中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4816-4821.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1420
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
基于活性胰岛素累积量模糊自适应比例-积分-微分闭环胰岛素的控制方法
余丽玲,张刚平,刘文平,徐彬锋,金浩宇
- 广东食品药品职业学院,广东省广州市 510520
A fuzzy adaptive proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control strategy based on insulin-on-board control method of closed-loop insulin infusion
Yu Liling, Zhang Gangping, Liu Wenping, Xu Binfeng, Jin Haoyu
- Guang Dong Food and Drug Vocational College, Guangzhou 510520, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
人工胰腺:它根据人体血糖波动情况输注胰岛素,在整个血糖控制过程中不需要患者的参与,能够自动控制糖尿病患者的血糖变化至正常水平,该控制系统主要包括3个部分:连续血糖监测系统、血糖闭环控制算法和胰岛素泵。随着血糖检测技术的突破,精确、便携胰岛素泵和连续动态血糖监测产品的出现,以及胰岛素泵和传感器之间无线通讯技术的进步与发展,才使得开发便携、具有血糖闭环控制功能的人工胰腺产品成为可能。针对人工胰腺开发过程中血糖闭环控制算法这一关键技术的研究,也重新吸引许多专家学者的关注。血糖闭环控制算法的研究已成为突破人工胰腺开发难题的关键,亟须更多的关注与研究。
比例-积分-微分控制算法:作为最早实用化的控制器,发展历史悠久,控制效果较优,目前应用范围广泛。比例-积分-微分设计的胰岛素输注速度可看作比例项、积分项和微分项这3部分的加权和。比例-积分-微分算法运用3个分量尽可能地模拟人体 β 细胞分泌胰岛素的生理传输过程。比例分量对应于实测血糖值偏离目标血糖值时的胰岛素分泌量,当实测血糖值等于目标血糖值时则为 0,因而该分量对于保持日常的基础胰岛素输注没有任何贡献;积分分量用于调整血糖围绕目标值上下微幅波动时的胰岛素分泌量,也是使血糖稳定在目标值时保持基础胰岛素输注量的唯一成分,由于积分分量仅在血糖围绕目标值微幅波动时微量调节胰岛素分泌,因而可确保血糖能稳定在目标值;微分分量对应于血糖快速变化时迅速调节胰岛素分泌。
背景:智能的血糖控制算法是闭环式人工胰腺的重要环节。
目的:为了有效控制1型糖尿病患者的血糖浓度,降低患者高、低血糖事件的发生概率,提出基于活性胰岛素累积量模糊自适应比例微积分的闭环胰岛素控制算法。
方法:根据实时监测的人体血糖数据,采用比例微积分算法模拟人体β细胞分泌胰岛素生理传输过程,然后不断优化比例-积分-微分控制器参数数值,利用活性胰岛素累积量进行修正模糊比例-积分-微分计算出来的胰岛素剂量,使得最终计算出适合该患者的最佳胰岛素泵给药量。
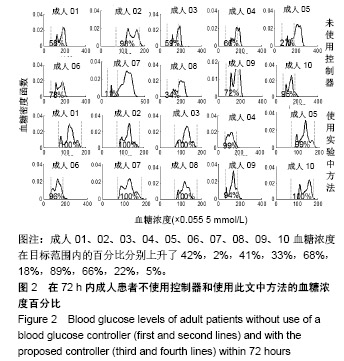
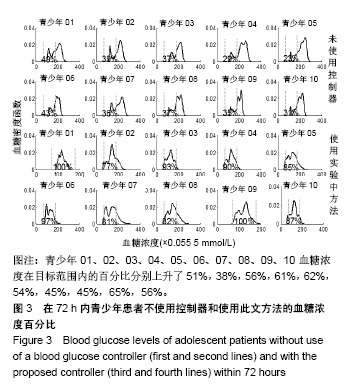
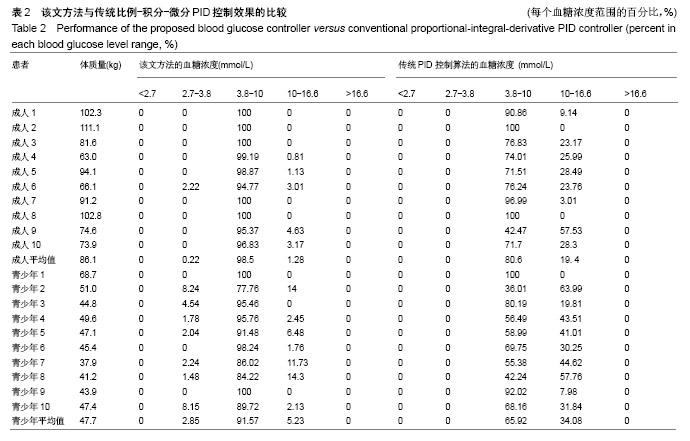
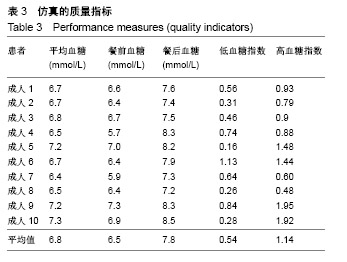
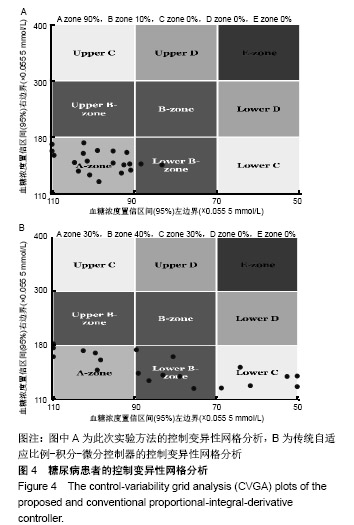
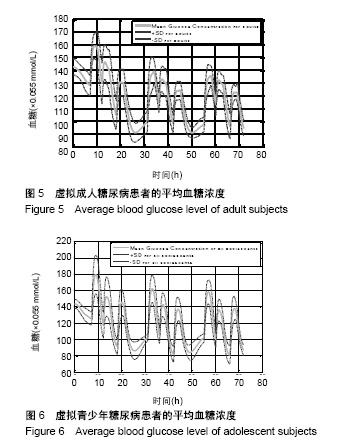
结果与结论:该算法在美国弗吉尼亚大学与意大利帕多氏联合开发的UVa /Padova 仿真平台进行了算法性能的测试,仿真实验结果表明该控制算法显著降低了低血糖事件,将血糖水平控制在设定的目标区间,提高了胰岛素注射疗法的精确性和有效性,显著降低了各种并发症的产生。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)