| [1] Lundborg G. A 25-year perspective of peripheral nerve surgery: evolving neuroscientific concepts and clinical significance. J Hand Surg Am. 2000; 25(3):391-414.[2] Zujovic V, Bachelin C, Baron-Van Evercooren A. Remyelination of the central nervous system: a valuable contribution from the periphery. Neuroscientist. 2007;13(4):383-391.[3] Gerth DJ, Tashiro J, Thaller SR. Clinical outcomes for Conduits and Scaffolds in peripheral nerve repair. World J Clin Cases. 2015;3(2): 141-147.[4] Pabari A, Lloyd-Hughes H, Seifalian AM, et al. Nerve conduits for peripheral nerve surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(6):1420-1430.[5] Kehoe S, Zhang XF, Boyd D. FDA approved guidance conduits and wraps for peripheral nerve injury: a review of materials and efficacy. Injury. 2012;43(5):553-572. [6] Wislet-Gendebien S, Laudet E, Neirinckx V, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and neural crest stem cells from adult bone marrow: characterization of their surprising similarities and differences. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(15):2593-2608. [7] Croft AP, Przyborski SA. Generation of neuroprogenitor-like cells from adult mammalian bone marrow stromal cells in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2004;13(4):409-420.[8] Lopez-Verrilli MA, Caviedes A, Cabrera A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes from different sources selectively promote neuritic outgrowth. Neuroscience. 2016;320:129-139. [9] Woodhoo A, Alonso MB, Droggiti A, et al. Notch controls embryonic Schwann cell differentiation, postnatal myelination and adult plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12(7):839-847. [10] Yanjie J, Jiping S, Yan Z, et al. Effects of Notch-1 signalling pathway on differentiation of marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons in vitro. Neuroreport. 2007;18(14):1443-1447.[11] Zou D, Chen Y, Han Y, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-124 promotes the neuronal differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(12):1241-1248.[12] Zhao Y, Jiang H, Liu XW, et al. MiR-124 promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into neurogenic cells for accelerating recovery in the spinal cord injury. Tissue Cell. 2015;47(2): 140-146.[13] Zhang P, Xue F, Kou Y, et al. The experimental study of absorbable chitin conduit for bridging peripheral nerve defect with nerve fasciculu in rats. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2008;36(4):360-371. [14] Yu K, Zhang C, Wang Y, et al. The protective effects of small gap sleeve in bridging peripheral nerve mutilation. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2009;37(6):257-264.[15] Wang J, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. The observation of phenotypic changes of Schwann cells after rat sciatic nerve injury. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2010;38(1):24-28.[16] Wang J, Ren KY, Wang YH, et al. Effect of active Notch signaling system on the early repair of rat sciatic nerve injury. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2015;43(6):383-389. [17] Yang T, Liu LY, Ma YY, et al. Notch signaling-mediated neural lineage selection facilitates intrastriatal transplantation therapy for ischemic stroke by promoting endogenous regeneration in the hippocampus. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(2):221-238. [18] Chuang JH, Tung LC, Lin Y. Neural differentiation from embryonic stem cells in vitro: An overview of the signaling pathways. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(2):437-447. [19] Xing Y, Chen X, Cao Y, et al. Expression of Wnt and Notch signaling pathways in inflammatory bowel disease treated with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation: evaluation in a rat model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6:101. [20] Xu H, Miki K, Ishibashi S, et al. Transplantation of neuronal cells induced from human mesenchymal stem cells improves neurological functions after stroke without cell fusion. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(16):3598-3609.[21] Osathanon T, Manokawinchoke J, Nowwarote N, et al. Notch signaling is involved in neurogenic commitment of human periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(8): 1220-1231.[22] Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, et al. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20(5): 515-524.[23] Guo Q, Chen Y, Guo L, et al. miR-23a/b regulates the balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Res. 2016;4:16022. [24] Foshay KM, Gallicano GI. Small RNAs, big potential: the role of MicroRNAs in stem cell function. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2007;2(4): 264-271.[25] Pandey A, Singh P, Jauhari A, et al. Critical role of the miR-200 family in regulating differentiation and proliferation of neurons. J Neurochem. 2015;133(5):640-652. [26] Ge XT, Lei P, Wang HC, et al. miR-21 improves the neurological outcome after traumatic brain injury in rats. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6718. [27] Zhao Y, Jiang H, Liu XW, et al. MiR-124 promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into neurogenic cells for accelerating recovery in the spinal cord injury. Tissue Cell. 2015;47(2): 140-146. [28] Zhou S, Zhang S, Wang Y, et al. MiR-21 and miR-222 inhibit apoptosis of adult dorsal root ganglion neurons by repressing TIMP3 following sciatic nerve injury. Neurosci Lett. 2015;586:43-49. [29] Junker F, Chabloz A, Koch U, et al. Dicer1 imparts essential survival cues in Notch-driven T-ALL via miR-21-mediated tumor suppressor Pdcd4 repression. Blood. 2015;126(8):993-1004.[30] Xiong Y, Zhang YY, Wu YY, et al. Correlation of over-expressions of miR-21 and Notch-1 in human colorectal cancer with clinical stages. Life Sci. 2014;106(1-2):19-24. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。
文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。.jpg) 文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。
文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。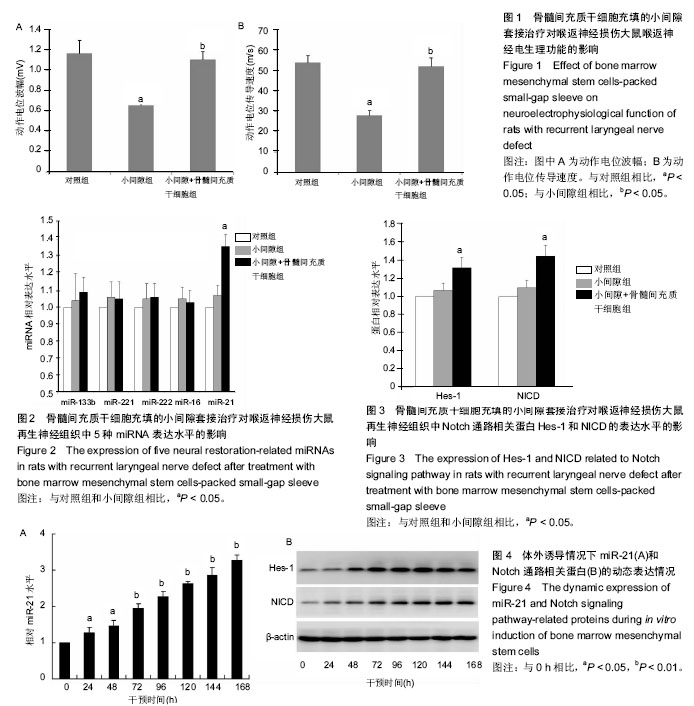
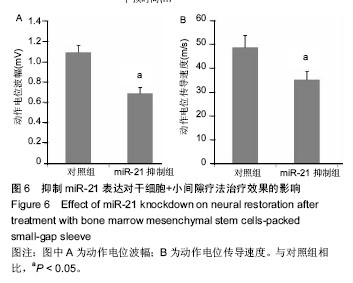
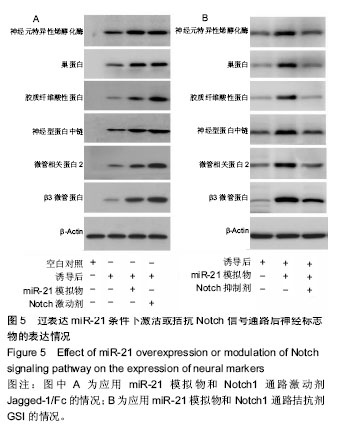
.jpg) 文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。
文题释义:
Notch信号通路:Notch是一类跨细胞膜受体蛋白,当其与受体结合并水解时,产生称为Notch胞内域的结构,作为转录因子调节目标基因表达。Notch信号通路与周围神经修复过程中的作用已经受到广泛关注。同时,Notch信号通路也被报道在维持干细胞特性以及介导数种干细胞向特定细胞系分化过程中均发挥重要作用。
微小RNA:是一类小分子的非编码单链RNA,其长度20-25个核苷酸。这些小RNA能够与特定的mRNA结合,调控或阻断蛋白编码基因的表达,控制其最终成为蛋白的过程。近年来,学者们发现其在骨髓间充质干细胞的多样化表达进程中具有重要调控作用,这种作用既可体现在转录水平上,又在转录后调控中得到显现,其中主要在转录后水平负性调控靶基因的表达。