中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4332-4337.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1381
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
牛膝总皂苷对骨关节炎模型兔软骨修复及低氧诱导因子1信号通路的影响
马笃军1,彭力平1,余 阗1,曹亚飞1,高 坤1,肖 伟1,胡烈奎2,徐文铭1
- (1深圳市中医院,广东省深圳市 518033;2广州中医药大学第四临床医学院,广东省深圳市 518033)
Influence of Achyranthes bidentata saponins on the repair of cartilage and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis
Ma Dujun1, Peng Liping1, Yu Tian1, Cao Yafei1, Gao Kun1, Xiao Wei1, Hu Liekui2, Xu Wenming1
- (1Shenzhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China; 2the Fourth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。
文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。
文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。摘要
背景:以往研究证实,牛膝能促进实验兔骨关节炎模型关节软骨修复,牛膝总皂苷含药血清体外能促进软骨细胞增殖。
目的:观察牛膝总皂苷对实验兔骨关节炎模型软骨修复及低氧诱导因子1信号通路的影响。
方法:新西兰大白兔32只由广东省实验动物中心提供,实验方案经广州中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号:2018023)。将32只实验兔进行骨关节炎模型造模,将造模成功的30只随机分为牛膝总皂苷组、硫酸氨基葡萄糖组、空白对照组,每组10只,分别予牛膝总皂苷、硫酸氨基葡萄糖、蒸馏水灌胃30 d,进行软骨组织苏木精-伊红染色观察、病理学改良Mankin’s评分及软骨细胞电镜观察,用qRT-PCR检测软骨组织低氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子、Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达。
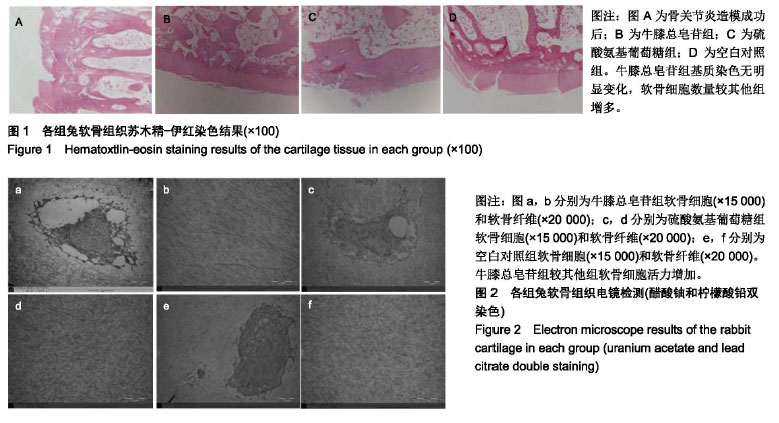
结果与结论:①灌胃30 d后牛膝总皂苷组与硫酸氨基葡萄糖组、空白对照组比较,苏木精-伊红染色观察、病理学改良Mankin’s评分明显改善(P < 0.05),电镜观察软骨细胞活力增加;②牛膝总皂苷组与硫酸氨基葡萄糖组、空白对照组比较,qRT-PCR检测软骨组织低氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子mRNA表达下调及Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达上调(P < 0.05);③牛膝总皂苷能有效提高细胞活力、促进软骨细胞增殖,下调低氧诱导因子1α、血管内皮生长因子mRNA表达及上调Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达,说明低氧诱导因子1信号通路在牛膝总皂苷对实验兔骨关节炎模型软骨修复过程中发挥了较大作用。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。
文题释义:
低氧诱导因子1:即缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1),是1992年Semenza和Wang首先发现的,随后确立了HIF-1的结构,并证明了其cDNA的编码顺序。HIF-1普遍存在于人和哺乳动物细胞内,常氧下(21%O2)也有表达,但合成的HIF-1蛋白很快即被细胞内氧依赖性泛素蛋白酶降解途径所降解,只有在缺氧条件下HIF-1才可稳定表达。
牛膝总皂苷:牛膝主要有效成分包含多糖类、皂苷类、甾酮类等。研究说明牛膝总皂苷具有促进软骨细胞增殖和抗炎症的作用。