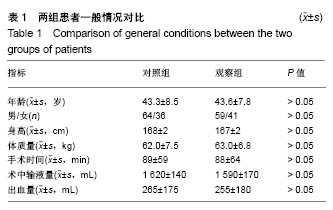
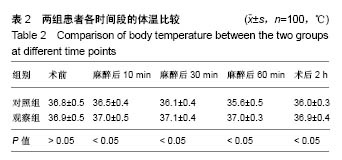
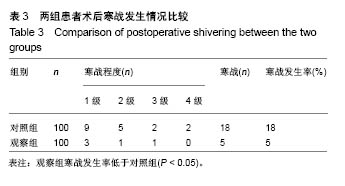
| [1] 张磊.围手术期导致寒战的原因及预防措施[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2008,6(10):1226.[2] 魏碧,闫红娟.围术期心理护理预防术中寒战[J].吉林医学, 2011, 32(21):4508.[3] 庄心良,曾因明,陈伯銮.现代麻醉学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2003:2039-2044.[4] Lopez MB.Postanaesthetic shivering - from pathophysiology to prevention. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2018;25(1):73-81.[5] 杨冬,薛富善.麻醉后寒战及其防治[J].国外医学(麻醉学与复苏分册),2003,24(1):19-23. [6] 张淑月,朱君宇,彭延增,等.术中低体温对患者麻醉恢复期的影响及护理干预[J].中华护理杂志,2003,38(3):16-18.[7] Matsuzaki Y,Matsukawa T,Ohki K,et al.Warming by resistive heating maintains perioper at ive normothermia as well as forced air heating.Br J Anaesth.2003;90(5):689-691. [8] 张苗苗,蒋奕红,杨连发.医用保温毯关键技术的研究[J].机电产品开发与创新,2008,21(6):51-53.[9] Wrench IJ,Singh P,Dennis AR,et al.The minimum effective doses of pethidine and doxapram in the treatment of post-anaesthetic shivering.Anaesthesia.1997;52(1):32-36.[10] Forstot RM. The etiology and management of inadvertent perioperative hypothermia.J Clin Anesth.1995;7(8):657-674.[11] Hart SR,Bordes B,Hart J,et al. Unintended perioperative hypothermia.Ochsner J.2011;11(3):259-270.[12] Sun Z,Honar H,Sessler DI,et al.Intraoperative core temperature patterns, transfusion requirement, and hospital duration in patients warmed with forced air. Anesthesiology. 2015;122(2):276-285.[13] 卢彬,李强,余璇.麻醉诱导前低体温的发生率及相关影响因素的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(13):104-108.[14] 罗俊.术中低体温预防的护理进展[J].临床护理杂志, 2013,12(1): 49-52.[15] 金云霞.导致麻醉期低体温的相关因素及预防措施[J].医学理论与实践,2014,27(22):3018-3019.[16] 蒋静,张蕾,陈秋红.老年患者术中低体温的相关因素、危害及其对策[J].医学信息,2011,24(7):4572-4573.[17] 杨建凤.老年手术患者低体温的相关因素危害及预防[J].基层医学论坛,2014,18(31):4201-4202.[18] 林晓薇.手术期间患者低体温的预防性护理[J].中国医药指南, 2014,12(29):354-355.[19] Boddu C, Cushner J, Scuderi GR.Inadvertent Perioperative Hypothermia During Orthopedic Surgery.Am J Orthop(Belle Mead NJ).2018;47(7).doi: 10.12788/ajo.2018.0056.[20] 张晓容.术中综合保温护理对手术患者术中低体温及术后感染发生情况的影响[J].大家健康:上旬版,2017,11(1):281-282.[21] 邹莉,金孝岠.围术期低体温临床研究进展[J].吉林医学, 2015, 36(1):116-117.[22] 刘小颖,吴新民.围术期低体温[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2003,23(9): 712-714.[23] Ruetzler K,Kurz A.Consequences of perioperative hypothermia. Handb Clin Neurol.2018;157:687-697.[24] Reynolds L,Beckmann J,Kurz A. Perioperative complications of hypothermia. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2008;22(4): 645-657.[25] Madrid E,Urrutia G,Roque FM,et al.Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2016;4:CD009016.[26] Sessler DI,Schroeder M.Heat loss in humans covered with cotton hospital blankets.Anesth Analq.1993;77(1):73-77.[27] Sessler DI.Perioperative thermoregulation and heat balance.Lancet.2016;387(10038):2655-2664.[28] Ruetzler K,Kovaci B, Güloglu E,et al.Forced-air and a novel patient-warming system (vitalHEAT vH2) comparably maintain normothermia during open abdominal surgery.Anesth Analq. 2011;112(3):608-614.[29] Nq V,Lai A,Ho V.Comparison of forced-air warming and electric heating pad for maintenance of body temperature during total knee replacement.Anaesthesia. 2006;61(11):1100-1104.[30] Ozqenel GY,Ozcan M.Heating-pad burn as a complication of abdominoplasty.Br J Plast Surg.2003;56(1):52-53. |
.jpg)



.jpg)