| [1]Hattner R, Epker BN, Frost HM.Suggested sequential mode of control of changes in cell behaviour in adult bone remodelling. Nature.1965; 206(983):489-490.[2]Martin TJ, Sims NA. Osteoclast-derived activity in the coupling of bone formation to resorption. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11(2):76-81.[3]Sims NA, Martin TJ. Coupling signals between the osteoclast and osteoblast: how are messages transmitted between these temporary visitors to the bone surface? Front Endocrinol. 2015;6: 41.[4]Zhu S, Yao F, Qiu H, et al. Coupling factors and exosomal packaging microRNAs involved in the regulation of bone remodelling. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018;93(1):469-480.[5]Sims NA, Martin TJ.Coupling the activities of bone formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep. 2014;3:481.[6]Furuya M, Kikuta J, Fujimori S, et al. Direct cell-cell contact between mature osteoblasts and osteoclasts dynamically controls their functions in vivo. Nature Commun. 2018;9(1):300.[7]Keller J, Catala-Lehnen P, Huebner AK, et al.Calcitonin controls bone formation by inhibiting the release of sphingosine 1-phosphate from osteoclasts. Nature Commun. 2014;5:5215.[8]Xie H, Cui Z, Wang L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.[9]Troen BR. Molecular mechanisms underlying osteoclast formation and activation. Exp Gerontol. 2003;38(6):605-614.[10]Han D, Zhang Q. An essential requirement for osteoclasts in refined bone-like tissue reconstruction in vitro. Med Hypotheses. 2006; 67(1): 75-78.[11]Dai XM, Zong XH, Akhter MP, et al.Osteoclast deficiency results in disorganized matrix, reduced mineralization, and abnormal osteoblast behavior in developing bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(9): 1441-1451.[12]Sakagami N, Amizuka N, Li M, et al. Reduced osteoblastic population and defective mineralization in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice. Micron. 2005;36(7-8):688-695.[13]Demiralp B, Chen HL, Koh AJ, et al. Anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone during bone growth are dependent on c-fos. Endocrinology. 2002;143(10):4038-4047.[14]Alatalo SL.Osteoclast-derived serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b in albers-schonberg disease (type ii autosomal dominant osteopetrosis). Clin Chem. 2004;50(5):883-890.[15]Del Fattore A. Clinical, genetic, and cellular analysis of 49 osteopetrotic patients: implications for diagnosis and treatment. J Med Genet. 2005; 43(4):315-325.[16]Thudium CS, Moscatelli I, Flores C, et al.A comparison of osteoclast-rich and osteoclast-poor osteopetrosis in adult mice sheds light on the role of the osteoclast in coupling bone resorption and bone formation. Cal Tissue Int. 2014;95(1):83-93.[17]Kreja L, Brenner RE, Tautzenberger A, et al.Non-resorbing osteoclasts induce migration and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009.[18]Kim BJ, Lee YS, Lee SY, et al.Afamin secreted from nonresorbing osteoclasts acts as a chemokine for preosteoblasts via the Akt-signaling pathway. Bone. 2012;51(3):431-440.[19]Karsdal MA, Martin TJ, Bollerslev J, et al. Are nonresorbing osteoclasts sources of bone anabolic activity? J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(4): 487-494.[20]Henriksen K, Andreassen KV, Thudium CS, et al. A specific subtype of osteoclasts secretes factors inducing nodule formation by osteoblasts. Bone. 2012;51(3):353-361.[21]Karsdal MA, Neutzsky-Wulff AV, Dziegiel MH, et al. Osteoclasts secrete non-bone derived signals that induce bone formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366(2):483-488.[22]Pederson L, Ruan M, Westendorf JJ, et al. Regulation of bone formation by osteoclasts involves Wnt/BMP signaling and the chemokine sphingosine-1-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(52): 20764-20769. [23]Henriksen K, Karsdal MA, Martin TJ. Osteoclast-derived coupling factors in bone remodeling. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;94(1):88-97.[24]Ryu J, Kim HJ, Chang EJ, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate as a regulator of osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast-osteoblast coupling. EMBO J. 2006;25(24):5840-5851.[25]Rahman MM, Matsuoka K, Takeshita S, et al. Secretion of PDGF isoforms during osteoclastogenesis and its modulation by anti-osteoclast drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;462(2): 159-164.[26]Sanchez-Fernandez MA, Gallois A, Riedl T, et al. Osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling. PloS one. 2008;3(10):e3537.[27]Khavandgar Z, Murshed M.Sphingolipid metabolism and its role in the skeletal tissues. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(5):959-969.[28]Boyce BF.Advances in osteoclast biology reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Rese. 2013;28(4): 711-722.[29]Hla T. Physiological and pathological actions of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15(5):513-520.[30]Avery K, Avery S, Shepherd J,et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates transcriptional regulation of key targets associated with survival, proliferation, and pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6):1195-1205.[31]Patmanathan SN, Wang W, Yap LF, et al. Mechanisms of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor signalling in cancer. Cell Signal. 2017;34:66-75.[32]Roelofsen T, Akkers R, Beumer W, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate acts as a developmental stage specific inhibitor of platelet-derived growth factor-induced chemotaxis of osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105(4): 1128-1138.[33]Dobrosak C, Gooi JH. Increased sphingosine-1-phosphate production in response to osteocyte mechanotransduction. Bone Rep. 2017;7:114-120.[34]Matsuzaki E, Hiratsuka S, Hamachi T, et al. Sphingosine-1- phosphate promotes the nuclear translocation of beta-catenin and thereby induces osteoprotegerin gene expression in osteoblast-like cell lines. Bone. 2013;55(2):315-324.[35]Zhang W, Yin L, Song G, et al. LKB1 loss cooperating with BRAF V600E promotes melanoma cell invasion and migration by up-regulation MMP-2 via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(69):113847-113857.[36]Huang Y, Mao Y, Li H, et al. Knockdown of Nrf2 inhibits angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells under hypoxic conditions. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018.[37]Badgwell DB, Lu Z, Le K, et al. The tumor-suppressor gene ARHI (DIRAS3) suppresses ovarian cancer cell migration through inhibition of the Stat3 and FAK/Rho signaling pathways. Oncogene. 2011;31(1): 68-79.[38]Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, et al.Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2005;24(42): 6406-6417.[39]Sartawi Z, Schipani E, Ryan KB, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) signalling: Role in bone biology and potential therapeutic target for bone repair. Pharmacol Res. 2017;125(Pt B):232-245.[40]Quint P, Ruan M, Pederson L, et al.Sphingosine 1-Phosphate (S1P) receptors 1 and 2 coordinately induce mesenchymal cell migration through S1P activation of complementary kinase pathways. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(8):5398-5406.[41]Cawthorn WP, Bree AJ, Yao Y, et al. Wnt6, Wnt10a and Wnt10b inhibit adipogenesis and stimulate osteoblastogenesis through a beta-catenin-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2012;50(2):477-489.[42]Rahman S, Czernik PJ, Lu Y, et al. beta-catenin directly sequesters adipocytic and insulin sensitizing activities but not osteoblastic activity of PPARgamma2 in marrow mesenchymal stem cells. PloS one. 2012; 7(12):e51746.[43]Hashimoto Y, Matsuzaki E, Higashi K, et al. Sphingosine-1- phosphate inhibits differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells into adipocyte. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;401(1-2):39-47.[44]Hashimoto Y, Kobayashi M, Matsuzaki E, et al.Sphingosine-1- phosphate-enhanced Wnt5a promotes osteogenic differentiation in C3H10T1/2 cells. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40(10):1129-1136.[45]Takeshita S, Fumoto T, Matsuoka K, et al.Osteoclast-secreted CTHRC1 in the coupling of bone resorption to formation. J Clin Invest. 2013,123(9): 3914-3924.[46]雷文龙,施斌.血小板衍生生长因子-BB在口腔种植领域中的作用[J].国际口腔医学杂志.2014,41(2):199-203. [47]Fiedler J, Etzel N, Brenner RE.To go or not to go: Migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells stimulated by isoforms of PDGF. J Cell Biochem. 2004;93(5):990-998.[48]Fiedler J, Roderer G, Gunther KP, et al. BMP-2, BMP-4, and PDGF-bb stimulate chemotactic migration of primary human mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Biochem. 2002;87(3): 305-312.[49]Tokunaga A, Oya T, Ishii Y, et al. PDGF receptor beta is a potent regulator of mesenchymal stromal cell function. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(9):1519-1528.[50]McCarthy HS, Williams JHH, Davie MWJ, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates osteoprotegerin production in osteoblastic cells. J Cell Phys. 2009;218(2):350-354.[51]Hollinger JO, Onikepe AO, MacKrell J, et al.Accelerated fracture healing in the geriatric, osteoporotic rat with recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-bb and an injectable beta-tricalcium phosphate/collagen matrix. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(1):83-90.[52]Camelo M, Nevins ML, Schenk RK, et al. Periodontal regeneration in human Class II furcations using purified recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rhPDGF-BB) with bone allograft. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23(3):213-225.[53]Nevins M, Camelo M, Nevins ML, et al. Periodontal regeneration in humans using recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rhPDGF-BB) and allogenic bone. J Periodontol. 2003;74(9): 1282-1292.[54]Maes C, Kobayashi T, Selig MK, et al. Osteoblast precursors, but not mature osteoblasts, move into developing and fractured bones along with invading blood vessels. Dev Cell. 2010;19(2):329-344.[55]Percival CJ, Richtsmeier JT. Angiogenesis and intramembranous osteogenesis. Dev Dyn. 2013;242(8):909-922.[56]Matsuyama J, Ohnishi I, Kageyama T, et al. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis in regenerating bone during transverse distraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(433):243-250.[57]Choi IH, Chung CY, Cho TJ, et al. Angiogenesis and mineralization during distraction osteogenesis. J Korean Med Sci. 2002;17(4): 435-447.[58]Lotinun S, Kiviranta R, Matsubara T, et al. Osteoclast-specific cathepsin K deletion stimulates S1P-dependent bone formation. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(2):666-681.[59]Bonnet N, Brun J, Rousseau JC, et al. Cathepsin K controls cortical bone formation by degrading periostin. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32(7):1432-1441.[60]Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK, Adams RH.Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328.[61]Zhao X, Guan JL.Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(8): 610-615.[62]Zhao LN, Wang P, Liu YH, et al. MiR-383 inhibits proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of glioma-exposed endothelial cells in vitro via VEGF-mediated FAK and Src signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2017;30:142-153. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。
文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。.jpg) 文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。
文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。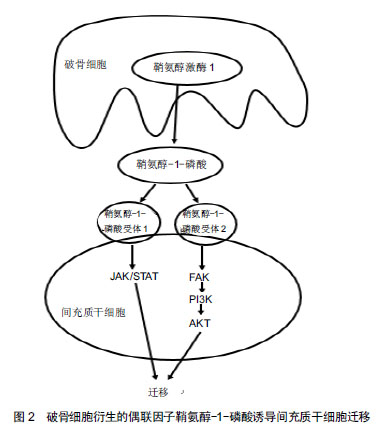
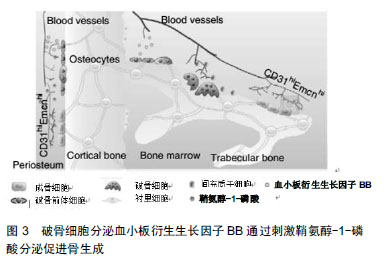
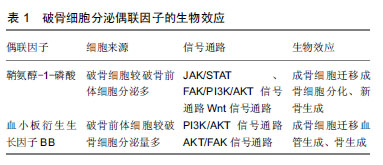
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。
文题释义:
偶联:在生理条件下,破骨细胞介导的骨吸收由成骨细胞介导的骨形成直接取代,这种现象称为偶联。
骨重建:是骨发育成熟后保持骨量和骨质量的基本过程,包括破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成的改建活动,而不断地更新骨组织。