| [1] Seuring T, Archangelidi O, Suhrcke M. The Economic Costs of Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Systematic Review. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015;33(8):811-831.[2] Xie CL, Pan YB, Hu LQ, et al. Propofol attenuates hydrogenperoxide-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via multiple signaling pathways. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015;68(5):488-495.[3] Chu C, Lu FJ, Yeh RH, et al. Synergistic antioxidant activity of resveratrol with genistein in high-glucose treated Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Biomed Rep. 2016;4(3):349-354.[4] Zhu D, Zhang N, Zhou X, et al. Cichoric acid regulates the hepatic glucose homeostasis via AMPK pathway and activates the antioxidant response in high glucose-induced hepatocyte injury. Rsc Advances.2017;7(3):1363-1375.[5] Nur H, Rao L, Frassanito MA, et al. Stimulation of invariant natural killer T cells by α-Galactosylceramide activates the JAK-STAT pathway in endothelial cells and reduces angiogenesis in the 5T33 multiple myeloma model. Br J Haematol. 2014;167(5):651-663.[6] Kim BH, Lee Y, Yoo H, et al. Anti-angiogenic activity of thienopyridine derivative LCB03-0110 by targeting VEGFR-2 and JAK/STAT3 Signalling. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24(7): 503-509.[7] Kusuyama J, Bandow K, Shamoto M, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) influences the multilineage differentiation of mesenchymal stem and progenitor cell lines through ROCK-Cot/Tpl2-MEK-ERK signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(15):10330-10344.[8] 冯天明,杨明聪,潘兰兰,等.低频超声联合曲安奈德对金黄地鼠颊黏膜溃疡愈合的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2017,26(4):379-383.[9] 杨少玲.低频超声联合微泡造影剂对前列腺增生的作用[C].重庆:第一届全国暨第二届国际超声分子影像学术会议论文集,2014.[10] 邢宇,宋晓彬,施克新,等.高血糖人群周围血管病变的患病率调查[J].中国冶金工业医学杂志,2017,34(4):432-433.[11] 薛亚,曹洁,陈荣华,等.急性缺血性卒中患者入院高血糖对血管内治疗结局的影响[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2018,15(3):124-128.[12] 黄燕,何婧,向阳,等.持续高血糖模型小鼠大脑皮质血管周围星形胶质细胞足突的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(20): 3218-3223.[13] Ku SK, Kwak S, Bae JS. Orientin inhibits high glucose-induced vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation. 2014;37(6):2164-2173.[14] Pan Y, Wang Y, Zhao Y, et al. Inhibition of JNK phosphorylation by a novel curcumin analog prevents high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes. 2014;63(10):3497-3511.[15] Renaud J, Bournival J, Zottig X, et al. Resveratrol protects DAergic PC12 cells from high glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis: effect on p53 and GRP75 localization. Neurotox Res. 2014;25(1):110-123.[16] Guo S, Yao Q, Ke Z, et al. Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;412: 85-94.[17] 王喜欢,张金华,胡亚南,等.紫草素对高糖诱导的血管内皮细胞凋亡和氧化应激的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2018,34(7): 1222-1227.[18] Peng H, Zhong W, Zhao H, et al. Lack of PGC-1α exacerbates high glucose-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through activation of VADC1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):4639-4650.[19] 祖海越,易雪婷,赵德伟.低强度脉冲超声促进骨与软骨再生的研究与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2593-2600.[20] Rossato DD, Dal Lago P, Hentschke VS, et al. Ultrasound modulates skeletal muscle cytokine levels in rats with heart failure. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(3):797-805.[21] Chongsatientam A, Yimlamai T. Therapeutic Pulsed Ultrasound Promotes Revascularization and Functional Recovery of Rat Skeletal Muscle after Contusion Injury. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(12):2938-2949.[22] Miyasaka M, Nakata H, Hao J, et al. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation Enhances Heat-Shock Protein 90 and Mineralized Nodule Formation in Mouse Calvaria-Derived Osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(23-24):2829-2839.[23] Novoselova EG, Khrenov MO, Parfenyuk SB, et al. The NF-κB, IRF3, and SAPK/JNK signaling cascades of animal immune cells and their role in the progress of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Dokl Biol Sci. 2014;457(1):255-257.[24] Barcelona PF, Saragovi HU. A Pro-Nerve Growth Factor (proNGF) and NGF Binding Protein, α2-Macroglobulin, Differentially Regulates p75 and TrkA Receptors and Is Relevant to Neurodegeneration Ex Vivo and In Vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 2015;35(19):3396-3408.[25] 侯瑞雪.广西眼镜蛇毒神经生长因子的精制及其对HSC--T6细胞SAPK/JNK信号通路的影响[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2016.[26] Choudhury S, Ghosh S, Gupta P, et al. Inflammation-induced ROS generation causes pancreatic cell death through modulation of Nrf2/NF-κB and SAPK/JNK pathway. Free Radic Res. 2015;49(11):1371-1383.[27] Glushkova OV, Khrenov MO, Novoselova TV, et al. The role of the NF-κB, SAPK/JNK, and TLR4 signalling pathways in the responses of RAW 264.7 cells to extremely low-intensity microwaves. Int J Radiat Biol. 2015;91(4):321-328.[28] Di Pietro R, Centurione L, Sabatini N, et al. Caspase-3 is dually regulated by apoptogenic factors mitochondrial release and by SAPK/JNK metabolic pathway in leukemic cells exposed to etoposide-ionizing radiation combined treatment. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004;17(2):181-190. |
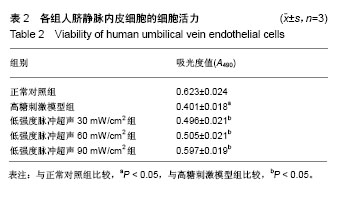
.jpg)
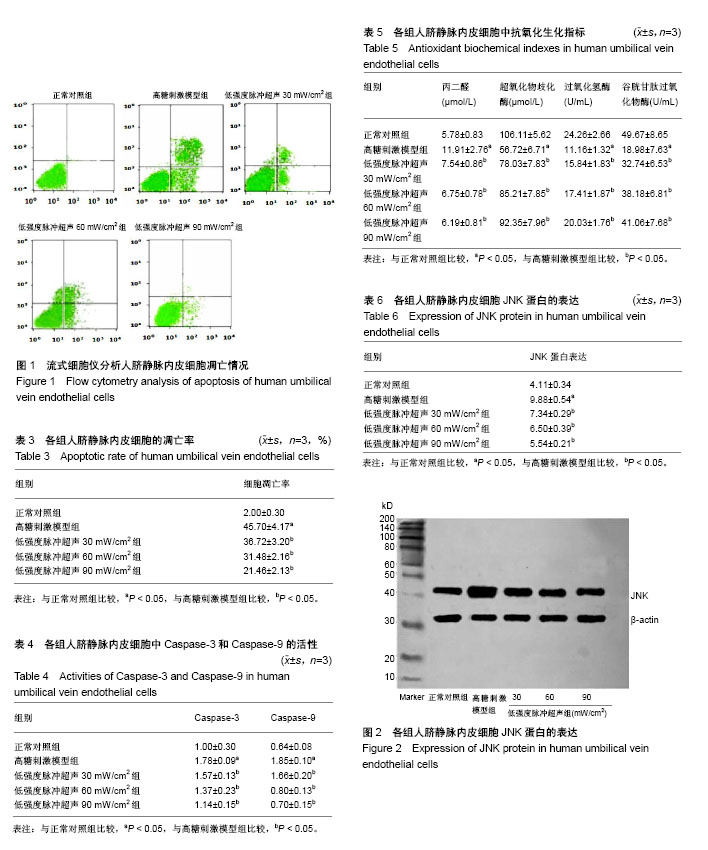

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)