中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3834-3839.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1293
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
两种手术方式重建“恐怖三联征”肘关节稳定性的有限元评价
宋 超1,丁志宏1,殷 涛1,李震时2,吴 亮1,周文超1,徐 波1,刘 粤1,孔德策1,杨铁毅1,张 岩1
- 1上海市浦东新区公利医院骨科,上海市 200135;2广西壮族自治区桂林市兴安界首中西医结合医院骨科,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541300
Finite element evaluation of the stability of the elbow joint in the “terrible triad injury” by two surgical methods
Song Chao1, Ding Zhihong1, Yin Tao1, Li Zhenshi2, Wu Liang1, Zhou Wenchao1, Xu Bo1, Liu Yue1, Kong Dece1, Yang Tieyi1, Zhang Yan1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai 200135, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Xing’an Jieshou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Guilin 541300, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
恐怖三联征:1996年Hotchkis首次将肱尺关节后脱位同时伴有尺骨冠状突和桡骨头骨折命名为肘关节“恐怖三联征”,它是严重的高能量创伤,“三联征”包括影像损伤(后脱位、桡骨头骨折、冠状突骨折),而“恐怖”含义是肘关节骨、韧带稳定结构的广泛损伤造成关节的严重失稳。
有限元分析:有限元法是根据变分法原理求解数学上可描述的物理问题的一种数值计算方法。它的主要优点是能够解决结构、材料性质和载荷情况比较复杂的问题。但有限元方法结果受诸多因素的影响,研究的基础和前提是建立精确的模型。
摘要
背景:肘关节“恐怖三联征”是严重复杂的骨折脱位损伤。能否通过修复内侧副韧带结构替代冠状突骨块的固定来重建肘关节的稳定性值得探讨研究。
目的:通过建立肘关节“恐怖三联征”的有限元模型,在肘关节外侧柱稳定性重建的基础上,比较尺骨冠状突骨折固定和内侧副韧带修补两种模式下,肘关节不同屈曲角度的力学值,评价两种手术方法对肘关节稳定性的影响。
方法:利用肘关节CT、MRI图片的相关数据,计算机生成命令流文件,建立肘关节实体模型,进行网格划分,去除1/3冠状突,去除桡骨小头及内外侧副韧带即为恐怖三联征模型。模拟内侧副韧带断裂后是否进行修复,冠状突骨块是否固定两种情况,并且对其分别施加纵向载荷,分析各种工况条件下肘关节关节面的应力分布,比较肘关节的稳定性。
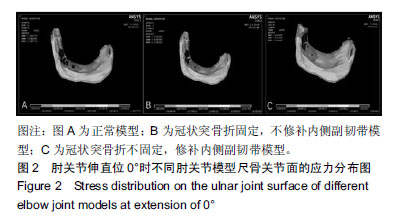
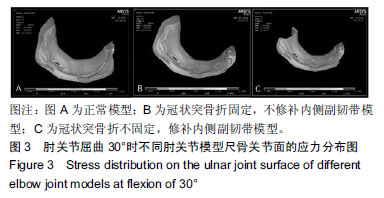
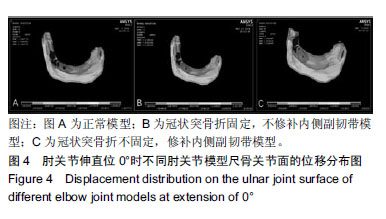
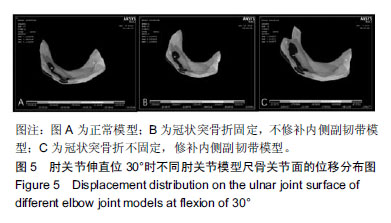
结果与结论:①肘关节伸直位0°时正常肘关节关节面的最大应力为0.78 MPa。将1/3冠状突骨折模型骨折做固定,内侧副韧带不修补,该模型关节面的最大应力为0.84 MPa,而冠状突骨折不做固定,仅修补内侧副韧带的肘关节模型关节面的最大应力也是0.84 MPa;②肘关节屈曲30°时正常肘关节模型关节面的最大应力为2.02 MPa,将1/3冠状突骨折模型骨折做固定,内侧副韧带不修补,该模型关节面的最大应力为2.02 MPa,而冠状突骨折不做固定,修补内侧副韧带的肘关节模型关节面的最大应力为2.07 MPa;③肘关节伸直位0°时正常肘关节关节面的最大位移为0.14 mm,将1/3冠状突骨折模型骨折做固定,内侧副韧带不修补,该模型关节面的最大位移为0.15 mm,而冠状突骨折不做固定,修补内侧副韧带的肘关节模型关节面的最大位移为 0.16 mm;④肘关节屈曲30°时正常肘关节模型关节面的最大位移为0.52 mm,将1/3冠状突骨折做固定,内侧副韧带不修补,该模型关节面的最大位移为0.52 mm,而冠状突骨折不做固定,修补内侧副韧带的模型关节面的最大位移为0.51 mm;⑤上述结果显示,实验成功建立肘关节“恐怖三联征”的有限元模型,将1/3冠状突骨折做固定,如果不修补内侧副韧带,该模型关节面的最大应力及位移略小于正常模型的数值。而冠状突骨折不做固定,仅修补内侧副韧带,其肘关节模型关节面的最大应力及位移大于或基本等于正常模型的该数值。因此,在肘关节外侧柱稳定性重建的基础上,内侧副韧带能够取代冠状突骨折的固定,重建肘关节的稳定性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-8647-0593(宋超)中图分类号:
R459.9|R605|R683
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)