2.1 类器官技术的发展历程
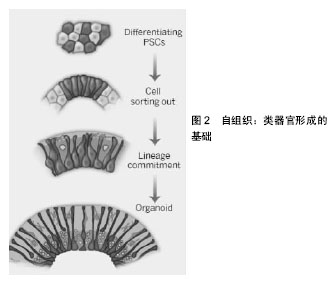
2.1.1 类器官概念的提出 1907年,Wilson[2]第1次证明了机械分离的海绵细胞可重新聚集并自我组织生成一个完整的有机体。然而,类器官领域的到来却始于2D培养基到3D培养基的转变,这使复杂三维器官结构的建立成为可能。自1987年以来,研究人员利用不同类型的干细胞产生大量类似体内正常组织器官的细胞群体[1],见图2。2009年,Clevers实验室证明了单个LGR5干细胞在没有间充质作为背景的条件下,体外构建成小肠隐窝-绒毛结构[3]。2010年,Unbekandt 和 Davies[4]利用小鼠胚胎干细胞产生了肾脏类器官。2013年,奥地利科学院的Madeline Lancaster证明脑组织的类器官可由人多能干细胞在Matrigel中生长而产生[5]。2014年, Shkumatov等[6]认为生理性僵硬度促进了胚胎干细胞的三维性形成和心肌细胞分化。Takebe等[7]通过组合多能干细胞来源的组织特异性祖细胞或内皮细胞相关组织样品和间充质干细胞,发现了不同组织形成器官芽的一般方法。他们认为相比于更高级阶段细胞产生的凝结物,通过自我组织凝结原理产生的较不成熟组织或器官芽可能是成熟器官功能重建的有效方法。科研人员虽然试图通过发育生物学实验来描述类器官发生过程,但都未对类器官做出概念。直到2014年,Lancaster和Knoblich[1]系统地提出的类器官的概念。这一概念的提出对生物医学发展以及疾病(特别是癌症)认识的发展提供了可靠理论基础。
2.1.2 类器官技术的关键问题 类器官主要由干细胞培养获得,干细胞可来源于多能胚胎干细胞及它们合成的诱导多能干细胞和器官限制性成体干细胞。这2种类型的干细胞都具有无限的体外扩展潜力,使干细胞成为目前类器官培养的最佳来源。与其他培养技术相比,类器官维持和扩展相对简单,并且其培养技术可根据来源组织的变化而变化。类器官可每一两周传代1次,其中最为关键的是培养类器官的培养基各不相同,这通常取决于起源组织的需求。例如,表皮细胞生长因子、R-spondin蛋白和头蛋白足以长期维持小肠的类器官生长,而结肠来源的类器官需要添加烟酰胺、p38抑制剂SB202190、前列腺素E2和Alk抑制剂A83-01[8]。
目前,3D培养基常使用细胞外基质Matrigel作为立体支架,是由Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm肿瘤系分泌的一种富含层粘连蛋白的细胞外基质。Matrigel中还含Ⅳ型胶原、硫酸乙酰肝素、蛋白多糖、内功素、转化生长因子β和胰岛素样生长因子1等多种蛋白酶和生长因子成分,均能参与调节细胞的生长、分化、迁移及组织形成[9-10]。
2.2 类器官在肿瘤研究中的应用 在过去的几十年里,人们对某些类型癌症的治疗取得了实质性进展,但癌症仍是全球最主要的健康问题。人们已认识到,基础科研研究到临床实际治疗的转化成了发展新肿瘤治疗方案的主要障碍之一,这主要是因为许多肿瘤模型仅仅对肿瘤组织进行了大体概括,无法很好地维持肿瘤细胞的高度异质性,正是这些原因,许多在传统癌症模型中有效的药物在临床试验中无法得到论证。虽然动物癌症模型已为癌症基础研究提供了重要的实验材料,但它们的繁殖周期是耗时、耗力的,并且这些模型无法充分地反映癌症患者的致病过程。例如,基因工程建立的小鼠癌症模型并不能反映人类癌症的组织复杂性和遗传异质性。随着类器官体外3D培养技术的发展,研究人员开发了新的、更符合人类癌症的研究模型——肿瘤类器官模型。目前,在人类癌症研究模型中,常用的模型包括了肿瘤细胞系、肿瘤组织小鼠移植模型及肿瘤类器官模型。
2.2.1 传统肿瘤模型的局限性 最初始的体外肿瘤模型,由原发癌症患者肿瘤细胞来源的癌细胞系获得。目前的肿瘤细胞系约有30余种,如:SW480、SW620、HCT116、T84、HT29、LS174T、INT-407、HT20-MTX及NCM460等[11-12]。但肿瘤细胞系无效的增殖和大量遗传改变,使其丢失了肿瘤细胞的异质性和肿瘤细胞在体内的特征;此外,无法展示免疫细胞和肿瘤细胞之间的相互作用。研究人员将来源于患者皮下肿瘤细胞或原位肿瘤细胞移植到免疫缺陷型小鼠上,获得了肿瘤组织小鼠移植模型模型。该模型能还原肿瘤细胞与免疫系统的相互作用,也能展示其与周围基质细胞及细胞外基质的相互作用,但它们在精准癌症治疗中受到限制,其主要原因是低效的移植率。此外,肿瘤组织小鼠移植模型价格昂贵、耗时,并且耗费资源,特别是肿瘤组织小鼠移植模型可能经历了小鼠特异性肿瘤进化过程,改变了原发肿瘤的特异性[13-14]。
2.2.2 肿瘤类器官模型的建立与探索 近年来,随着体外3D细胞培养技术(如类器官培养技术)的出现,研究者们试图采用新的肿瘤模型来克服传统肿瘤模型的弊端。肿瘤类器官模型为癌症研究和治疗提供了可靠的模型,特别是为个性化癌症治疗开辟了新的视野。肿瘤来源的类器官是源自组织或肿瘤特异性干细胞的三维组织细胞簇,它可模拟体内肿瘤的特征及肿瘤细胞异质性。最早从癌症组织中建立类器官的研究人员之一是Sato等。他们首先建立了小鼠结肠隐窝的培养条件,并通过调整培养环境培养人小肠和结肠的类器官,再通过进一步优化调整,从结肠腺瘤和腺癌及Barrett食管中建立肿瘤类器官模型。Barrett食管是一种柱状上皮化生的恶性肿瘤,被认为是食管腺癌的前体[8]。癌症患者来源肿瘤类器官模型的建立,被认为是一项重大突破,并且肿瘤类器官模型具有将生物医学研究转变为更关注患者方法的潜力。Weeber[15]及其同事开发了一种肿瘤类器官模型培养条件,并对14种结肠肿瘤类器官模型和其来源原始肿瘤的1 977个癌症相关基因进行了基因测序,发现在发育的肿瘤类器官模型和活组织检查之间有90%的体细胞突变和DNA拷贝数分布得以保存。Van de Wetering[16]和他的同事通过对全部外显子测序分析,证明了结肠肿瘤类器官模型保留了原始肿瘤样本中的亚型。这些发现表明了该肿瘤类器官模型在长期培养过程中能够维持基因组的稳定性,并为类器官技术在个性化治疗方面提供了一定的可能性。Gao等[17]成功地从转移性前列腺癌组织及液体活组织检查中培养了类器官。到目前为止,这是为数不多来自血液样本肿瘤类器官模型培养成功的案例。这可能为“液体活检”创造新机会。Boj等[18]成功培养了胰腺腺癌类器官。由于肿瘤的基质成分较大,因此这是一种特别难以建立的肿瘤细胞系。Bartfeld[19]及其同事成功培养了胃的类器官,并用它来建立幽门螺杆菌感染的模型系统,用以阐明细菌感染后发生的级联事件。相同的培养条件也可用于培养胃癌类器官。最近,Pauli等[20]培养来自多种不同肿瘤类型的肿瘤类器官模型,总成功率达到了39%。总之,肿瘤类器官模型可从一系列不同的肿瘤类型中建立,这为更成功的药物开发和精准医学铺平了道路。与传统肿瘤模型(例如肿瘤组织小鼠移植模型)需要大量的样本量特点相比,肿瘤类器官模型可从小样本中培养,甚至仅来自针吸活组织检查取下来的样本,通过有效的培养就有能获得较高的成功率。肿瘤类器官模型还具有其他很多优点,包括可保持长期扩增、冷冻保存及基因改造等。这种新的模型在基因药物相关性研究、抗癌药物的临床前筛选、药物反应和患者预后的预测中具有巨大潜力。
研究表明,肿瘤类器官模型本身的生长速度慢于其相应的正常组织类器官生长速度,甚至在许多情况下以较慢的速率生长,这可能与失败的有丝分裂和分裂之后的细胞死亡有关[21]。因此,实验中需要避免残存正常组织的上皮类器官在肿瘤类器官模型中过度生长,并且必须使用纯肿瘤细胞样本或在选择性培养条件下去培养肿瘤类器官模型。例如,在绝大多数结直肠癌中,Wnt信号传导通路中的激活突变是存在的[22]。在这些情况下,通过使用不含Wnt和R-spondins因子等的培养基获得纯肿瘤类器官模型培养物[8]。在正常组织中,Wnt和R-spondins信号是结肠类器官生长的必需生长因子。
2.2.3 肿瘤类器官在癌症研究中的具体应用 目前,科研人员通过优化各种培养条件成功产生了许多肿瘤类器官模型,包括结肠癌[3]、前列腺癌[17,23]、胃癌[24]、乳腺癌[25]、胰腺癌[25-26],以及子宫内膜/卵巢癌、子宫癌肉瘤、尿路上皮癌和肾癌[27]。
结直肠肿瘤类器官:结直肠肿瘤类器官模型可模拟肠道恶性肿瘤发生发展中的病理机制及不同信号通路突变的作用。Sato是肠道类器官发展的先驱,他在Clevers实验室通过结合类器官和CRISPR/Cas9技术来模拟人类结肠癌的早期发展阶段[28]。Barker等[29]报道了在他莫昔芬诱导下CRE工具鼠的Lgr5干细胞形成了小鼠肠腺瘤。他们在诱导后10 d分离出肠道腺瘤并在适合的条件下培养,肠道腺瘤形成了无芽的囊性类器官结构。由此表明,可在体外重现结直肠肿瘤的发生发展过程。Fumagalli等[30]通过利用包含不同结直肠癌突变联合的人类结肠类器官,来分析腺瘤-癌在体内演进过程,表明了Wnt、表皮生长因子受体、p53和转化生长因子β信号通路的基因改变导致了肿瘤生长、迁移和转移灶形成。Van de Wetering等[16]成功创建了具有22例结肠肿瘤类器官模型的样本库。Fujii等[31]建立了一个包含55个结直肠肿瘤类器官的模型库,且包含各种不同的肿瘤亚型。相比前者,结直肠癌类器官的培养更为复杂,尤其是直肠癌和晚期结肠癌。结直肠肿瘤类器官模型库的建立,为结肠癌发病机制特别是晚期结直肠癌的治疗提供了新平台。
胰腺和肝脏肿瘤类器官:众所周知,胰腺癌是一种难以预测和治疗的癌症[32]。虽然科研人员已建立了一些非常有前瞻性的异种移植模型和动物模型[33-34],但这些模型非常昂贵,并且无法快速预测患者的药物反应,因此仍然需要更多的临床前工具来评估。胰腺导管腺癌类器官培养中的发展可部分解决当前模型的一些缺点。最近,Huang等[35]通过诱导人类胚胎干细胞分化出胰腺外分泌谱系。该谱系可用于了解人类胰腺外分泌的发生发育及作用机制,还可用于模拟人类的疾病,如胰腺癌。为了防止正常胰腺上皮细胞在Wnt受限的肿瘤类器官模型培养基中过度扩张,Seino等[36]利用当前已知的信号通路开发了一种新的培养方法,即通过排除诸如Wnt3a和表皮生长因子等因子并诱导P53降解来重建细胞龛的具体条件。他们根据是否具有Wnt依赖性将胰腺导管腺癌患者来源的肿瘤类器官模型分为3个亚型:依赖于外源性Wnt配体的类器官,产生自分泌Wnt且对阻断分泌的药物敏感的类器官,不依赖于Wnt的类器官。Huang等进一步证明Wnt2和Wnt2b是基质来源的Wnt配体,Wnt7b和Wnt10a是调节胰腺导管腺癌生长的上皮来源的Wnt配体。通过基因表达谱分析比较胰腺导管腺癌与不同的Wnt依赖性,确定了沉默的GATA6为不依赖Wnt的类器官形成做出贡献。同样,GATA6的重新表达导致不依赖Wnt的胰腺导管腺癌类器官需要Wnt的补充。综上可知,GATA6在胰腺导管腺癌是否需要Wnt调节上起到重要作用,这对胰腺癌靶向药物治疗提出了新的思路。
虽然胰腺和肝脏共享发育谱系,但产生肝细胞模型的类器官一直是生物工程领域的一个挑战。Huch等[37]成功培养正常肝细胞类器官,并且发现在去除R-spondin和Wnt3a的情况下可诱导肝脏肿瘤类器官模型的生长。他们分别从肝细胞癌、胆管癌和肝细胞胆管癌这3种不同的肝癌类型中建立了肿瘤类器官模型,通过组织学、免疫组织化学和基因组学方法,Huch等证明了这些肿瘤类器官模型保持了器官位点特异性的组织学和遗传特征,并且在将肿瘤类器官模型移植到免疫受损小鼠的肾囊膜下时,发现其有不同的成瘤和侵袭转移能力,这表明可在体外重现肝癌的发生发展过程。随后,他们通过运用肿瘤类器官模型培养技术,证明了在肝癌中过表达的19个基因,并鉴定出了3种类型的肝癌中表达的11种新的生物标志物。Huch等使用29种药物进行了药物筛选,并在异种移植模型中验证了对ERK抑制剂的敏感性。这项工作成功将明显加快在肝癌研究领域的发展。
前列腺肿瘤类器官:目前已建立的前列腺类器官模型包括鼠前列腺组织、人正常前列腺组织[38]、前列腺癌患者转移灶样本及去势抵抗性前列腺癌患者循环肿瘤细胞来源的类器官[39]。李飞等[40]在实验室利用前列腺肿瘤转移灶样本成功建立起前列腺肿瘤类器官。经过长期培养的前列腺类器官可很好地维持肿瘤细胞在体内的特征,通过基因测序转移灶样本和相关来源类器官显示,每个类器官与其来源的患者基因基本一致,见表1。他们成功培养的7株类器官中,其中1株是来源于去势抵抗性前列腺癌患者的肿瘤循环细胞。去势抵抗性前列腺癌类器官的成功建立,为研究前列腺癌恶性转化和转移机制研究提供了理想模型。有实验证明,常用的前列腺癌转基因工程鼠来源的肿瘤类器官模型在组织学上与转基因鼠体内表现相吻合,如PBCRE PTENloxP/ loxP(敲除PTEN基因)前列腺类器官在组织学上表现为高级别上皮内瘤变,而PBCRE ROSA26LSL-ERG(过表达ERG)前列腺类器官在组织学上则表现为正常管腔结构,在PBCRE PTENloxP/loxPROSA26LSL-ERG(同时敲除PTEN 基因和过表达ERG)前列腺类器官中可见许多指状突触伸入Matrigel基质,提示其具有侵袭性[41]。因此,体外培养的前列腺类器官在表型上确实可模拟体内情况。同时,前列腺类器官可在体外进行慢病毒与CRISPR/Cas9系统的基因编辑[38,42],从而在研究前列腺癌相关基因方面发挥巨大作用。由此可见,前列腺类器官体外研究模型既能很好地模拟体内情况,又可像肿瘤细胞系一样长期培养,并且具还具有体外基因编辑的特点,势必成为研究前列腺肿瘤的重要工具。

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)