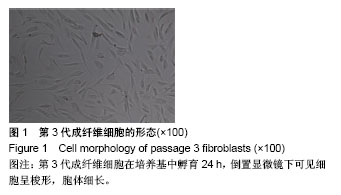
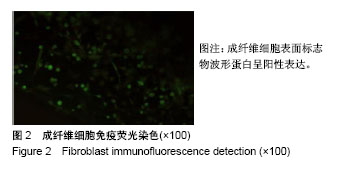
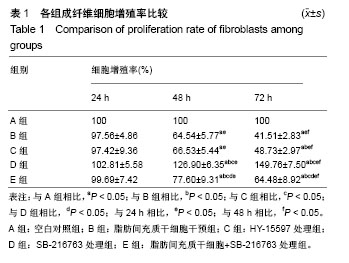
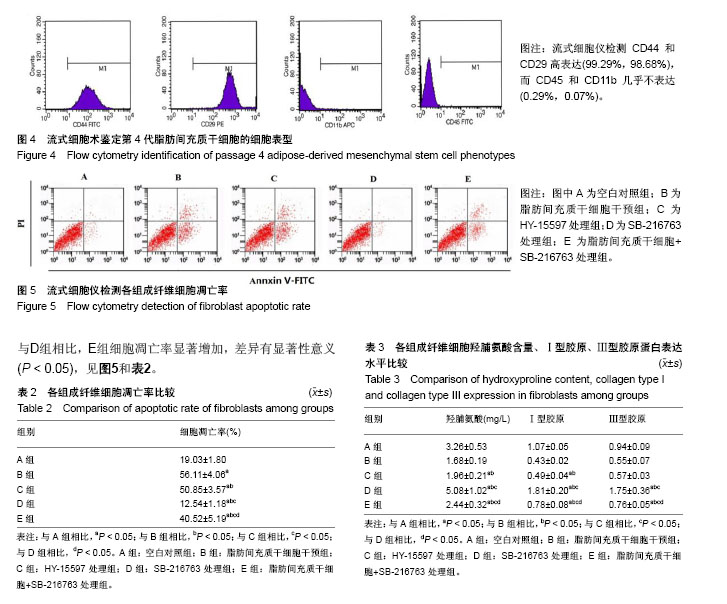
| [1] 杨书琦,张慧芳,宋书林,等.系统性硬化症发病机制的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018,24(1):17-21.[2] Garret SM, Frost DB, Feghali-Bostwick C. The mighty fibroblast and its utility in scleroderma research. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2017;2(2):69-134. [3] 李晶冰,丁敏,牟萍,等.积雪草甙对系统性硬皮病成纤维细胞增殖、胶原蛋白合成及分泌TGF-β1的影响[J].江苏医药, 2014, 40(20):2387-2389.[4] 窦晶莉,白力,庞春艳,等.脂肪间充质干细胞对博来霉素诱导的硬皮病小鼠模型的治疗作用[J].北京大学学报(医学版), 2016,48(6): 970-976.[5] 卞媛媛,梁久龙,韩悦,等.兔自体脂肪来源干细胞对增生性瘢痕的作用研究[J].实用皮肤病学杂志,2013,6(1):3-6.[6] Marangoni RG, Varga J, Tourtellotte WG. Animal models of scleroderma: recent progress. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016; 28(6):561-570. [7] 王永祥,王春燕.脂多糖对皮肤成纤维细胞增殖的影响与机制[J].南昌大学学报(医学版),2017,57(3):24-26.[8] 喇文军,林孝发,蒋伟,等.不同培养基对皮肤来源的成纤维细胞增殖、衰老及胶原蛋白分泌的影响[J].中国美容医学杂志, 2017, 26(2):68-72.[9] Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(9):582-598. [10] Sun YB, Qu X, Caruana G, et al. The origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that trigger fibrosis. Differentiation. 2016;92(3):102-107. [11] 武艳,张春雷,刘阳,等.骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养液对瘢痕成纤维细胞生物活性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(7): 1009-1014.[12] 武艳.基于骨髓间充质干细胞对微环境的调控作用影响皮肤瘢痕形成的实验研究[D].天津:南开大学,2013.[13] Baig MT, Ali G, Awan SJ, et al. Serum from CCl4-induced acute rat injury model induces differentiation of ADSCs towards hepatic cells and reduces liver fibrosis. Growth Factors. 2017;35(4-5):144-160. [14] Meza-Ríos A, García-Benavides L, García-Bañuelos J, et al. Simultaneous Administration of ADSCs-Based Therapy and Gene Therapy Using Ad-huPA Reduces Experimental Liver Fibrosis. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0166849. [15] De Luca C, Mikhal'chik EV, Suprun MV, et al. Skin Antiageing and Systemic Redox Effects of Supplementation with Marine Collagen Peptides and Plant-Derived Antioxidants: A Single-Blind Case-Control Clinical Study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4389410. [16] Li P, Wu G. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids. 2018; 50(1):29-38. [17] Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999. [18] 施剑明,邬亚华,耿书国,等.间充质干细胞增殖、衰老及分化:Wnt信号通路经典与非经典的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(41):6719-6724.[19] Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal, tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 2016;3(1):11-40. [20] Silva AK, Yi H, Hayes SH, et al. Lithium chloride regulates the proliferation of stem-like cells in retinoblastoma cell lines: a potential role for the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Vis. 2010;16:36-45. [21] Katoh M, Katoh M. WNT signaling pathway and stem cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(14):4042-4045. [22] Wei J, Melichian D, Komura K, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling induces skin fibrosis and subcutaneous lipoatrophy: a novel mouse model for scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(6): 1707-1717. [23] 刘金娟,刘彤.Wnt2、Wnt3a和β-catenin在SSc患者皮损中的作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2012,32(12):1781-1786.[24] Duran F, Yildirim A, Yolbas S, et al. AB0215 Paricalcitol Inhibits WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Dermal Fibrosis Bleomycin Induced Scleroderma Model: Figure 1. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015;74(Suppl 2):963. 1-963. [25] Wei J, Fang F, Lam AP, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is hyperactivated in systemic sclerosis and induces Smad-dependent fibrotic responses in mesenchymal cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2734-2745. [26] Beyer C, Schramm A, Akhmetshina A, et al. β-catenin is a central mediator of pro-fibrotic Wnt signaling in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(5):761-767. [27] Dees C, Distler JH. Canonical Wnt signalling as a key regulator of fibrogenesis - implications for targeted therapies. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22(11):710-713. [28] Li J, Dai Y, Zhu H, et al. Endometriotic mesenchymal stem cells significantly promote fibrogenesis in ovarian endometrioma through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by paracrine production of TGF-β1 and Wnt1. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(6):1224-1235. [29] Ni W, Fang Y, Xie L, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation Alleviates Renal Injury in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015;63(11):842-853. [30] 李志,张梦莹,李雪琴,等.Wnt/β-catenin通路参与脂肪间充质干细胞对大鼠肾小球系膜细胞增殖的调控[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2016,32(11):1486-1490. |
.jpg)


.jpg)