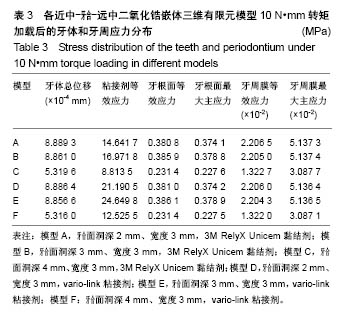
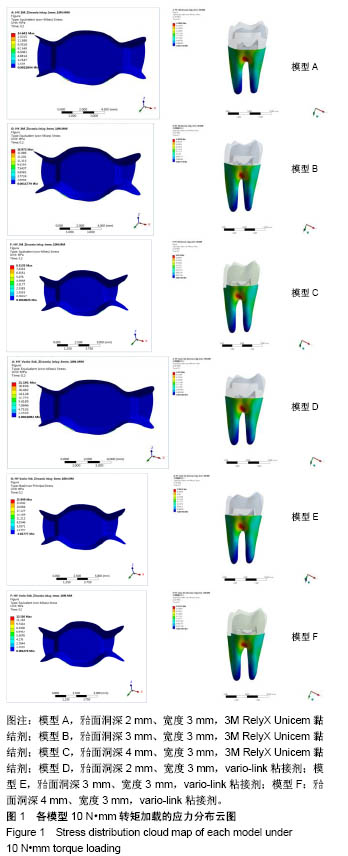
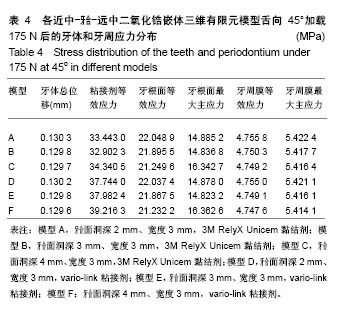
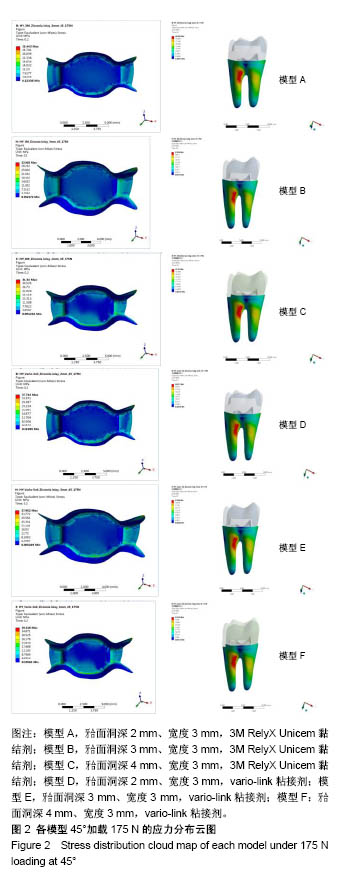
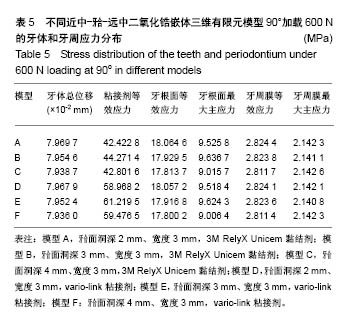
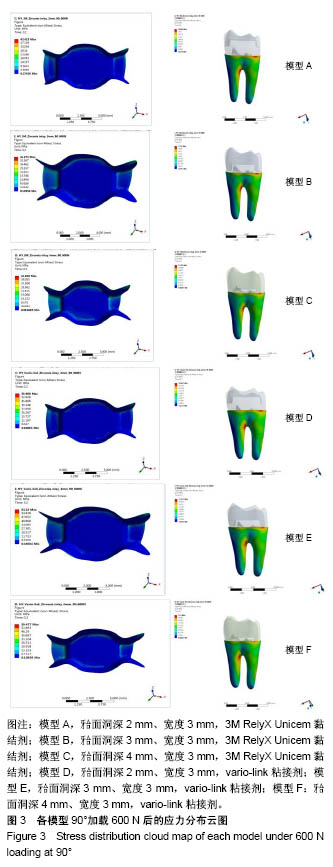
| [1] 唐旭炎.氧化锆合面嵌体近远中面制备固位沟对其粘结固位力影响的实验研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2017:1-41.[2] Dbradovi?-Djurici? K,Medi? V, Dodi? S,et al.Dilemmas in zirconia bonding: a review. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2013;141(5-6): 395-401.[3] Xiao X,Zheng K,Liao W.Theoretical model for cutting force in rotary ultrasonic milling of dental zirconia ceramics.Int J Adv Manuf Technol.2014;75:1263-1277. [4] Ozen J Caglar A,Beydemir B,et al. Three-dimensional finite element stress analysis of different core materials in maxillary implant-supported fixed partial dentures.Quintessence Int. 2007;38(6):e355-363. ?[5] Hopp CD,Land MF.Considerations for ceramic inlays in posterior teeth: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2013; 5:21-32. ?[6] Ayyildiz S,Emir F,Pak Tunc EP,et al.Shear bond strength of various luting cements to fixed prosthodontic restorative materials.Appl Adhes Sci.2015;3:13. [7] Kumbuloglu O,Lassila LV,User A,et al.Shear bond strength of composite resin cements to lithium disilicate ceramics. J Oral Rehabil.2005;32(2):128-133. ?[8] 陈婧娉.嵌体修复下颌第一磨牙的有限元应力分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.[9] 刘利军,缪羽.三种不同材料的带桩高嵌体修复上颌第一前磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].中华老年病学杂志,2015,13(3):168-172.[10] 李冰,武秀萍,马雅静,等.粘接剂种类对全瓷桩核冠修复效果影响的三维有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2015,31(8):459-461.[11] Holberg C,Rudzki-Janson I,Wichelhaus A,et al.Ceramic inlays: is the inlay thickness an important factor influencing the fracture risk? J Dent.2013;41(7):628-635.[12] 文成超,仇丽鸿.全瓷嵌体修复 MOD 洞型对牙体组织应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2018,11(4): 234-238.[13] 殷家悦,包扬,艾红军,等.不同表面处理方式对二氧化锆基全瓷崩瓷树脂修补剪切强度的影响[J].口腔医学研究, 2009,25(5): 629-631.[14] Çelik Köycü B,Imirzalio?lu P,Özden UA. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in inlay-restored mandibular first molar under simultaneous thermomechanical loads.Dent Mater J. 2016;35(2):180-186.[15] 张丹,白保晶,张振庭.垫底厚度对全瓷嵌体修复应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].北京口腔医学, 2015,23(2):105-108.[16] Guven S,Akdogan M,Oz C,et al.Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of two ceramic inlay restorations with different cavity designs.Biotechnol Biotec Eq. 2015;29(3): 579-585.[17] 傅云婷,杜瑞钿,耿发云,等.CAD/CAM氧化锆全瓷与IPS e.max Press铸瓷固定局部义齿修复的临床对比研究[J].口腔疾病防治, 2016,24(9):524-527. [18] 张孝霞,韩丁,朱庆林,等.大面积缺损的下颌第一前磨牙桩核冠与高嵌体修复的三维有限元分析[J].牙体牙髓牙周病杂志, 2018, 28(5):265-269.[19] Zhang Z,Thompson M,Field C,et al. Fracture behavior of inlay and onlay fixed partial dentures - An in-vitro experimental and XFEM modeling study.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;59: 279-290.[20] Dog?an MS,Demirci F,Eratilla E,et al.Evaluation of stress distribution of a new restorative material and composite resin: a finite- element analysis study.Biotechnol Biotec Eq. 2017;31(6): 1216-1220. [21] Stawarczyk B,Liebermann A,Eichberger M,et al.Evaluation of mechanical and optical behaviour of current esthetic dental restorative CAD/CAM composites. J Mech Behaviour Biomed Mater. 2015;55:1-11. [22] Yoshihara K,Nagaoka N,Sonoda A,et al.Effectiveness and stability of silane coupling agent incorporated in ‘universal’ adhesives.Dent Mater.2016;10:1218-1225. [23] Duarte S,Sartori N,Phark JH.Ceramic-reinforced polymers: CAD/CAM hybrid restorative materials. Curr Oral Health Rep. 2016;3:198-202. [24] Tzanakakis EG,Tzoutzas IG,Koidis PT.Is there a potential for durable adhesion to zirconia restorations? A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent.2016;115(1):9-19.[25] 胡伟.口腔正畸治疗牙周病致前牙移位的效果分析及对血清细胞因子水平影响[J].中国临床医生杂志,2017,45(7):89-91. [26] 赵彧卓,张华.围绝经期妇女慢性牙周炎与骨质疏松的相关性分析[J].中国医刊,2017,52(6):22-25. [27] 付佳乐,陈丽薇,李斯文,等.六种自酸蚀粘接剂与牙本质粘接强度的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2017,10(3):163-167.[28] 崔悦,张祖太,葛丽华,等.五种牙本质粘接剂对乳牙牙本质边缘封闭性的比较[J].北京口腔医学, 2016,24(2):66-70. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)