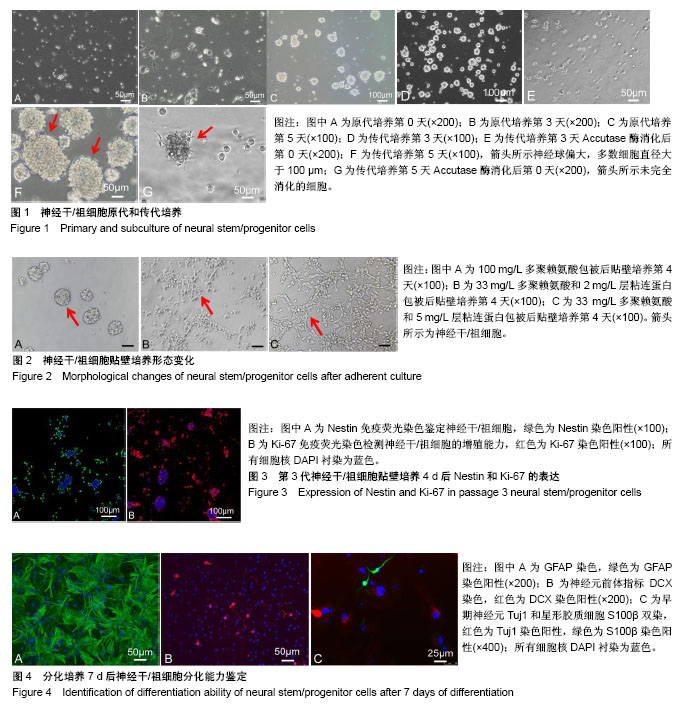
| [1] Qin W, Chen S, Yang S, et al. The Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Aging Dis. 2017;8(6):792-811.[2] Aimone JB, Li Y, Lee SW, et al. Regulation and function of adult neurogenesis: from genes to cognition. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(4):991-1026.[3] Altman J. Are new neurons formed in the brains of adult mammals. Science. 1962;135(3509):1127-1128.[4] Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124(3):319-335.[5] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.[6] Marei HE, Althani A, Rezk S,et al.Therapeutic potential of human olfactory bulb neural stem cells for spinal cord injury in rats. Spinal Cord. 2016;54(10):785-797.[7] Wu S, Sasaki A, Yoshimoto R,et al. Neural stem cells improve learning and memory in rats with Alzheimer’s disease. Pathobiology.2008; 75(3): 186-194.[8] Wu W, Chen X, Hu C, et al. Transplantation of neural stem cells expressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α(HIF-1α) behavioral recovery in a rat stroke model. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17(1): 92-95.[9] Paul A, Chaker Z, Doetsch F. Hypothalamic regulation of regionally distinct adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis. Science. 2017;356(6345):1383-1386.[10] Bacigaluppi M, Pluchino S, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, et al. Delayed post-ischemic neuroprotection following systemic neural stem cell transplantation involves multiple mechanisms. Brain.2009;132(Pt8): 2239-2251.[11] Wang C, Lu CF, Peng J, et al.Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(12):2106-2112.[12] Hou B, Ma J, Guo X, et al. Exogenous Neural Stem Cells Transplantation as a Potential Therapy for Photothrombotic Ischemia Stroke in Kunming Mice Model. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(2):1254-1262.[13] Ho SY, Ling TY, Lin HY, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 Signaling Maintains Stemness Signature in Mouse Neural Stem/ Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2493752.[14] Ziaee SM, Tabeshmehr P, Haider KH, et al. Optimization of time for neural stem cells transplantation for brain stroke in rats. Stem Cell Investig. 2017;4:29.[15] Telias M, Ben-Yosef D.Neural stem cell replacement: a possible therapy for neurodevelopmental disorders?Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2):180-182.[16] Faigle R, Song H. Signaling mechanisms regulating adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(2):2435-2448.[17] Homem CC, Repic M, Knoblich JA. Proliferation control in neural stem and progenitor cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015; 16(11):647-659.[18] Jessberger S, Toni N, Clemenson GD Jr, et al. Directed differentiation of hippocampal stem/progenitor cells in the adult brain. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(8):888-893.[19] Aguirre A, Rubio ME, Gallo V. Notch and EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and self-renewal. Nature. 2010;467(7313):323-327.[20] Homayouni Moghadam F, Sadeghi-Zadeh M, Alizadeh-Shoorjestan B, et al. Isolation and Culture of Embryonic Mouse Neural Stem Cells. J Vis Exp. 2018;(141). doi: 10.3791/58874. [Epub ahead of print][21] Jadasz JJ, Tepe L, Beyer F, et al. Human mesenchymal factors induce rat hippocampal- and human neural stem cell dependent oligodendrogenesis. Glia. 2018;66(1):145-160.[22] Usui T, Sakurai M, Kawasaki H, et al. Establishment of a novel three-dimensional primary culture model for hippocampal neurogenesis. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(12): e13318.[23] Pachenari N, Kiani S, Javan M. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 increased subventricular zone stem cells proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;93:1074-1082.[24] Zhao L, Zhou C, Li L, et al. Acupuncture Improves Cerebral Microenvironment in Mice with Alzheimer's Disease Treated with Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(7):5120-5130.[25] Chen M, Puschmann TB, Marasek P, et al. Increased Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Progenitor Cells Derived from Phosphovimentin-Deficient Mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2018; 55(7):5478-5489.[26] Kumar V, Pandey A, Jahan S, et al. Differential responses of Trans-Resveratrol on proliferation of neural progenitor cells and aged rat hippocampal neurogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 28142.[27] Kim JY, Lee JH, Sun W. Isolation and Culture of Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Mouse Subcallosal Zone. J Vis Exp. 2016; (118). doi: 10.3791/54929.[28] Ludwig PE, Thankam FG, Patil AA, et al. Brain injury and neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(1):7-18.[29] Gao X,Zhang J,Zhang J,et al.Identification of rat respiratory mucosa stem cells and comparison of the early neural differentiationpotential with the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Cell Mol Neurobiol.2014,34(2):247-268.[30] Jiang DQ, Wei MD, Wang KW, et al. Nicotine contributes to the neural stem cells fate against toxicity of microglial-derived factors induced by Aβ via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Neurosci. 2016;126(3):257-268.[31] Bergström T, Holmqvist K, Tararuk T, et al. Developmentally regulated collagen/integrin interactions confer adhesive properties to early postnatal neural stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(8):2526-2532.[32] Zhang J, Li X, Zhang S, et al. Stromal cell derived factor-1α-laminin crosstalk induced neural stem cells migration and differentiation in vitro. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017;29(1):57-60.[33] Mimura T, Yamagami S, Uchida S, et al. Isolation of adult progenitor cells with neuronal potential from rabbit corneal epithelial cells in serum- and feeder layer-free culture conditions. Mol Vis. 2010;16:1712-1719.[34] Park D, Xiang AP, Mao FF, et al. Nestin is required for the proper self-renewal of neural stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010; 28(12):2162-2171.[35] Ren M, Du C, Herrero Acero E, et al. A biofidelic 3D culture model to study the development of brain cellular systems. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24953.[36] Ahmed AI, Shtaya AB, Zaben MJ, et al. Endogenous GFAP-positive neural stem/progenitor cells in the postnatal mouse cortex are activated following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(5):828-842.[37] Choi HW, Hong YJ, Kim JS, et al. In vivo differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into neural stem cells by chimera formation. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0170735.[38] Petrik D, Latchney SE, Masiulis I, et al. Chromatin Remodeling Factor Brg1 Supports the Early Maintenance and Late Responsiveness of Nestin-Lineage Adult Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33(12):3655-3665.[39] Radu BM, Dumitrescu DI, Mustaciosu CC, et al. Dual effect of methylglyoxal on the intracellular Ca2+ signaling and neurite outgrowth in mouse sensory neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(6):1047-1057.[40] Li RL, Zhang ZZ, Peng M, et al. Postoperative impairment of cognitive function in old mice: a possible role for neuroinflammation mediated by HMGB1, S100B, and RAGE. J Surg Res. 2013;185(2):815-824.[41] Sachewsky N, Leeder R, Xu W, et al. Primitive neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain give rise to GFAP-expressing neural stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2(6):810-824.[42] Huang F, Lan Y, Qin L, et al. Astragaloside IV Promotes Adult Neurogenesis in Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Mouse through CXCL1/CXCR2 Signaling. Molecules. 2018;23(9): E2178.[43] Raponi E, Agenes F, Delphin C, et al. S100B expression defines a state in which GFAP-expressing cells lose their neural stem cell potential and acquire a more mature developmental stage. Glia. 2007;55(2):165-177. |
.jpg)
.jpg)