiency of serum-derived exosome extraction methods. Clin Biochem. 2014;47(13-14):1286-1292.[16]Alvarez ML, Khosroheidari M, Kanchi Ravi R, et al. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012;82(9):1024-1032.[17]宋君来,李满,孙麟,等.抑制高迁移率族蛋白1减轻大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞氧糖剥夺/复氧后的损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(28): 4537-4543.[18]Jian Z, Ding S, Deng H, et al. Probenecid protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in primary astrocytes by regulating inflammasome activity. Brain Res. 2016;1643:123-129.[19]Ou-Yang L, Liu Y, Wang BY, et al. Carnosine suppresses oxygen-glucose deprivation/recovery-induced proliferation and migration of reactive astrocytes of rats in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(1):24-34.[20]Takebayashi H, Nabeshima Y, Yoshida S, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix factor olig2 is essential for the development of motoneuron and oligodendrocyte lineages. Curr Biol. 2002;12(13): 1157-1163. [21]Jian Z, Ding S, Deng H, et al. Probenecid protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in primary astrocytes by regulating inflammasome activity. Brain Res. 2016;1643:123-129.[22]Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, et al. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308.[23]Rosselli DD, Mumaw JL, Dickerson V, et al. Efficacy of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell administration in a model of acute ischemic kidney injury in cats. Res Vet Sci. 2016;108:18-24.[24]Wang D, Wang S, Ji B, et al. Spatiotemporal expression of FOXA1 correlates with reactive gliosis after spinal cord injury. Neuropeptides. 2017;66:36-44.[25]Nathan FM, Li S.Environmental cues determine the fate of astrocytes after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):1964-1970.[26]Abdullah M, Takase H, Nunome M, et al. Amyloid-β Reduces Exosome Release from Astrocytes by Enhancing JNK Phosphorylation. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;53(4):1433-1441.[27]王天仪,刘勇,原文琦,等.微小RNA-199a-5p下调后通过c-jun氨基端激酶通路促进脊髓后索损伤修复的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2015, 32(7):1498-1502.[28]Tang Z, Sun X, Huo G, et al. Protective effects of erythropoietin on astrocytic swelling after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation: mediation through AQP4 expression and MAPK pathway. Neuropharmacology. 2013;67:8-15.[29]Buffo A, Rolando C, Ceruti S. Astrocytes in the damaged brain: molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79(2):77-89.[30]Cho YE, Seo W, Kim DK, et al. Exogenous exosomes from mice with acetaminophen-induced liver injury promote toxicity in the recipient hepatocytes and mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16070.[31]Jia C, Keasey MP, Lovins C, et al. Inhibition of astrocyte FAK-JNK signaling promotes subventricular zone neurogenesis through CNTF. Glia. 2018;66(11):2456-2469. |
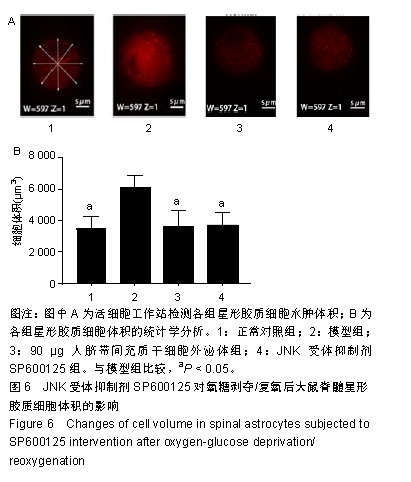
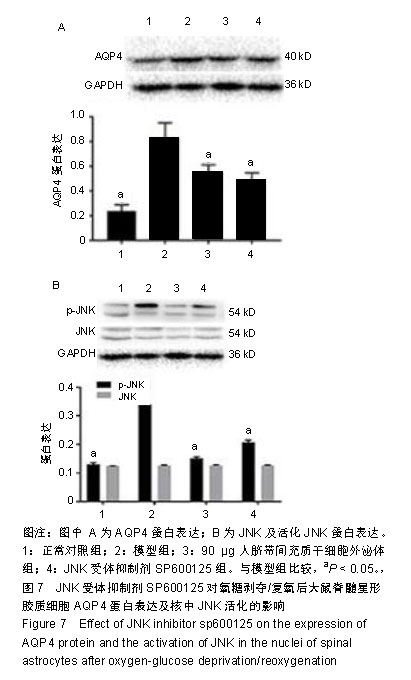
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)