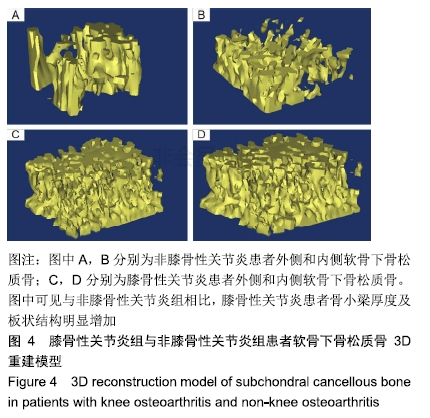
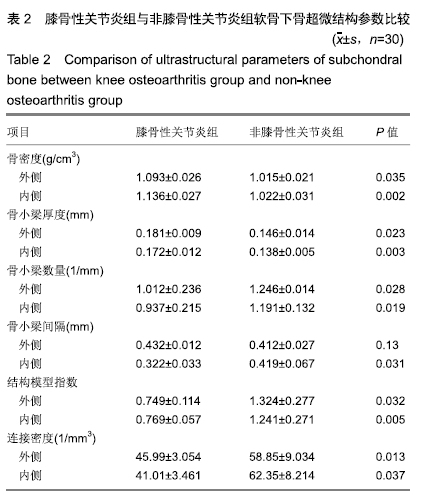
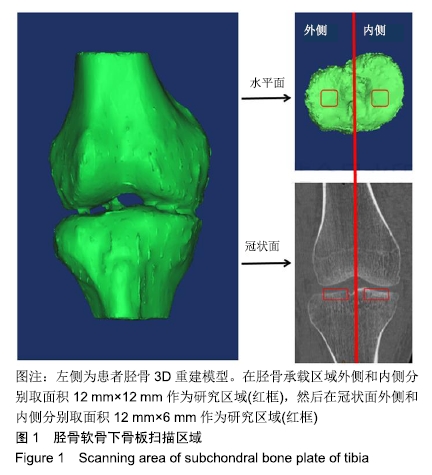
[1] ABRAMSON SB, ATTUR M. Developments in the scientific understanding of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(3):227.
[2] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[3] RADIN EL, PAUL IL, ROSE RM. Role of mechanical factors in pathogenesis of primary osteoarthritis. Lancet. 1972;1(7749): 519-522.
[4] CLOUET J, VINATIER C, MERCERON C, et al. From osteoarthritis treatments to future regenerative therapies for cartilage. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14(19-20):913-925.
[5] FELSON DT, NEOGI T. Osteoarthritis: is it a disease of cartilage or of bone? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):341-344.
[6] MANSELL JP, COLLINS C, BAILEY AJ. Bone, not cartilage, should be the major focus in osteoarthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3(6):306-307.
[7] FINDLAY DM, KULIWABA JS. Bone-cartilage crosstalk: a conversation for understanding osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2016;4:16028.
[8] OMOUMI P, BABEL H, JOLLES BM, et al. Relationships between cartilage thickness and subchondral bone mineral density in non-osteoarthritic and severely osteoarthritic knees: In vivo concomitant 3D analysis using CT arthrography. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(4):621-629.
[9] BOUSSON V, LOWITZ T, LAOUISSET L, et al. CT imaging for the investigation of subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23 Suppl 8:S861-S865.
[10] OMOUMI P, BABEL H, JOLLES BM, et al. Quantitative regional and sub-regional analysis of femoral and tibial subchondral bone mineral density (sBMD) using computed tomography (CT): comparison of non-osteoarthritic (OA) and severe OA knees. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(11): 1850-1857.
[11] KELLGREN JH, LAWRENCE JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-502.
[12] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.骨关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(6):416-419.
[13] GBD 2016 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211-1259.
[14] ANDERSON-MACKENZIE JM, QUASNICHKA HL, STARR RL, et al. Fundamental subchondral bone changes in spontaneous knee osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(1):224-236.
[15] BETTICA P, CLINE G, HART DJ, et al. Evidence for increased bone resorption in patients with progressive knee osteoarthritis: longitudinal results from the Chingford study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(12):3178-3184.
[16] MACNEIL JA, BOYD SK. Bone strength at the distal radius can be estimated from high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and the finite element method. Bone. 2008;42(6):1203-1213.
[17] BAY-JENSEN AC, HOEGH-MADSEN S, DAM E, et al. Which elements are involved in reversible and irreversible cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis? Rheumatol Int. 2010;30(4): 435-442.
[18] KARSDAL MA, BAY-JENSEN AC, LORIES RJ, et al. The coupling of bone and cartilage turnover in osteoarthritis: opportunities for bone antiresorptives and anabolics as potential treatments? Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(2):336-348.
[19] EDD SN, OMOUMI P, ANDRIACCHI TP, et al. Modeling knee osteoarthritis pathophysiology using an integrated joint system (IJS): a systematic review of relationships among cartilage thickness, gait mechanics, and subchondral bone mineral density. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(11): 1425-1437.
[20] NAKAMURA T, MIZUNO S. The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(6):588-610.
[21] DING M, ODGAARD A, DANIELSEN CC, et al. Mutual associations among microstructural, physical and mechanical properties of human cancellous bone. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(6):900-907.
[22] GOULET RW, GOLDSTEIN SA, CIARELLI MJ, et al. The relationship between the structural and orthogonal compressive properties of trabecular bone. J Biomech. 1994;27(4):375-389.
[23] PATEL V, ISSEVER AS, BURGHARDT A, et al. MicroCT evaluation of normal and osteoarthritic bone structure in human knee specimens. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(1):6-13.
[24] MURRAY RC, VEDI S, BIRCH HL, et al. Subchondral bone thickness, hardness and remodelling are influenced by short-term exercise in a site-specific manner. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(6):1035-1042.
[25] WANG T, WEN CY, YAN CH, et al. Spatial and temporal changes of subchondral bone proceed to microscopic articular cartilage degeneration in guinea pigs with spontaneous osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21(4):574-581.
[26] BETANCOURT MC, LINDEN JC, RIVADENEIRA F, et al. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry analysis contributes to the prediction of hip osteoarthritis progression. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(6):R162.
[27] BURR DB, SCHAFFLER MB. The involvement of subchondral mineralized tissues in osteoarthrosis: quantitative microscopic evidence. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;37(4):343-357.
[28] SNIEKERS YH, WEINANS H, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Oestrogen is important for maintenance of cartilage and subchondral bone in a murine model of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R182.
[29] BETTICA P, CLINE G, HART DJ, et al. Evidence for increased bone resorption in patients with progressive knee osteoarthritis: longitudinal results from the Chingford study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(12):3178-3184.
[30] HERRERO-BEAUMONT G, ROMAN-BLAS JA, LARGO R, et al. Bone mineral density and joint cartilage: four clinical settings of a complex relationship in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(9):1523-1525.
[31] LEONG DJ, GU XI, LI Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in articular cartilage is upregulated by joint immobilization and suppressed by passive joint motion. Matrix Biol. 2010;29(5): 420-426.
|