中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 361-366.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0593
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
吊环十字支撑类动作对人体背阔肌、斜方肌、肱三头肌、大圆肌和三角肌参与程度和控制能力及主要肌群贡献率分析
兰庆士
- (郑州科技学院,河南省郑州市 450064)
Participation degree and control ability of human latissimus dorsi, trapezius, triceps, musculus and deltoid during cross support of hand ring: analysis on contribution rate of major muscle group
Lan Qingshi
- (Zhengzhou University of Science and Technology, Zhengzhou 450064, Henan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。
文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。
.jpg) 文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。
文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。摘要
背景:当前研究缺乏大样本优秀与一般吊环运动员十字支撑类难度动作的运动学和表面肌电的比较。
目的:探讨优秀吊环运动员十字支撑类动作时间、角度及主要肌群表面肌电(sEMG)特点,比较优秀与一般运动员间差异。
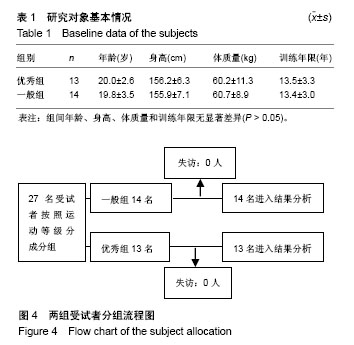
方法:2台高速摄像机和MegawinT8表面肌电分析仪同步采集了优秀组(n=13,为优秀和一级运动员)和一般组(n=14,为二级运动员)正十字、倒十字和水平十字支撑的运动学(时间和角度)和表面肌电(采集斜方肌、背阔肌、大圆肌、三角肌、肱三头肌、胸大肌、前锯肌和肱二头肌)数据。
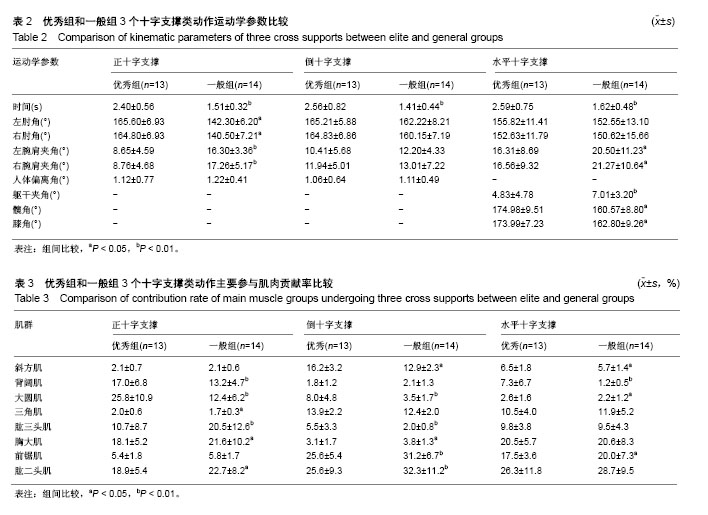
结果与结论:①相比一级组,优秀组正十字支撑的动作时间增大58.9%(P < 0.01),左、右肘角分别增大16.4%和17.3%(P < 0.05),左、右腕肩连线与水平面夹角分别减小46.9%和49.2%(P < 0.01)。背阔肌、大圆肌和三角肌贡献率分别增加28.8%、108.1%(P < 0.01)和5.8%(P < 0.05),肱三头肌、胸大肌和肱二头肌贡献率分别减小47.8%(P < 0.01)、16.2%和16.7%(P < 0.05);②相比一级组,倒十字支撑的动作时间增大81.6%(P < 0.01)。斜方肌、大圆肌和肱三头肌贡献率分别增大25.6%、128.6%和175.0%(P < 0.01),前锯肌和肱二头肌贡献率分别减小17.9%和20.7%(P < 0.01);③水平十字支撑的动作时间、髋角和膝角分别增大59.9%(P < 0.01)、9.0%和6.9%(P < 0.05),左右腕肩夹角、躯干夹角分别减小20.4%、22.1%和31.1%(P < 0.01)。斜方肌、背阔肌、大圆肌贡献率分别增大14.0%(P < 0.05)、508.3%和18.2%(P < 0.01),前锯肌贡献率减小12.5%(P < 0.05);④结果提示,加强十字支撑类动作时间控制和身体姿势角度到位的意识,强化背阔肌、斜方肌、肱三头肌、大圆肌和三角肌参与程度和控制能力,有利于更好完成吊环十字支撑类动作。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5456-9679(兰庆士)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。
文题释义:
人体偏离角:眉心与两足尖中点连线和垂线的夹角。用来衡量直角、倒十字支撑动作运动员身体是否与水平面垂直。
肌肉贡献率:由积分肌电计算单块肌肉积分肌电值与所有测试8块肌肉总积分肌电的百分比。