| [1] Okano H, Sawamoto K. Neural stem cells: involvement in adult neurogenesis and CNS repair. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008;363(1500):2111-2122.[2] Bond AM, Ming GL, Song H. Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis: Five Decades Later. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(4):385-395.[3] Hong JY, Lee SH, Lee SC, et al. Therapeutic potential of induced neural stem cells for spinal cord injury. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(47):32512-32525.[4] Göritz C, Frisén J. Neural stem cells and neurogenesis in the adult. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):657-659.[5] Yoneyama T, Arai MA, Akamine R, et al. Notch Inhibitors from Calotropis gigantea That Induce Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells. J Nat Prod. 2017;80(9):2453-2461.[6] Zhang X, He X, Li Q, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Mediates Valproic Acid-Induced Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells through Epigenetic Modifications. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8(5):1256-1269.[7] Faigle R, Song H. Signaling mechanisms regulating adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(2):2435-2448.[8] 索磊,杨印祥,汤文燕,等. Lingo-1在中枢神经系统损伤疾病中的应用[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2016, 15(4): 421-424.[9] Okafuji T, Tanaka H. Expression pattern of LINGO-1 in the developing nervous system of the chick embryo. Gene Expr Patterns. 2005;6(1):57-62.[10] 马英,陆莹. Lingo-1研究进展及其对神经系统疾病的相关影响[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2016,23(4):287-292.[11] Yin W, Hu B. Knockdown of Lingo1b protein promotes myelination and oligodendrocyte differentiation in zebrafish. Exp Neurol. 2014;251:72-83.[12] Lööv C, Fernqvist M, Walmsley A, et al. Neutralization of LINGO-1 during in vitro differentiation of neural stem cells results in proliferation of immature neurons. PLoS One. 2012; 7(1):e29771.[13] Connor B. Concise Review: The Use of Stem Cells for Understanding and Treating Huntington's Disease. Stem Cells. 2018;36(2):146-160.[14] Reis C, Wilkinson M, Reis H, et al. A Look into Stem Cell Therapy: Exploring the Options for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3267352.[15] Xiong Z, Zhao S, Mao X, et al. Selective neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells induced by nanosecond microplasma agitation. Stem Cell Res. 2014;12(2):387-399.[16] Hou S, Lu P. Direct reprogramming of somatic cells into neural stem cells or neurons for neurological disorders. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(1):28-31.[17] Shao Z, Lee X, Huang G, et al. LINGO-1 Regulates Oligodendrocyte Differentiation through the Cytoplasmic Gelsolin Signaling Pathway. J Neurosci. 2017;37(12): 3127-3137.[18] Gresle MM, Liu Y, Kilpatrick TJ, et al. Blocking LINGO-1 in vivo reduces degeneration and enhances regeneration of the optic nerve. Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2016;2: 2055217316641704.[19] Sun JJ, Ren QG, Xu L, et al. LINGO-1 antibody ameliorates myelin impairment and spatial memory deficits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14235.[20] Wang J, Ye Z, Zheng S, et al. Lingo-1 shRNA and Notch signaling inhibitor DAPT promote differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells into neurons. Brain Res. 2016;1634: 34-44.[21] Mi S, Miller RH, Lee X, et al. LINGO-1 negatively regulates myelination by oligodendrocytes. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(6): 745-751.[22] 韩佳寅,易艳,梁爱华,等. Rho/ROCK信号通路研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2016,51(6): 853-859.[23] Wu X, Walker CL, Lu Q, et al. RhoA/Rho Kinase Mediates Neuronal Death Through Regulating cPLA2 Activation. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(9):6885-6895.[24] 辛延乐,李艳花,张辉,等. Rho激酶抑制剂:治疗神经系统变性疾病的潜在药物[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2015,22(4): 288-290.[25] Ding J, Li QY, Wang X, et al. Fasudil protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by suppressing microglial inflammatory responses in mice. J Neurochem. 2010;114(6):1619-1629.[26] Liu C, Li Y, Yu J, et al. Targeting the shift from M1 to M2 macrophages in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice treated with fasudil. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e54841.[27] Hou SW, Liu CY, Li YH, et al. Fasudil ameliorates disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, acting possibly through antiinflammatory effect. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(11):909-917.[28] Chen N, Cen JS, Wang J, et al. Targeted Inhibition of Leucine-Rich Repeat and Immunoglobulin Domain-Containing Protein 1 in Transplanted Neural Stem Cells Promotes Neuronal Differentiation and Functional Recovery in Rats Subjected to Spinal Cord Injury. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(3):e146-157.[29] Andrews JL, Fernandez-Enright F. A decade from discovery to therapy: Lingo-1, the dark horse in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015;56: 97-114.[30] Zhang Y, Zhang YP, Pepinsky B, et al. Inhibition of LINGO-1 promotes functional recovery after experimental spinal cord demyelination. Exp Neurol. 2015;266:68-73. |
.jpg)
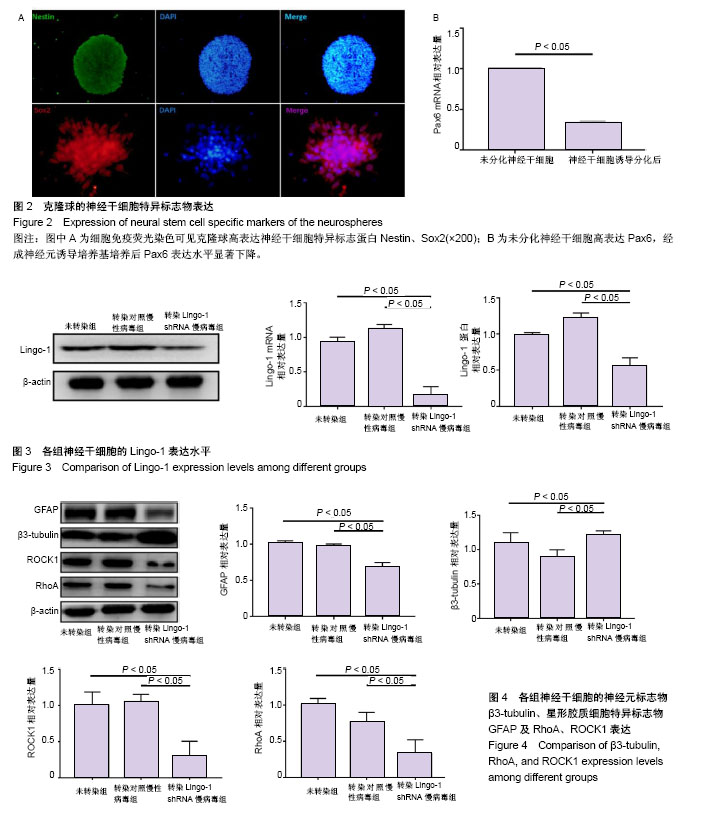
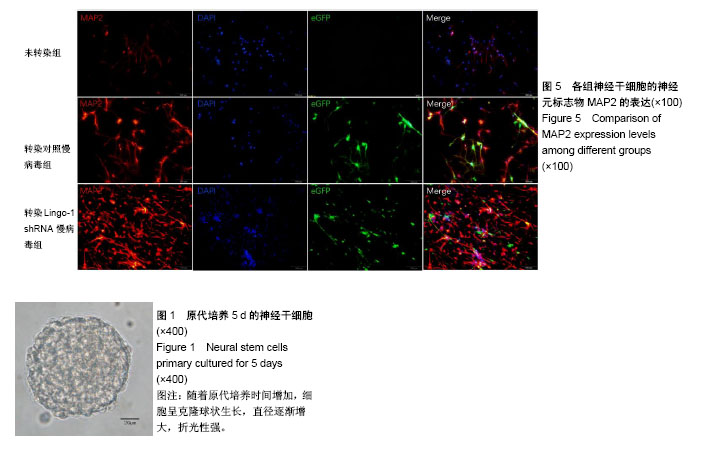
.jpg)