中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (15): 2405-2409.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2570
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
髋臼骨折固定中3D打印技术辅助虚拟手术计划的疗效评价
张忠岩1,祁同宁2,穆怀昭1,王 瑜1,金 宇1
- 1承德医学院附属医院创伤骨科,河北省承德市 067000;2承德市医院骨伤科,河北省承德市 067000
Efficacy of 3D printing technology-assisted virtual surgical planning in acetabular fracture fixation
Zhang Zhongyan1, Qi Tongning2, Mu Huaizhao1, Wang Yu1, Jin Yu1
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Chengde Municipal Hospital, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
3D打印技术:即快速成型技术的一种,它是一种以数字模型文件为基础,运用粉末状金属或塑料等可黏合材料通过逐层打印方式来构造物体的技术。
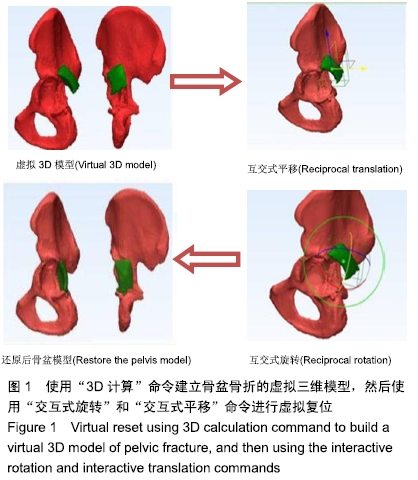
虚拟手术计划:虚拟手术仿真系统是虚拟现实技术在医学领域的一个典型应用。虚拟手术是由医学图像数据出发,应用计算机图形学重构出虚拟人体软组织模型,模拟出虚拟的医学环境,并利用触觉交互设备与之进行交互的手术系统。虚拟手术系统为医生提供一个虚拟的3D环境及可交互操作平台,逼真地模拟临床手术全过程。与传统的手术教学相比,虚拟手术具有无损伤性、可重复性和可指定性等优点。
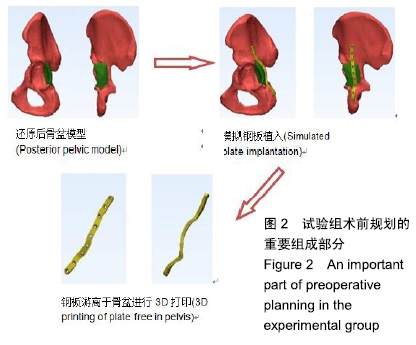
背景:髋臼骨折因其复杂的解剖结构导致治疗难度加大,目前临床上仍以切开复位和内固定作为髋臼移位骨折的标准治疗方法。利用3D打印技术配合术前虚拟手术计划制作的患者专用预轮廓重建模板,可减少手术的侵袭性、简化手术流程。
目的:评价3D打印技术辅以虚拟手术计划与传统髋臼骨折复位重建治疗髋臼骨折的效果差异。
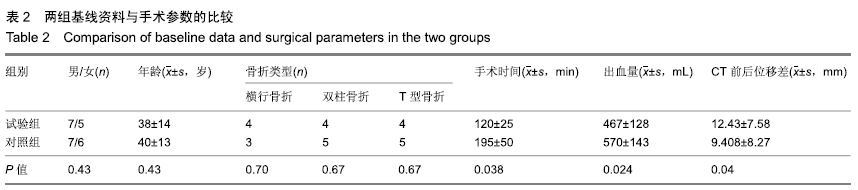
方法:选择2017-10-01/2018-03-01承德医学院附属医院收治的25例髋臼骨折患者,其中男14例,女11例,年龄21-60岁。采用计算机随机分为试验组(n=12)和对照组(n=13),试验组采用3D打印技术辅助虚拟手术计划预轮廓重建钢板内固定,对照组采用骨折复位后术中手工轮廓重建钢板内固定。术后X射线、非对比计算机断层扫描分析两组骨折复位情况;术后随访两组患者目测类比评分与Majeed功能评分及并发症发生情况。研究通过承德医学院附属医院伦理委员会伦理审查(批准号:LL007)。
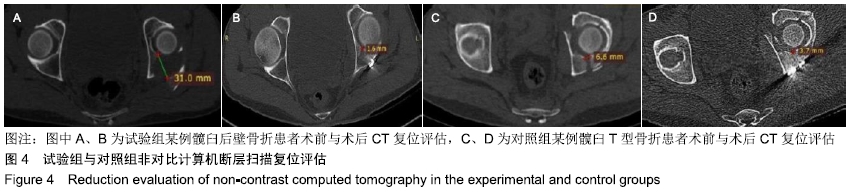
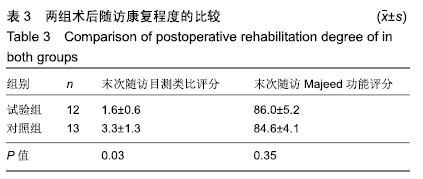
结果与结论:①X射线片显示试验组复位效果优于对照组(P=0.038);非对比计算机断层扫描显示,试验组手术前后复位位移差优于对照组[(12.43±7.58)mm,(9.408±8.27)mm,P < 0.05];②术后随访6-12个月,试验组末次随访时的目测类比评分低于对照组[(1.6±0.6),(3.3±1.3)分,P < 0.05],两组末次随访时的Majeed功能评分比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.079);③两组术后均未出现伤口迁延不愈、内固定失效或深静脉血栓等手术相关并发症,均未发生与植入器械相关的生物相容性不良反应;④结果表明,3D打印技术辅助虚拟手术计划在髋臼骨折固定中可提高复位质量,提高髋臼骨折手术效果,减少患者术后痛苦。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9039-8435(张忠岩)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: