| [1] Magnusson SP, Aagard P, Simonsen E, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of cyclic and static stretch in human skeletal muscle. Int J Sports Med.1998;19(5):310-316.[2] Magnusson SP, Simonsen EB, Aagaard P, et al. Mechanical and physiological responses to stretching with and without preisometric contraction in human skeletal muscle. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996; 77(4):373-378. [3] Endlich K, Kliewe F, Endlich N. Stressed podocytes-mechanical forces, sensors, signaling and response. Pflugers Arch. 2017;469(7-8):937-949. [4] Wang W, Yu XD, Mo X, et al. Limb ischemic preconditioning attenuates cerebral ischemic injury in rat model. Perfusion.2014;29(3):210-218.[5] Zhao Y, Li J, Lin A, et al. Improving angiogenesis and muscle performance in the ischemic limb model by physiological ischemic training in rabbits. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;90(12):1020-1029.[6] [Zhao HG, Li WB, Li QJ, et al. Limb ischemic preconditioning attenuates apoptosis of pyramidal neurons in the CA1 hippocampus induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004;56(3):407-412.[7] Li T, Li Y, Lin Y, et al. Significant and sustaining elevation of blood oxygen induced by Chinese cupping therapy as assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed Opt Express.2017;8(1):223-229.[8] Munk N, Symons B, Shang Y, et al. Noninvasively measuring the hemodynamic effects of massage on skeletal muscle: a novel hybrid near-infrared diffuse optical instrument. J Bodyw Mov Ther.2012; 16(1): 22-28.[9] Shang Y, Lin Y, Henry BA, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of electrical stimulation impacts on muscle hemodynamics via integrating diffuse optical spectroscopies with muscle stimulator. J Biomed Opt.2013; 18(10):105002.[10] Li T, Sun Y, Chen X, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of deep vein thrombosis in clinics by near-infrared spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt.2015;20(1):10502.[11] de Sá RB, Pessoa MF, Cavalcanti AG L, et al. Immediate effects of respiratory muscle stretching on chest wall kinematics and electromyography in COPD patients. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017;242:1-7.[12] Lawand P, Lombardi Júnior I, Jones A, et al. Effect of a muscle stretching program using the global postural reeducation method for patients with chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Joint Bone Spine.2015;82(4):272-277.[13] 张帆,王长生,叶志强.不同拉伸方式对股后肌群柔韧素质影响的对比试验研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2014,29(1):61-65.[14] 过家兴. 运动训练学[M]. 北京:北京体育学院出版社,1986.[15] 吕乙林,袁运平,刘永东. 动静态伸展运动在高校田径技术教学中的实验研究[J]. 首都体育学院学报,2003,15(1):78-81.[16] 毛志帮,张玲莉,赖小勇,等. 静态拉伸与下肢肌力锻炼在老年平衡能力中的意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(42):6803-6807.[17] 陈蒙.不同组合拉伸方式对股后肌群柔韧素质影响效应的实验比较研究[D]. 天津:天津体育学院,2016.[18] Chen HM, Wang HH, Chen CH, et al. Effectiveness of a stretching exercise program on low back pain and exercise self-efficacy among nurses in Taiwan: a randomized clinical trial. Pain Manag Nurs.2014; 15(1):283-291.[19] Leelarungrayub D, Pothongsunun P, Yankai A, et al. Acute clinical benefits of chest wall-stretching exercise on expired tidal volume, dyspnea and chest expansion in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A single case study. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2009; 13(4):338-343.[20] Xiong Y, Berrueta L, Urso K, et al. Stretching Reduces Skin Thickness and Improves Subcutaneous Tissue Mobility in a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2017;8:124.[21] Iwasawa H, Nomura M, Sakitani N, et al. Stretching After Heat But Not After Cold Decreases Contractures After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2016;474(12):2692-2701.[22] Gurley K, Shang Y, Yu G. Noninvasive optical quantification of absolute blood flow, blood oxygenation, and oxygen consumption rate in exercising skeletal muscle. J Biomed Opt.2012;17(7):75010.[23] Otah KE,Otah E,Clark LT,等. 在患有外周动脉疾病的患者及正常志愿者中下肢皮肤血流量与踝臂指数的关系[J]. 世界核心医学期刊文摘:心脏病学分册,2006,2(1):55-56.[24] Henry B, Zhao M, Shang Y, et al. Hybrid diffuse optical techniques for continuous hemodynamic measurement in gastrocnemius during plantar flexion exercise. J Biomed Opt.2015;20(12):125006.[25] Jr C, We K, G S, et al. Endothelial cells of hematopoietic origin make a significant contribution to adult blood vessel formation. Circ Res. 2000; 87(9):728-730.[26] Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Remote ischaemic preconditioning: underlying mechanisms and clinical application. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79(3):377-386.[27] SK, Ge A, Kj G, et al. Functional small-diameter neovessels created using endothelial progenitor cells expanded ex vivo.Nature Med. 2001;7(9):1035-1040.[28] Chen WQ, Zhong L, Zhang L, et al. Oral rapamycin attenuates inflammation and enhances stability of atherosclerotic plaques in rabbits independent of serum lipid levels. Br J Pharmacol. 2009; 156(6):941-951.[29] Miyamoto N, Hirata K, Miyamoto-Mikami E, et al. Associations of passive muscle stiffness, muscle stretch tolerance, and muscle slack angle with range of motion: individual and sex differences. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8274. |
.jpg)
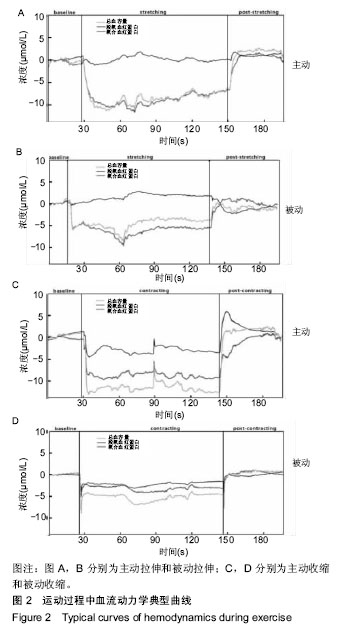
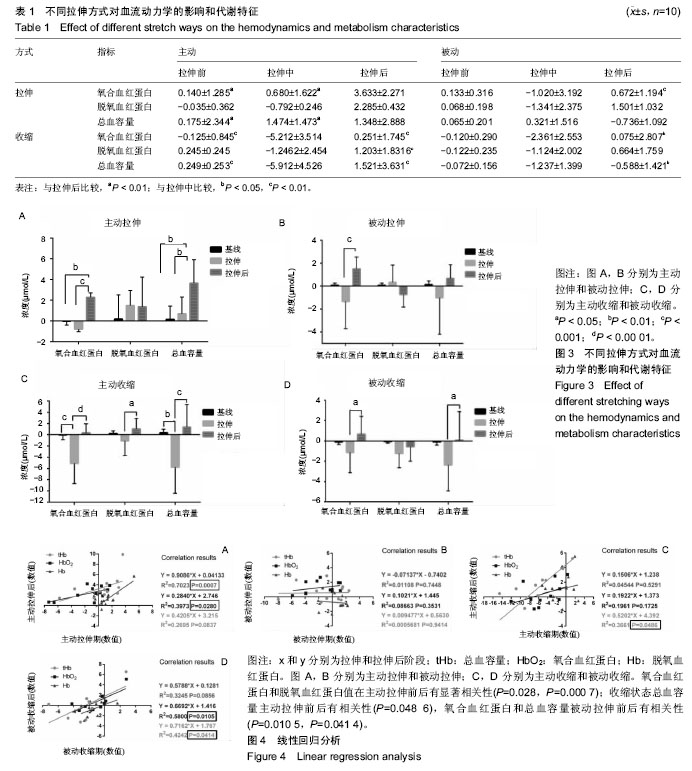
.jpg)
.jpg)