中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3019-3024.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1188
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
膝骨性关节炎模型大鼠接受推拿治疗后软骨Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88信号转导通路的变化
刘 姣1,2,3,曲崇正2,3,谢平金1,2, 4,叶大林1,2,4,罗 臻1,2,4,梁正辉1,2,5,陶 静2,3,江钢辉2,3
- (1广州中医药大学岭南医学研究中心中医骨伤科学实验室,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510405;广州中医药大学第三附属医院, 3针灸推拿科,4骨科,广东省广州市 510240;5广州中医药大学第一附属医院骨科,广东省广州市 510405)
Changes of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signal transduction in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated with massage
Liu Jiao1, 2, 3, Qu Chongzheng2, 3, Xie Pingjin1, 2, 4, Ye Dalin1, 2, 4, Luo Zhen1, 2, 4, Liang Zhenghui1, 2, 5, Tao Jing2, 3, Jiang Ganghui2, 3
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
一指禅推法:为一指禅流派治疗方法的精华,该手法是以拇指持续摆动作用于所施治的穴位处,每分钟摆动120 次左右,力量集中,接触面小,可以达到以指代针的目的,对于身体面积小的大鼠也可操作,保障了此次实验的可操作性及重复性。
木瓜蛋白酶:木瓜蛋白酶关节腔内注射制作膝骨关节炎是常用的造模方法之一,木瓜蛋白酶能够降解软骨基质的蛋白多糖,使软骨的弹性和抗压性下降,使软骨细胞被破坏,诱发炎症。木瓜蛋白酶造模周期短,操作方便简单,所需费用低,动物死亡率低,可以通过控制药物剂量来控制模型病变程度。该方法复制的膝骨关节炎模型贴近此次实验所需模型。
.jpg)
文题释义:
一指禅推法:为一指禅流派治疗方法的精华,该手法是以拇指持续摆动作用于所施治的穴位处,每分钟摆动120 次左右,力量集中,接触面小,可以达到以指代针的目的,对于身体面积小的大鼠也可操作,保障了此次实验的可操作性及重复性。
木瓜蛋白酶:木瓜蛋白酶关节腔内注射制作膝骨关节炎是常用的造模方法之一,木瓜蛋白酶能够降解软骨基质的蛋白多糖,使软骨的弹性和抗压性下降,使软骨细胞被破坏,诱发炎症。木瓜蛋白酶造模周期短,操作方便简单,所需费用低,动物死亡率低,可以通过控制药物剂量来控制模型病变程度。该方法复制的膝骨关节炎模型贴近此次实验所需模型。
摘要
背景:研究表明,Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88信号转导通路可诱导各类炎症反应,且膝骨关节炎的发生与Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88信号转导通路密切相关,而推拿可以降低白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子的表达水平,起到消炎止痛的作用,且对膝骨关节炎防治有一定的疗效。
目的:对建立的大鼠膝骨关节炎模型行推拿治疗,观察其软骨Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、核转录因子κB p65 mRNA及蛋白表达,来探讨推拿治疗膝骨关节炎的效果及其机制。
方法:采用随机化的原则,抽取10只大鼠为空白组,余下40只大鼠采用木瓜蛋白酶关节注射建立大鼠膝骨关节炎模型,待造模成功后,再将造模大鼠随机分为模型组、推拿组、塞来昔布组、推拿加塞来昔布组,每组10只。空白组、模型组常规饲养,推拿组一指禅手法治疗,塞来昔布组塞来昔布灌胃,推拿加塞来昔布组予以上2种治疗,各组均治疗4周。
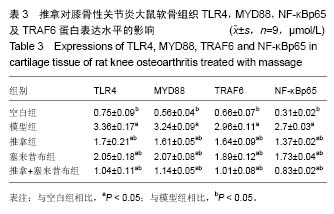
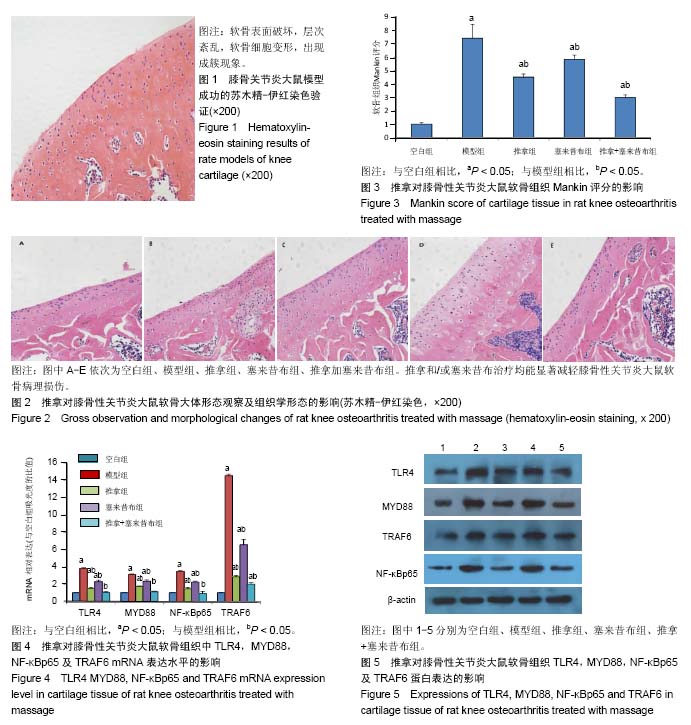
结果与结论:①与模型组相比,推拿和/或塞来昔布治疗均能显著降低大鼠软骨Mankin评分;②与模型组相比,推拿和/或塞来昔布治疗均能明显下调大鼠软骨组织中Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、核转录因子κΒp65以及肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6 mRNA与蛋白的表达水平,且推拿加塞来昔布组软骨组织中Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88以及核转录因子κΒp65 mRNA与空白组接近;③提示推拿防治膝骨关节炎的机制可能是通过下调Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、核转录因子κΒp65 mRNA和蛋白的表达,从而延缓膝骨关节炎的发展进程。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-4371-5850(曲崇正)
背景:研究表明,Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88信号转导通路可诱导各类炎症反应,且膝骨关节炎的发生与Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88信号转导通路密切相关,而推拿可以降低白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子的表达水平,起到消炎止痛的作用,且对膝骨关节炎防治有一定的疗效。
目的:对建立的大鼠膝骨关节炎模型行推拿治疗,观察其软骨Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、核转录因子κB p65 mRNA及蛋白表达,来探讨推拿治疗膝骨关节炎的效果及其机制。
方法:采用随机化的原则,抽取10只大鼠为空白组,余下40只大鼠采用木瓜蛋白酶关节注射建立大鼠膝骨关节炎模型,待造模成功后,再将造模大鼠随机分为模型组、推拿组、塞来昔布组、推拿加塞来昔布组,每组10只。空白组、模型组常规饲养,推拿组一指禅手法治疗,塞来昔布组塞来昔布灌胃,推拿加塞来昔布组予以上2种治疗,各组均治疗4周。
结果与结论:①与模型组相比,推拿和/或塞来昔布治疗均能显著降低大鼠软骨Mankin评分;②与模型组相比,推拿和/或塞来昔布治疗均能明显下调大鼠软骨组织中Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、核转录因子κΒp65以及肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6 mRNA与蛋白的表达水平,且推拿加塞来昔布组软骨组织中Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88以及核转录因子κΒp65 mRNA与空白组接近;③提示推拿防治膝骨关节炎的机制可能是通过下调Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、核转录因子κΒp65 mRNA和蛋白的表达,从而延缓膝骨关节炎的发展进程。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-4371-5850(曲崇正)
中图分类号:
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
一指禅推法:为一指禅流派治疗方法的精华,该手法是以拇指持续摆动作用于所施治的穴位处,每分钟摆动120 次左右,力量集中,接触面小,可以达到以指代针的目的,对于身体面积小的大鼠也可操作,保障了此次实验的可操作性及重复性。#br#
木瓜蛋白酶:木瓜蛋白酶关节腔内注射制作膝骨关节炎是常用的造模方法之一,木瓜蛋白酶能够降解软骨基质的蛋白多糖,使软骨的弹性和抗压性下降,使软骨细胞被破坏,诱发炎症。木瓜蛋白酶造模周期短,操作方便简单,所需费用低,动物死亡率低,可以通过控制药物剂量来控制模型病变程度。该方法复制的膝骨关节炎模型贴近此次实验所需模型。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
一指禅推法:为一指禅流派治疗方法的精华,该手法是以拇指持续摆动作用于所施治的穴位处,每分钟摆动120 次左右,力量集中,接触面小,可以达到以指代针的目的,对于身体面积小的大鼠也可操作,保障了此次实验的可操作性及重复性。#br#
木瓜蛋白酶:木瓜蛋白酶关节腔内注射制作膝骨关节炎是常用的造模方法之一,木瓜蛋白酶能够降解软骨基质的蛋白多糖,使软骨的弹性和抗压性下降,使软骨细胞被破坏,诱发炎症。木瓜蛋白酶造模周期短,操作方便简单,所需费用低,动物死亡率低,可以通过控制药物剂量来控制模型病变程度。该方法复制的膝骨关节炎模型贴近此次实验所需模型。#br#
#br#