中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (18): 2806-2811.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1732
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
载重组人骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释微球的复合生物支架修复超临界骨缺损
周思睿,肖红利,黄文良,邓 江,叶 鹏
- 遵义医科大学第三附属医院骨科一病区,贵州省遵义市 563000
Supercritical bone defect repaired by composite bioscaffolds loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2/poly(lactic acid)
Zhou Sirui, Xiao Hongli, Huang Wenliang, Deng Jiang, Ye Peng
- First Ward of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
重组人骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释微球:重组人骨形态发生蛋白2是目前公认的修复骨缺损最重要的生长因子之一,与骨修复呈正相关;聚乳酸是可缓慢降解及生物相容性良好的生物高分子材料,作为缓释载体,具有良好的粒径及较稳定释药率,可使重组人骨形态发生蛋白2在骨骼缺损区持续释放,促进局部骨骼修复。
超临界骨缺损:骨骼缺损达到一定范围及距离后,机体自身无法自行修复,该临界点即为临界骨缺损。1986年Schmitz等基于动物实验模型提出了长骨干缺损达到长骨干直径的1.5倍即可认定为临界骨缺损,目前临床上将临界骨缺损的长度定义为1.5-3.0 cm。
背景:前期研究制备了丝素/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石复合生物支架与重组人骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释系统。
目的:观察载重组人骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释微球的复合生物支架,修复犬桡骨超临界骨缺损的效果。
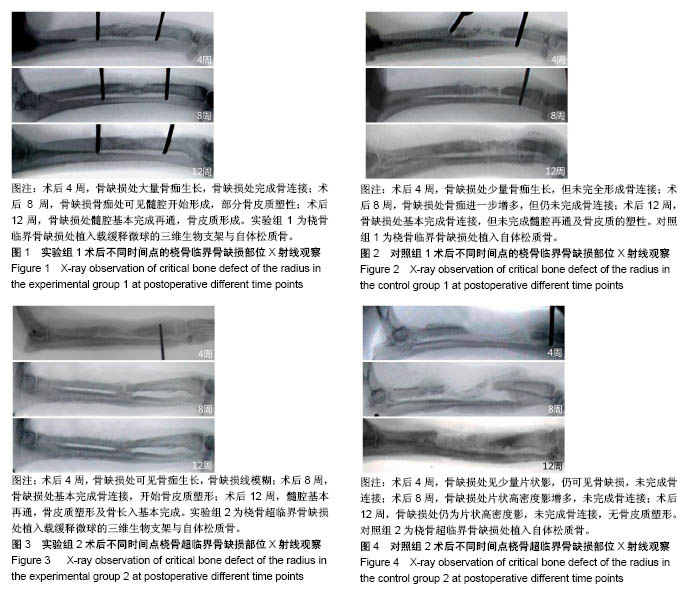
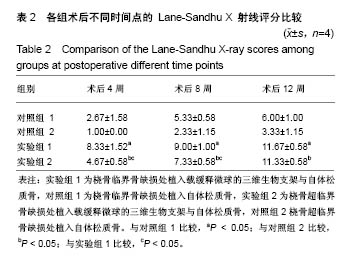
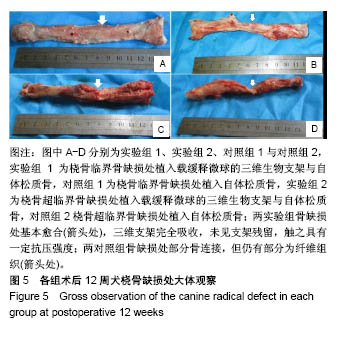
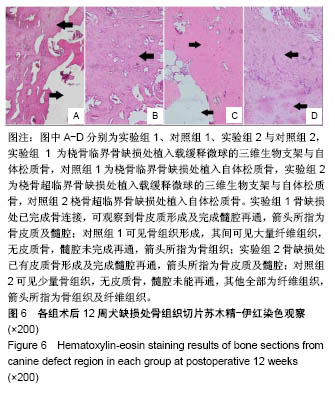
方法:采用真空冷冻干燥及化学交联法制备丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石生物支架,采用复乳挥发法制备重组人骨形态发生蛋白2/聚乳酸缓释微球,将二者整合后制备成载缓释微球的三维生物支架。取8只成年犬(遵义医科大学实验动物中心提供),制作桡骨临界骨缺损模型(桡骨中段截骨3 cm),其中4只骨缺损处植入载缓释微球的三维生物支架与自体松质骨(实验组1),另4只仅植入自体松质骨(对照组1);另取8只成年犬,制作桡骨超临界骨缺损模型(桡骨中段截骨5 cm),其中4只骨缺损处植入载缓释微球的三维生物支架与自体松质骨(实验组2),另4只仅植入自体松质骨(对照组2)。术后 4,8,12周进行X射线检查;术后12周,取出缺损区桡骨,行组织病理学观察。实验已通过遵义医科大学伦理委员会审查,批准号:伦审(2016)2-071号。
结果与结论:①X射线:术后12周,实验组1缺损处髓腔基本再通,骨皮质形成,对照组1缺损处基本完成骨连接,但未完成髓腔再通与皮质骨塑形;实验组2髓腔基本再通,骨皮质塑形与骨长入基本完成,对照组2未完成骨连接,无皮质骨塑形;②组织学观察:实验组1骨缺损处已完成骨连接,可观察到骨皮质形成及完全髓腔再通,对照组1可见骨组织形成,其间可见大量纤维组织,无皮质骨,髓腔未完成再通;实验组2骨缺损处已有皮质骨形成及完成髓腔再通,对照组2可见少量骨组织,无皮质骨形成及髓腔再通;并且实验组1骨修复效果优于实验组2;③结果表明载重组人骨形态发生蛋白2缓释微球的丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石三维生物支架,能有效修复一定范围内的犬桡骨临界及超临界骨缺损。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)