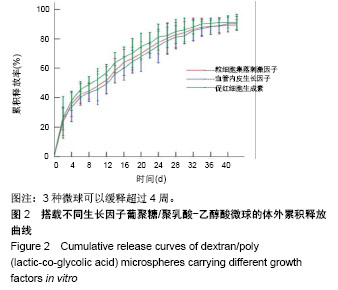
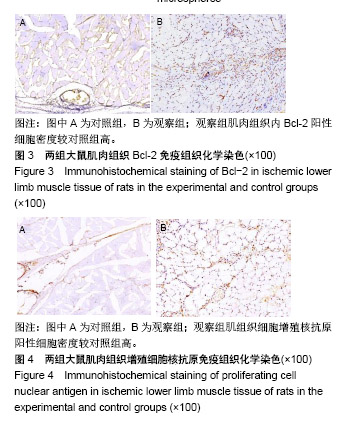
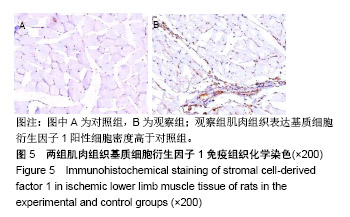
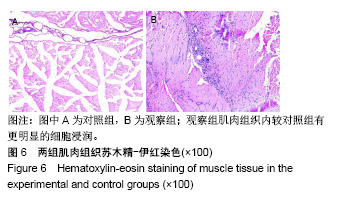
| [1]Sato K, Wu T, Laham RJ, et al. Efficacy of intracoronary or intravenous VEGF165 in a pig model of chronic myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol.2001;37(2):616-623.[2]Grunewald M, Avraham I, Dor Y, et al. VEGF-induced adult neovascularization: recruitment, retention, and role of accessory cells. Cell.2006;124(1):175-189.[3]Klopsch C, Skorska A, Ludwig M, et al.Intramyocardial angiogenetic stem cells and epicardial erythropoietin save the acute ischemic heart. Dis Model Mech.2018;11(6).pii: dmm033282. doi: 10.1242/dmm.033282.[4]Kimáková P, Solár P, Solárová Z, et al. Erythropoietin and Its Angiogenic Activity. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18(7).pii: E1519. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071519.[5]Spadaccio C, Rainer A, Trombetta M, et al. A G-CSF functionalized scaffold for stem cells seeding: a differentiating device for cardiac purposes. J Cell Mol Med.2011;15(5):1096-108.[6]Cleland JL,Duenas ET, Park A, et al. Development of poly-(D,L-lactide--coglycolide) microsphere formulations containing recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor to promote local angiogenesis. J Control Release. 2001;72(1-3):13-24.[7]Iwanaga K,Takano H,Ohtsuka M,et al. Effects of G-CSF on cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction in swine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2004;325(4):1353-1359.[8]Körbling M,Reuben JM,Gao H,et al.Recombinant human granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor-mobilized and apheresis- collected endothelial progenitor cells: a novel blood cell component for therapeutic vasculogenesis. Transfusion. 2006;46(10):1795-1802.[9]Misao Y, Takemura G, Arai M, et al. Importance of recruitment of bone marrow-derived CXCR4+ cells in post-infarct cardiac repair mediated by G-CSF. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71(3):455-465.[10]Deindl E, Zaruba MM, Brunner S, et al. G-CSF administration after myocardial infarction in mice attenuates late ischemic cardiomyopathy by enhanced arteriogenesis.FASEB J. 2006;20(7):956-958.[11]Ohki Y, Heissig B, Sato Y, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor promotes neovascularization by releasing vascular endothelial growth factor from neutrophils. FASEB J.2005;19(14):2005-2007.[12]Ohtsuka M,Takano H,Zou Y,et al.Cytokine therapy prevents left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction after myocardial infarction through neovascularization.FASEB J. 2004;18(7):851-853. [13]Janmaat ML,Heerkens JL, de Bruin AM,et al.Erythropoietin accelerates smooth muscle cell-rich vascular lesion formation in mice through endothelial cell activation involving enhanced PDGF-BB release.Blood. 2010;115(7):1453-1460.[14]Darnell JE, Kerr IM,Stark GR.Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264(5164):1415-1421.[15]Watowich SS,Hilton DJ,Lodish HF.Activation and inhibition of erythropoietin receptor function: role of receptor dimerization.Mol Cell Biol.1994;14(6):3535-3549.[16]Haller H,Christel C,Dannenberg L,et al.Signal transduction of erythropoietin in endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 1996;50(2):481-488.[17]Pelekanou V, Kampa M, Kafousi M,et al. Erythropoietin and its receptor in breast cancer: correlation with steroid receptors and outcome. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16(10):2016-2023.[18]Heeschen C,Aicher A,Lehmann R,et al.Erythropoietin is a potent physiologic stimulus for endothelial progenitor cell mobilization. Blood. 2003;102(4):1340-1346.[19]Brines M,Cerami A.Discovering erythropoietin's extra-hematopoietic functions: biology and clinical promise.Kidney Int.2006;70(2):246-250.[20]Westenbrink BD,Lipsic E, van der Meer P, et al. Erythropoietin improves cardiac function through endothelial progenitor cell and vascular endothelial growth factor mediated neovascularization. Eur Heart J.2007; 28(16):2018-2027.[21]Kobayashi H, Minatoguchi S, Yasuda S, et al. Post-infarct treatment with an erythropoietin-gelatin hydrogel drug delivery system for cardiac repair.Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79(4):611-620.[22]Noguchi CT, Wang L,Rogers HM,et al.Survival and proliferative roles of erythropoietin beyond the erythroid lineage.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008; 10:e36.[23]Santhanam AV, d'Uscio LV, Peterson TE, et al. Activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is critical for erythropoietin-induced mobilization of progenitor cells.Peptides. 2008;29(8):1451-1455.[24]Kawachi K, Iso Y, Sato T,et al. Effects of erythropoietin on angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in porcine. Heart Vessels.2012;27(1):79-88.[25]Lin JS,Chen YS,Chiang HS,et al.Hypoxic preconditioning protects rat hearts against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: role of erythropoietin on progenitor cell mobilization. J Physiol. 2008;586(23):5757-5769.[26]Kato S, Amano H,Ito Y, et al.Effect of erythropoietin on angiogenesis with the increased adhesion of platelets to the microvessels in the hind-limb ischemia model in mice.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;112(2):167-175.[27]Jin DK, Shido K, Kopp HG, et al. Cytokine-mediated deployment of SDF-1 induces revascularization through recruitment of CXCR4+ hemangiocytes. Nat Med. 2006;12(5):557-567.[28]Petit I,Jin D,Rafii S.The SDF-1-CXCR4 signaling pathway: a molecular hub modulating neo-angiogenesis.Trends Immunol. 2007;28(7):299-307.[29]Kucia M, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ. Bone marrow as a source of circulating CXCR4+ tissue-committed stem cells. Biol Cell. 2005;97(2): 133-146.[30]Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, et al. Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy.Lancet. 2003;362(9385):697-703.[31]Abbott JD, Huang Y, Liu D, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the absence of injury. Circulation. 2004;110(21):3300-3305.[32]Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, et al. Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med.2004;10(8):858-864.[33]De Falco E,Porcelli D,Torella AR,et al.SDF-1 involvement in endothelial phenotype and ischemia-induced recruitment of bone marrow progenitor cells. Blood. 2004;104(12):3472-3482.[34]Lamagna C, Bergers G. The bone marrow constitutes a reservoir of pericyte progenitors. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80(4):677-681.[35]Seeger FH, Rasper T, Koyanagi M, et al. CXCR4 expression determines functional activity of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells for therapeutic neovascularization in acute ischemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(11):1802-1809. |
.jpg)

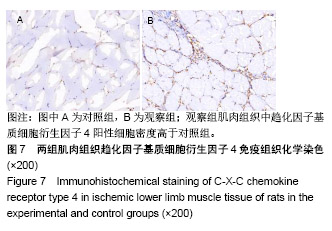
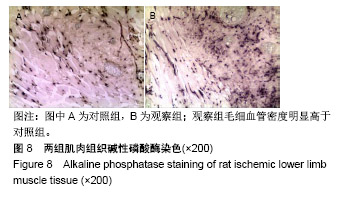
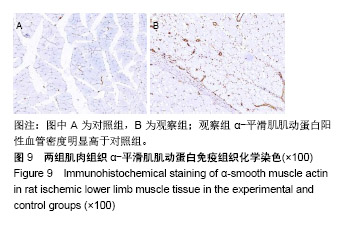
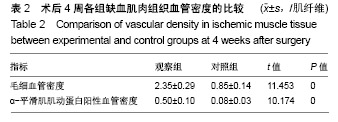

.jpg)