2.1 与多囊蛋白相关的参与骨形成机制的转录因子和信号网络 近年来的研究发现多囊蛋白作为骨的主要机械传感器参与了骨形成机制。多囊蛋白中最主要的亚型多囊蛋白1由常染色体显性遗传性多囊肾病中突变基因PKD1编码,调节包括骨骼发育在内的一系列过程[9]。多囊蛋白1是一种跨膜受体,具有广泛的N末端胞外部分,包含约3 000个氨基酸,这部分包含域的组合有:富含亮氨酸重复序列(LRRs),免疫球蛋白样结构域(ILDs或PKD 重复序列),G蛋白偶联受体蛋白水解位点(GPS),C型凝集素样结构域(CLD)等,多囊蛋白1通过这些蛋白基序与其他蛋白或分子相互作用[10]。多囊蛋白2由常染色体显性遗传性多囊肾病中突变基因PKD2编码,多囊蛋白2作为瞬时受体电位(TRP)通道家族的一员,形成Ca2+通透型的非选择性阳离子通道,主要分布于内质网(ER)、初级纤毛和质膜上。多囊蛋白1和多囊蛋白2与多种细胞类型、组织和不同细胞位置的许多蛋白有关。多囊蛋白与不同蛋白间的相互作用具有多种功能,包括运输、调节、信号转导、降解及与相关蛋白形成大型多蛋白复合物[11]。多囊蛋白1、多囊蛋白2还和初级纤毛在成骨细胞系中表达,包括成骨细胞和骨细胞,形成一个多囊蛋白-初级纤毛信号复合物,作为骨的主要机械传感器参与调节骨形成[12]。
初级纤毛是非活动性的依赖于微管的细胞器,从人体几乎所有细胞的顶端表面延伸,如肝和肾内皮细胞,上皮细胞和骨细胞,表现为细胞的“天线”,可接收包括机械刺激和化学信号在内的多种细胞外信号并将其转化为细胞内信号反应[13]。初级纤毛存在于所有骨细胞上,对细胞的分化很重要[14]。TAZ(transcriptional coactivator with PDZ binding motif)是一种具有pdz结合基序的转录共激活因子,可调节细胞的分化、增殖和发育。TAZ与多囊蛋白1相互作用调节骨发育[9]。
骨组织由骨祖细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞4种主要的细胞类型组成,它们可以感知流体的剪切应力、压力和应变[3]。机械刺激在骨骼的发育和维持中起着至关重要的作用。这一功能需要骨骼细胞感知细胞外机械信号,并将其转化为调节细胞基因表达的细胞内生化反应,这一系列事件被称为机械转导。机械转导调节成骨细胞的分化、脂肪的生成和骨块的形成,这一作用是通过多囊蛋白和机械敏感结构促进的,如初级纤毛以及与多囊蛋白1和多囊蛋白2相关的下游信号通路[12,15-16]。
就信号转导途径而言,已有研究显示在骨组织中协调机械转导的大量信号通路和关键信号分子,主要有Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路、calcium-cAMP/PKA信号通路、Calcineurin/NFAT信号通路等,研究表明多囊蛋白通过与以上信号通路中的蛋白或分子作用调节骨的形成[4-5,7,17]。其中β-catenin是骨细胞机械转导反应中最重要的分子之一,通过维持骨细胞活力来维持骨稳态和机械转导,而Wnt/β-catenin通路的激活增强了成骨细胞/骨细胞对机械负荷的敏感性[18]。CAMP通路中的关键转录因子runt-related transcription factor-2(Runx2)是调节骨形成的主要转录因子,是成骨细胞生成的最早标志物之一,是引导间充质前体细胞向成骨细胞分化的关键[15],其表达由丝裂原-活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)调节[19]。多囊蛋白1还可通过Calcineurin/NFAT信号级联调节成骨细胞基因转录,从而调节骨细胞分化[17]。
2.2 多囊蛋白在骨形成机制中的作用 骨骼组织是一种动态组织,通过骨骼吸收和骨骼合成的循环不断再生,这一过程称为骨骼重塑[20]。这一重要功能取决于机械转导,它参与了骨骼生理学及癌变过程中的相应病理生理机制[21]。体外研究和动物模型研究均已证明瞬时受体电位多囊蛋白(TRPPs)亚家族——多囊蛋白1 (TRPP1),多囊蛋白2 (TRPP2)作为机械感受器,感知外部机械力,包括应变、拉伸和流体剪切应力,触发一系列参与成骨细胞生成和最终骨骼形成的信号通路,从而对骨稳态产生调节作用[8]。多囊蛋白1可与定位于黏附点、黏附连接和桥粒的蛋白相互作用[10]。多囊蛋白1受到调控而裂解,释放其C末端尾部,该尾部转移到细胞核,以调节参与增殖和凋亡的转录途径[9];多囊蛋白1还通过其羧基末端域与多囊蛋白2耦合[22],且多囊蛋白1和多囊蛋白2具有感知多种物理力的结构特性[23]。
2.2.1 多囊蛋白与初级纤毛及TAZ 多囊蛋白初级纤毛复合体负责骨的机械感应,能够将多种环境信号整合到已知的调节骨骼发育的多种信号转导途径中[6]。纤毛对于骨膜祖细胞和人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化是必要的[14]。MOORE等[14]的研究表明,骨膜的软骨祖细胞在体内具有惊人的增殖和生成新骨的能力,且初级纤毛在骨膜软骨祖细胞感知机械刺激和以成骨方式对流体剪切力做出反应这两方面是至关重要的。kinesin-2 family protein A(Kif3a)是驱动蛋白Ⅱ纤毛内转运(IFT)蛋白的亚基,IFT参与初级纤毛的形成、维持和功能行使。Kif3a缺失小鼠由于成骨细胞中初级纤毛形成的破坏而出现骨质减少和机械感觉受损 [24]。Kif3a的C末端区域与多囊蛋白2的C末端区域结合,介导多囊蛋白定位于成骨细胞和骨细胞中的初级纤毛来调节成骨细胞的功能[25]。研究发现在骨细胞和成骨细胞中有条件敲除骨中PKD1,PKD2,Kif3a的情况下,新骨形成均减少[24,26],提示多囊蛋白与初级纤毛具有相互依赖的功能。
TAZ作为转录共激活因子,与多囊蛋白相互作用促进骨发育[9]。成骨细胞谱系中PKD1的选择性缺失调节成骨细胞的生成和脂肪生成[27]。机械拉伸的应用和细胞外基质的硬度增加刺激了机械诱导共激活剂TAZ、多囊蛋白1 和多囊蛋白2之间核复合物的形成,这与通过激活Runx2表达来增加骨形成和通过失活PPARγ来抑制脂肪形成有关[27]。最新研究发现,多囊蛋白1羧基末端尾部(PC-1- CTT)裂解后显著增强转录共激活因子TAZ 的活性,TAZ是Runx2必不可少的共激活因子。为了增强前成骨细胞中Runx2的表达,PC-1-CTT与TAZ结合形成功能复合体,以TAZ依赖的方式刺激前成骨细胞的Runx2转录活性。PC-1-CTT和TAZ之间的相互作用增加了TAZ和Runx2之间的相互作用,并增强了p300转录共调节蛋白对TAZ/Runx2 / PC-1 -CTT复合物的募集,从而形成PC-1/TAZ/p300/ Runx2激活复合物促进骨发育[9]。多囊蛋白、初级纤毛和TAZ正在成为整合骨对流体流动和细胞外基质环境的反应的主要候选分子[12]。
2.2.2 多囊蛋白与calcium-cAMP/PKA信号通路 多囊蛋白1是细胞内calcium-cAMP/PKA信号通路的调节因子,这是骨形成的关键途径[7]。QIU等[25]在稳定敲除人类成骨细胞样MG-63细胞中的PKD1后,发现细胞中PKD1降低了53%,导致初级纤毛长度和细胞增殖增加,成骨分化受损和成脂作用增强,以及较低的细胞内钙浓度,从而导致细胞内钙信号对流体剪切应力的反应减弱。而用PKA抑制剂H89处理PKD1-shRNA MG-63细胞后,初级纤毛的长度、细胞增殖和成骨分化得以恢复,成骨基因标志物Runx2显著增加,成脂标志物aP2显著减少。PKA是cAMP 信号通路的下游靶点,这些发现表明,人MG-63细胞中PKD1的下调通过细胞内calcium-cAMP/PKA信号通路导致成骨细胞功能缺陷,细胞对机械刺激反应下降,从而影响骨形成过程[7]。前成骨细胞和成熟成骨细胞中PKD1和PKD2的条件性缺失抑制了流体诱导的钙离子内流,从而显示出较低的细胞内钙浓度[28-29]。
2.2.3 多囊蛋白与Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin通路 多囊蛋白1作为机械传感器,刺激Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin信号通路,进而增强Runx2表达。多囊蛋白1在机械刺激作用下影响骨细胞的增殖和分化。小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1中PKD1的稳定下调与成骨细胞分化标志物表达降低有关,其中包括Runx2[30]。有实验表明,在成骨细胞系MC3T3-E1中多囊蛋白1感知外部机械刺激,从而将机械信号转化为细胞内钙离子信号的增强。然后钙依赖的Akt磷酸化并导致糖原合酶3β(GSK-3β)磷酸化。GSK-3β的磷酸化抑制了β-catenin的蛋白水解,从而调控与成骨细胞增殖和分化相关的基因(如Runx2)的转录,表明成骨细胞需要机械感觉分子多囊蛋白1通过下游Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin信号通路来感觉诱导成骨和增殖的机械张力[31]。
2.2.4 多囊蛋白与STAT3和p38 MAPK信号通路 PKD1还通过激活STAT3和p38 MAPK信号通路,上调成骨细胞标志物[Runx2,osterix(OSX),collagenase I(COL-α1)等]的表达,促进成骨细胞分化和骨发育[32]。在体外培养的人牙周韧带组织中获得的成骨细胞(即具有向成熟成骨细胞分化潜能的细胞)中也观察到类似现象:机械载荷作用下,从人牙周韧带组织中获得的成骨细胞中的多囊蛋白1的羧基末端(CP-1- CTT)与JAK2特异性结合,触发其激活并导致STAT3磷酸化,然后,STAT3的活性形式易位到细胞核,与Runx2启动子结合,并与Runx2协同作用,增强Runx2转录,从而控制成骨细胞分化并最终控制骨形成[33]。
2.2.5 多囊蛋白与calcineurin/NFAT信号通路 在一项研究中,使用拉伸设备对来自人类牙周韧带组织的成骨前细胞给予拉伸刺激,结果提示多囊蛋白1可以感知来自环境的机械应变,在机械负荷刺激下,多囊蛋白1作为主要的机械诱导分子,通过calcineurin/NFAT信号通路调节成骨细胞基因转录,从而促进骨细胞分化[17]。
综上所述,在机械刺激下,多囊蛋白1和多囊蛋白2诱导下游信号传导级联并调节黏着斑复合物,以支持细胞极性、分化、迁移增加、血管生成和增殖[21]。因此,成骨细胞谱系中的每一种细胞类型都具有通过多囊蛋白对机械力作出反应的内在潜力。
2.3 多囊蛋白在骨质丢失中的作用机制 有研究表明,多囊蛋白的编码基因PKD1的缺失导致软骨形成缺陷、成骨细胞形成受损和骨质丢失,所有的效应都与细胞内钙水平的降低有关,并与骨形成和钙稳态进一步相关[6]。脂肪生成在骨髓和成骨细胞中也很明显,表明骨形成的功能障碍[7,32]。有研究进一步证实,成骨细胞中PKD1的条件性缺失可导致出生后有缺陷的骨形成和骨吸收[7]。
2.3.1 多囊蛋白和初级纤毛功能缺陷 复合PKD1和Kif3a缺陷小鼠中出现骨质丢失,其特征在于骨矿物质密度、骨小梁体积和皮质骨厚度降低[34]。此外,PKD1的缺乏与成骨细胞分化障碍有关,并伴有原代成骨细胞和/或骨髓基质细胞培养中的脂肪生成。这些变化还与成骨细胞基因和转录因子有关,如Runx2和PPARγ,其水平分别降低和升高[34]。细胞外基质硬度的增加和对多能性间充质细胞的机械拉伸的应用刺激PC-1-CTT / TAZ复合物的核易位,从而导致Runx2介导的成骨基因表达增加,提示PC/TAZ复合物可能是增加骨质量的潜在治疗靶点[27]。
2.3.2 多囊蛋白与Runx2 多囊蛋白1通过调节Runx2在骨质丢失中发挥重要作用。复合Runx2和PKD1杂合子小鼠对降低骨量有叠加效应。此外,多囊蛋白1和多囊蛋白2耦合以响应成骨细胞的机械载荷,PKD1对Runx2启动子活性的影响是通过与PKD2钙通道耦合和调节钙信号通路来介导的。成骨细胞中相应的多囊蛋白2缺乏或多囊蛋白1缺乏均可导致骨丢失。多囊蛋白1缺乏可能导致成骨标志物Runx2水平降低和脂肪细胞分子标志物PPARγ升高,而PKD2缺乏导致Runx2和PPARγ表达均减少。因此,PKD1和PKD2对成骨细胞的分化具有协同促进作用,对脂肪生成则具有相反的作用,提示PKD1和PKD2信号通路可以各自独立影响骨间充质细胞的分化方向[29]。与对照组小鼠相比,成熟小鼠成骨细胞中,敲除PKD1和PKD2导致骨骼中成骨相关基因Runx2、骨钙素、骨桥蛋白、骨唾液蛋白、Sost和碱性成纤维细胞23表达减少,出现骨矿物质密度、松质骨体积、皮质骨厚度和矿物沉积率降低以及体外成骨细胞分化受损[29]。成骨细胞中PKD1的缺失导致RankL表达下降,血清Trap水平(骨吸收的标志物)也降低。缺乏PKD1的小鼠的骨形成和骨吸收标志物都有很大程度的减少,表明PKD1介导的骨质丢失是由于骨形成率低而不是骨吸收增加所致[35]。
2.3.3 多囊蛋白与Bicc1 Bicc1是bicaudal C同系物1,其编码RNA结合蛋白,多囊蛋白2的编码基因PKD2是Bicc1的下游靶点。使用siRNA介导敲除成骨细胞中PKD2的研究表明,多囊蛋白2缺失与体外成骨细胞分化受损有关,Bicc1通过调节PKD2转录水平来刺激成骨细胞和骨密度。抑制Bicc1和PKD2会破坏成骨细胞生成,而PKD2过表达可以逆转Bicc1缺乏导致的成骨细胞中矿化结节形成减少,Bicc1表达的减少还导致股骨骨密度的降低[36]。
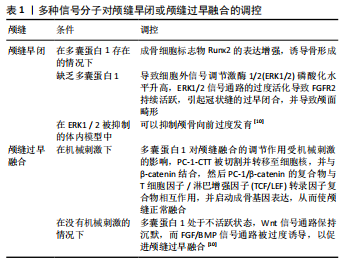
2.4 多囊蛋白与骨疾病 骨骼是由复杂的骨骼网络调节的,因此,骨细胞和其他骨系细胞如何感知机械信号,目前还不清楚。尽管如此,许多机械力的介质被提出,包括初级纤毛和多囊蛋白。一些研究表明,在体外或体内,成骨细胞和骨细胞中多囊蛋白基因的选择性缺失或全部缺失导致骨丢失,表现为骨矿物质密度降低、骨量减少、骨质疏松、颅缝早闭或钙信号传导和内环境平衡的普遍抑制,从而干扰骨形成和骨吸收平衡[10,35]。多囊蛋白介导的信号传导并不只发生在多囊肾疾病中,它也存在于其他临床骨相关疾病的发展过程中,如成骨肉瘤、骨质丢失、颅缝早闭等[37]。
2.4.1 多囊蛋白在颅面发育中的作用机制 由于多囊蛋白对骨形成有明显的影响,一些研究发现多囊蛋白在颅面骨发育中也存在独特机制。众所周知,骨骼组织对机械应力的反应能力已被用于正畸牙移动,牵张成骨和腭中缝扩张,以诱导骨塑造/重塑。虽然体外力学模型提供了相对简单的系统来研究在机械刺激下基因表达和细胞行为的变化,但在这种模型中无法再现体内生物力学环境和研究组织反应。任何骨骼的机械调节模型最终都必须进行体内测试,因为只有在体内的生理环境才能得出骨的功能适应的结论[38-39]。
在神经嵴衍生物和前软骨组织以及MC3T3-E1成骨细胞和MLO-Y4骨细胞中检测到Pkd1转录。此外,已经报道了一些缺乏Pkd1动物的骨骼异常。然而,多囊蛋白1是否在体内骨骼组织对机械应力的反应中发挥作用尚不清楚。为了解决这个问题,HOU等[40]学者对神经嵴细胞、成骨细胞或软骨细胞中有条件的降低多囊蛋白1表达的小鼠进行腭中缝扩张实验,结果显示缺乏多囊蛋白1的软骨生成细胞中细胞凋亡增加,鼻软骨中软骨细胞的排列改变,这些结果表明,软骨生成细胞中的多囊蛋白1对腭中缝扩张引起的机械组织应力反应起到关键作用。有研究通过体外和体内的骨特异性条件性PKD1-敲除(PKD1- KO)小鼠模型证明,PKD1功能缺失通过STAT3和p38 MAPK信号通路介导成骨细胞标志物下降,导致骨发育功能和成骨细胞分化下降。与野生鼠相比,这些小鼠出现了明显的颅面发育不良、肩胛骨发育不良、长骨短以及体质量下降[32]。
此外,在KHONSARI等[41]的研究中,利用Wnt1Cre小鼠分析颅面组织中PKD2的表达,敲除神经嵴细胞中的PKD2,PKD2的突变导致小鼠表现出许多机械创伤的迹象,诸如磨牙牙根断裂、切牙变形、牙槽骨丢失、颞下颌关节变形,甚至表现出异常的颅骨形态。多囊蛋白1调节的calcium-cAMP/PKA信号通路失活导致骨疾病,膜内骨化有明显缺陷,并导致骨软骨发育不良[7]。
PKD1基因突变可能导致颅缝早闭。颅缝早闭是颅缝过早融合引起的。颅缝的形成由多种信号分子参与调控完成,如FGFRs,MSX2,TWIST1,骨形态发生蛋白,Runx2,转化生长因子β和Wnt等, 这些分子的突变导致信号通路异常,可造成颅缝细胞增殖、迁移、成骨能力异常,导致颅缝过早融合[42](表1)。
2.4.2 多囊蛋白在骨肿瘤及囊性病变中的作用机制 多囊蛋白作为介导癌细胞增殖特别是侵袭和转移的分子,在肿瘤发展中起重要作用,关于多囊蛋白在上皮组织来源恶性肿瘤中的作用及调节机制已有多数报道[43-44],近年来发现多囊蛋白1还参与了间叶组织来源恶性肿瘤如骨肉瘤的细胞功能的调控[21]。多囊蛋白与研究骨肉瘤的体外模型——人成骨细胞MG-63细胞的分子机制有关,MG-63细胞中稳定的PKD1敲除导致细胞增殖增加和成骨细胞分化受损,与对照组shRNA MG-63细胞相比,表现为溴脱氧尿嘧啶核苷编入增加,碱性磷酸酶活性降低,钙沉积以及Runx2和OSTERIX表达降低,这表明PKD1通过cAMP/PKA通路调控人成骨细胞MG-63细胞的增殖及分化功能[7、21]。Adamopoulos C团队[21]的初步数据表明,多囊蛋白1功能抑制会损害MG-63细胞的增殖和迁移并激活细胞内致癌信号[雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)途径的哺乳动物靶标]。
NADAR SINGARAYAN等[45]的研究证实了发生于颌骨的含牙囊肿的上皮细胞胞质中多囊蛋白1异常的免疫组织化学存在和表达。表明多囊蛋白1在含牙囊肿以及其他牙源性囊肿的发病和进展中可能发挥的作用,这需要通过更多的研究和分子生物技术的应用来进一步评估;对于其他颌骨内疾病则未见研究报道。