中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3013-3018.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1248
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
基于Cre/LoxP系统建立软骨组织特异性印第安刺猬蛋白 基因敲除小鼠模型
袁 涛1,王勇卓1,黄远章1,席 刚1,魏 垒1,2,张 民1
- (1山西医科大学附属第二临床医学院,骨与软组织损伤修复山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001;2美国布朗大学医学院骨科/罗德岛州医院骨科,RI02903美国罗德岛州)
Establishment of Indian hedgehog protein conditional knockout mouse models based on Cre/LoxP system
Yuan Tao1, Wang Yongzhuo1, Huang Yuanzhang1, Xi Gang1, Wei Lei1, 2, Zhang Min1
- (1Second Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Brown University Hospital/Rhode Island Hospital, Rhode Island RI02903, USA)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。
文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。
.jpg) 文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。
文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。摘要
背景:印第安刺猬蛋白(Ihh)条件性基因敲除小鼠动物模型的建立,实现了印第安刺猬蛋白条件性基因敲除能够在时间和组织上具有选择性,能够为进一步研究与生长板有关的严重遗传病提供实验基础。
目的:基于Cre/LoxP系统建立软骨组织特异性印第安刺猬蛋白基因敲除小鼠模型,并进一步观察其表型变化差异。
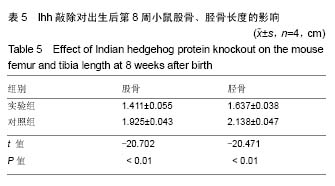
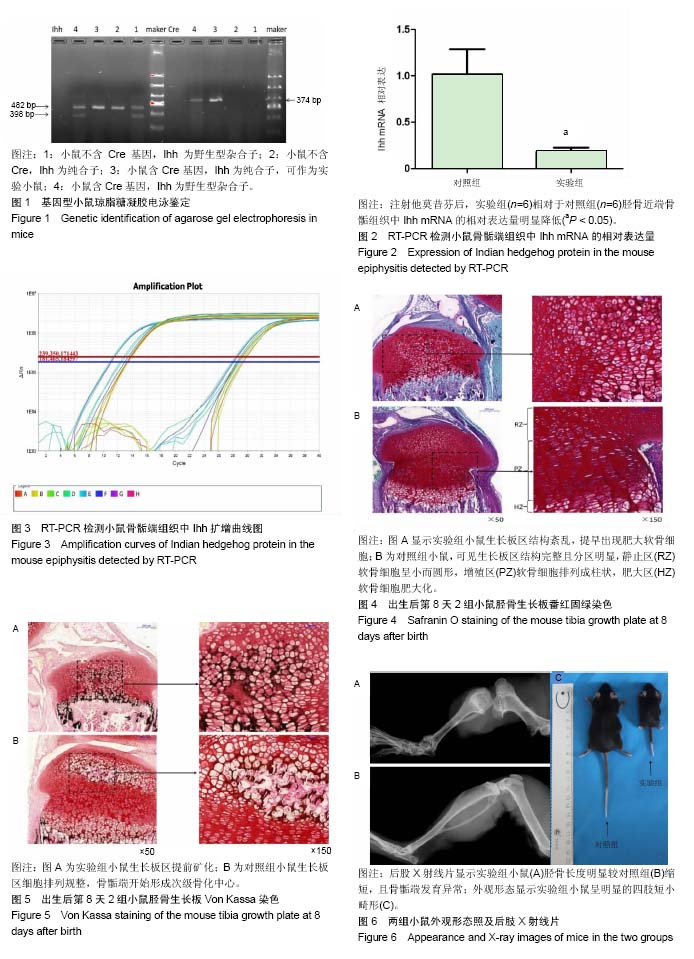
方法:SPF级亲代Ihhfl/fl小鼠与Col2a1-CreERT2小鼠,均由美国布朗大学魏垒教授赠予。将亲代Ihhfl/fl小鼠与Col2a1-CreERT2小鼠杂交,获得基因型Col2a1- CreERT2,Ihhfl/-小鼠;再将此基因型小鼠自交,获得刚出生的小鼠。通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳对刚出生小鼠进行基因鉴定,随机分为2组:实验组小鼠于出生后第1天开始腹腔注射玉米油溶解的20 g/L 他莫昔芬10 μL,连续注射3 d;对照组小鼠腹腔注射等量玉米油。出生后第6天RT-qPCR检测印第安刺猬蛋白基因的敲除率;第8天小鼠膝关节行番红固绿染色、Von Kassa染色进行初步表型观察;第8周行小鼠大体形态观察、记录后肢股骨/胫骨长度,后肢X射线片观察。
结果与结论:①通过RT-qPCR证实了印第安刺猬蛋白条件性基因敲除率为76.83%,8周龄小鼠大体形态表现为肢体短小畸形(P < 0.01);②X射线显示敲除小鼠胫骨明显缩短且骨骺端发育异常;③番红固绿染色显示印第安刺猬蛋白条件性敲除表达在发育中的小鼠胫骨生长板软骨组织这一特定区域;④Von Kassa染色显示Ihhd/d小鼠生长板过早闭合;⑤初步建立了印第安刺猬蛋白条件性基因敲除小鼠模型,印第安刺猬蛋白条件性基因敲除后引起小鼠生长板区软骨细胞增殖紊乱,生长板区软骨细胞提前矿化,生长板过早骨化闭合,小鼠表现为肢体短小畸形。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4599-4091(袁涛)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。
文题释义:
印第安刺猬蛋白(Indian hedgehog,Ihh)基因:是刺猬蛋白(Hedgehog,Hh)家族中的一员,其主要在软骨细胞中表达,并在软骨细胞增殖和分化的过程中起着重要的调控作用。
基因敲除(knockout):是指一种遗传工程技术,针对某个序列已知但功能未知的序列,改变生物的遗传基因,令特定的基因功能丧失作用,从而使部分功能被屏障,并可进一步对生物体造成影响,进而推测出该基因的生物学功能。