中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3170-3175.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1236
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓水肿与股骨头坏死“带塌陷生存”相关性的X射线评估
陈群群1,周 驰2,何 伟2
- 1广州中医药大学第三附属医院,广东省广州市 510378;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405
Relationship between bone marrow edema and “survival with collapse” of osteonecrosis of the femoral head assessed by X-ray
Chen Qunqun1, Zhou Chi2, He Wei2
- 1the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
骨髓水肿:是股骨头坏死病情发展过程中的一种常见伴随征象,多数学者认为机械应力因素是骨髓水肿发生的主要原因,在股骨头坏死的中晚期,股骨头因坏死与修复反应导致机械应力异常分布,股骨头内存在不稳定,在不适当的负重外力作用下,不稳定可造成头内应力集中,骨髓内压力迅速增加,使相应骨髓局部充血,细胞液外渗而发生反应性水肿,磁共振上表现为骨髓水肿。
带塌陷生存:“带塌陷生存”是指对于塌陷后的股骨头坏死,通过“保髋”干预,塌陷虽未能完全纠正,但达到髋关节基本无痛,功能良好,并能长期维持(>10年)较好的生存状态。“带塌陷生存”必须要满足4个条件:①坏死要较好的修复;②股骨头与髋臼要匹配;③关节内外要稳定;④关节软骨较好,关节间隙保留。
摘要
背景:股骨头坏死塌陷后骨髓水肿广泛存在,骨髓水肿可能是评估股骨头坏死“带塌陷生存”的重要影像学指标。
目的:分析股骨头坏死塌陷后骨髓水肿存在情况与股骨头影像学改变的关系,探讨骨髓水肿在股骨头坏死“带塌陷生存”治疗中的意义。
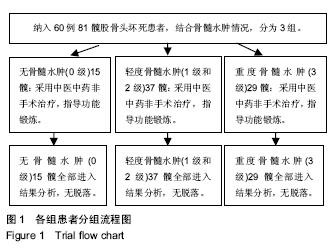
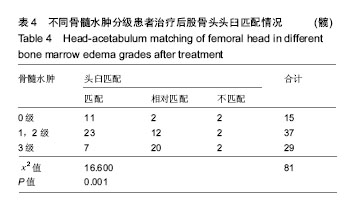
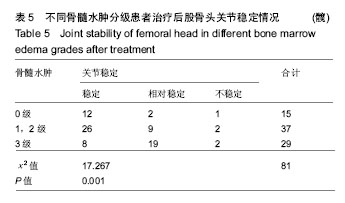
方法:病例资料来自于广州中医药大学第一附属医院股骨头坏死专科门诊(2012至2016年),为“广东省优势病种(股骨头坏死)突破项目”登记入组的股骨头坏死非手术治疗患者,对其中60例(81髋)已塌陷的股骨头坏死病例进行随访,其中男43例61髋,女17例20髋,按照改良的骨髓水肿分级(无骨髓水肿、轻度骨髓水肿、重度骨髓水肿)进行分组,其中无骨髓水肿(0级)15髋,轻度骨髓水肿(1级和2级)37髋,重度骨髓水肿(3级)29髋。所有患者对治疗及试验方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。采用中医药非手术治疗,并指导功能锻炼。每3个月复查双髋关节正蛙位X射线片,观察入组病例在正蛙位塌陷、头臼匹配、关节稳定方面X射线改变,分析骨髓水肿分级对股骨头坏死塌陷后X射线改变的影响。
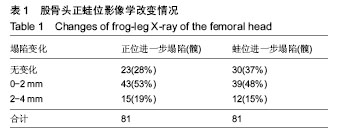
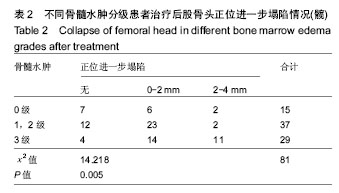
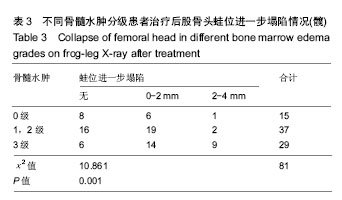
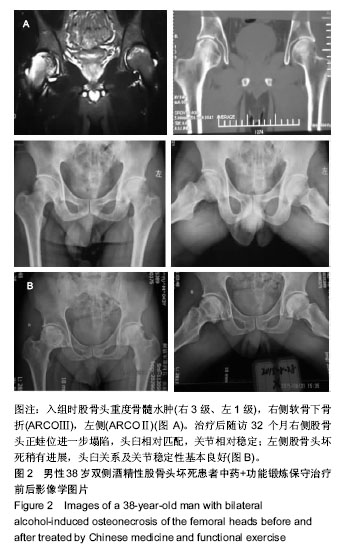
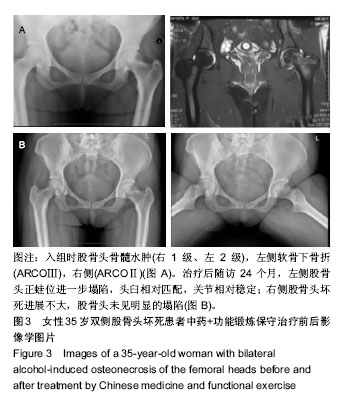
结果与结论:①60例(81髋)已塌陷病例随访资料完整,随访时间为4-72个月;②经R*C列联表的χ2检验,不同骨髓水肿分级会全面影响股骨头坏死塌陷后的X射线进展(正蛙位塌陷、头臼匹配、关节稳定),并且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③提示股骨头坏死塌陷后骨髓水肿广泛存在,骨髓水肿会全面影响塌陷后的X射线改变;骨髓水肿分级越高,正蛙位塌陷、头臼匹配、关节稳定出现X射线进展的概率越大;骨髓水肿是评估股骨头坏死塌陷后治疗的重要影像学指标。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-1046-2650(陈群群)
中图分类号:
.jpg)