| [1]Bruyère O, Cooper C, Arden N, et al. Can we identify patients with high risk of osteoarthritis progression who will respond to treatment? A focus on epidemiology and phenotype of osteoarthritis. Drugs Aging. 2015;32(3):179-187. [2]中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [3]薛庆云,王坤正,裴福兴,等.中国40岁以上人群原发性骨关节炎患病状况调查[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(12):1206-1212. [4]Allen KD, Golightly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):276-83.[5]Turkiewicz A, Gerhardsson de Verdier M, Engström G, et al. Prevalence of knee pain and knee OA in southern Sweden and the proportion that seeks medical care. Rheum. 2015; 54(5):827-835. [6]Driban JB, Eaton CB, Amin M, et al. Glucose homeostasis influences the risk of incident knee osteoarthritis: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(10): 2282-2287.[7]Chen A, Gupte C, Akhtar K, et al. The global economic cost of osteoarthritis: how the UK compares. Arthritis. 2012;2012: 698709.[8]Kotlarz H, Gunnarsson CL, Fang H, et al. Insurer and out-of-pocket costs of osteoarthritis in the US: evidence from national survey data. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;6(12):3546-53. doi: 10.1002/art.24984.[9]Rosen AD, Chastney EE. Effect of long term exposure to 0.5 T static magnetic fields on growth and size of GH3 cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2009;30(2):114-119.[10]Sullivan K, Balin AK, Allen RG. Effects of static magnetic fields on the growth of various types of human cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2011;32(2):140-147.[11]Galli C, Pedrazzi G, Mattioli-Belmonte M, Guizzardi S. The use of pulsed electromagnetic fields to promote bone responses to biomaterials in vitro and in vivo. Int J Biomater. 2018;2018:8935750. [12]Salamanna F, Veronesi F, Maglio M, et al. New and emerging strategies in platelet-rich plasma application in musculoskeletal regenerative procedures: general overview on still open questions and outlook. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:846045.[13]Brossi PM, Moreira JJ, Machado TS, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopedic therapy: a comparative systematic review of clinical and experimental data in equine and human musculoskeletal lesions. BMC Vet Res. 2015;11:98. [14]火焱,陈德志,王昭玲,等.低频脉冲电磁场治疗骨关节炎的有效性及安全性观察[J].中国医药科学,2013,3(13):9-11.[15]Bagnato GL, Miceli G, Marino N, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields in knee osteoarthritis: A double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Rheumatology (United Kingdom). 2016;55(4):755-762.[16]Ay S, Evcik D. The effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2009;29(6):663-666.[17]Taniguchi Y, Yoshioka T, Kanamori A, et al. Intra-articular platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections for treating knee pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee in the Japanese population: a phase I and IIa clinical trial. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2018;80(1):39-51.[18]Smith PA. Intra-articular autologous conditioned plasma injections provide safe and efficacious treatment for knee osteoarthritis: an FDA-sanctioned, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(4):884-891.[19]Rahimzadeh P, Imani F, Faiz SHR, et al. The effects of injecting intra-articular platelet-rich plasma or prolotherapy on pain score and function in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:73-79.[20]Jubert NJ, Rodriguez L, Reverte-Vinaixa MM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma injections for advanced knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded clinical trial. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(2): 2325967116689386. [21]王一帆,李小峰,罗道明,等.不同浓度富血小板血浆治疗膝关节骨性关节炎临床疗效研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2018,47(9): 1113-1118.[22]Nabi BN, Sedighinejad A, Mardani-Kivi M, et al. Comparing the effectiveness of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroid injection under ultrasound guidance on pain control of knee osteoarthritis. Iranian Red Crescent Med J. 2018;20(3):e62157.[23]Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H, et al. Knee osteoarthritis injection choices: platelet-rich plasma (PRP) versus hyaluronic acid (A one-year randomized clinical trial). Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;8: 1-8.[24]吕帅洁,厉驹,何斌,等.富血小板血浆关节内注射治疗膝骨关节炎的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2016,32(7):626-631.[25]翟文亮,周亮,刘晖,等.富血小板血浆与透明质酸钠治疗膝关节骨关节炎的临床观察[J].中华关节外科杂志,2017,11(1):96-100.[26]Ahmad HS, Farrag SE, Okasha AE, et al. Clinical outcomes are associated with changes in ultrasonographic structural appearance after platelet-rich plasma treatment for knee osteoarthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(5):960-966.[27]Lana JFSD, Weglein A, Sampson SE, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing hyaluronic acid, platelet-rich plasma and the combination of both in the treatment of mild and moderate osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 12(2):69-78.[28]Di Sante L, Villani C, Santilli V, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid vs platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis. Med Ultrason. 2016;18(4):463-468.[29]Akan O, Sarikaya NO, Kocyigit H. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma administration in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis: Can platelet-rich plasma administration delay arthroplasty in this patient population? Int J Clin Exp Med. 2018;11(9):9473-9483.[30]Montanez-Heredia E, Irizar S, Huertas PJ, et al. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of osteoarthritic knee pain: a randomized clinical trial in the context of the spanish national health care system. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):E1064.[31]Rayegani SM, Raeissadat SA, Taheri MS, et al. Does intra articular platelet rich plasma injection improve function, pain and quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee? A randomized clinical trial. Orthopedic Reviews. 2014;6(3): 112-117.[32]Lisi C, Perotti C, Scudeller L, et al. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis: platelet-derived growth factors vs. hyaluronic acid. A randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(3): 330-339.[33]Hassan AS, El-Shafey AM, Ahmed HS, et al. Effectiveness of the intra-articular injection of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of patients with primary knee osteoarthritis. Egyptian Rheumatologist. 2015;37(3):119-124.[34]Louis ML, Magalon J, Jouve E, et al. Growth factors levels determine efficacy of platelets rich plasma injection in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double blind noninferiority trial compared with viscosupplementation. Arthroscopy. 2018; 34(5):1530-1540.[35]Mariani E, Canella V, Cattini L, et al. Leukocyte-rich Platelet-rich Plasma injections do not up-modulate intra- articular pro-inflammatory cytokines in the osteoarthritic knee. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156137.[36]Simental-Mendia M, Vilchez-Cavazos JF, Pena-Martinez VM, et al. Leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma is more effective than the conventional therapy with acetaminophen for the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(12):1723-1732.[37]Huang G, Hua S, Yang T, et al. Platelet-rich plasma shows beneficial effects for patients with knee osteoarthritis by suppressing inflammatory factors. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(3): 3096-3102.[38]Parate D, Franco-Obregón A, Fröhlich J, et al. Enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis with short-term low intensity pulsed electromagnetic fields. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):9421. [39]郭燕庆.富血小板血浆(PRP)治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效评价[D].济南:山东大学,2017.[40]Zou J, Chen Y, Qian J, et al. Effect of a low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field on expression and secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. J Int Med Res. 2017; 45(2):462-470.[41]Zhu SZ, He H, Wang Q, et al. Abnormal bone and cartilage metabolism could be antagonised by pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFS) and TNF-alpha and IL-6 gene knockouts in a similar mechanism. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2018;77:897-898.[42]Wu J, Huang JF, Qin XX, et al. Platelet-rich plasma inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in rabbit cartilage cells activated by IL-1beta. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;55:282-289.[43]Yang X, He H, Gao Q, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field improves subchondral bone microstructure in knee osteoarthritis rats through a Wnt/beta-catenin signaling- associated mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics. 2018;39(2): 89-97.[44]周予靖,王朴,陈红英,等.脉冲电磁场对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖?成骨分化和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2015,46(3):347-353.[45]王谦,王朴,刘小菁,等.脉冲电磁场调控干细胞增殖与分化[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(2):180-183.[46]陶可,熊养,曾晖.Wnt信号通路与骨关节炎关系的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2011,15(8):564-568.[47]Zhou Y, Wang T, Hamilton JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in osteoarthritis and in other forms of arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53.[48]Alonso-Pérez A, Franco-Trepat E, Guillán-Fresco M, et al. Role of toll-like receptor 4 on osteoblast metabolism and function. Front Physiol. 2018;9:504. [49]Barreto G, Sandelin J, Salem A, et al. Toll-like receptors and their soluble forms differ in the knee and thumb basal osteoarthritic joints. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(3):326-333. |
.jpg)
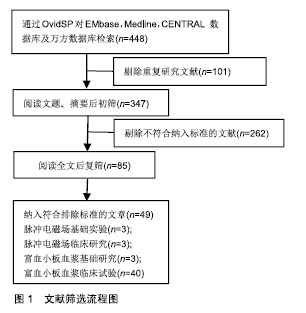
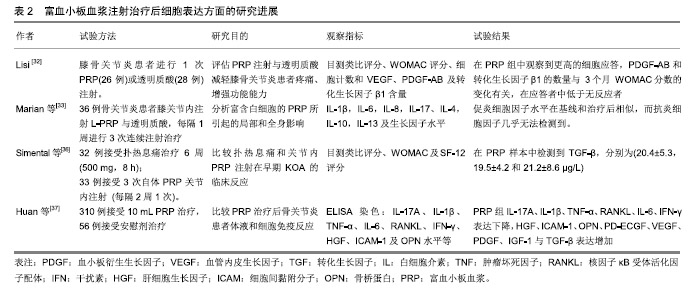
.jpg)
.jpg)