| [1] 夏穗生.肝移植进展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2005,12(2):97-99.[2] 黄勋,邓子德,倪语星,等.多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识[J].中国感染控制杂志,2015,14(1):1-9.[3] 中华人民共和国卫生部.多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制技术指南(试行)[J].中国危重病急救医学, 2011,23(2):65.[4] Shukla A,Vadeyar H,Rela M,et al. Liver Transplantation: East versus West.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2013,3(3):243-253.[5] Wang FS,Fan JG,Zhang Z,et al.The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology. 2014;60(6):2099-2108.[6] Li C,Wen TF,Mi K,et al.Analysis of infections in the first 3-month after living donor liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(16):1975-1980.[7] Linares L,Garcia-Goez JF,Cervera C,et al.Early bacteremia after solid organ transplantation.Transplant Proc.2009;41(6): 2262-2264.[8] Kim SI.Bacterial infection after liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(20):6211-6220.[9] Santoro-Lopes G,de Gouvea EF.Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections after liver transplantation: an ever-growing challenge.World J Gastroenterol.2014,20(20):6201-6210.[10] 李明霞,彭贵主,王忍,等.肝移植术后感染研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2015,21(7):494-497.[11] 杨富,陈兰,方芳,等.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染危险因素的系统评价[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2015,35(7):1015-1022.[12] [Magiorakos AP,Srinivasan A,Carey RB, et al.Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance.Clin Microbiol Infect.2012;18(3):268-281.[13] Shields RK,Clancy CJ,Gillis LM,et al.Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and outcomes of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections among solid organ transplant recipients.PLoS One.2012;7(12):e52349.[14] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 医院感染诊断标准(试行)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2001,81(5):314-320.[15] 陈佰义,何礼贤,胡必杰,等.中国鲍曼不动杆菌感染诊治与防控专家共识[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(8):3-8.[16] Kim SI,Kim YJ,Jun YH,et al.Epidemiology and risk factors for bacteremia in 144 consecutive living-donor liver transplant recipients.Yonsei Med J.2009;50(1):112-121.[17] Friedrich-Rust M, Wanger B, Heupel F, et al. Influence of antibiotic- regimens on intensive-care unit-mortality and liver-cirrhosis as risk factor.World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(16):4201-4210.[18] 谢秀华,孔心涓,饶伟.肝移植术后感染并发症的研究现状及进展[J].实用器官移植电子杂志, 2017,5(1):61-64.[19] Netsvyetayeva I,Sikora M,Golas M,et al.Acinetobacter baumannii multidrug-resistant strain occurrence in liver recipients with reference to other high-risk groups.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(8): 3116-3120.[20] Hand J,Patel G.Multidrug-resistant organisms in liver transplant: Mitigating risk and managing infections.Liver Transpl.2016;22(8): 1143-1153.[21] Reddy P,Zembower TR,Ison MG,et al.Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections after organ transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis.2010;12(1):87-93.[22] Sun HY, Cacciarelli TV, Singh N. Impact of pretransplant infections on clinical outcomes of liver transplant recipients.Liver Transpl.2010;16(2):222-228.[23] Bellier C,Bert F,Durand F,et al.Risk factors for Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia after liver transplantation.Transpl Int.2008;21(8): 755-763.[24] Siniscalchi A,Aurini L,Benini B,et al.Ventilator associated pneumonia following liver transplantation: Etiology, risk factors and outcome.World J Transplant.2016;6(2):389-395.[25] Lim S, Kim E J, Lee T B, et al. Predictors of postoperative infectious complications in liver transplant recipients: experience of 185 consecutive cases. Korean J Intern Med. 2018 Feb 23. [26] 杨富,方芳,陈兰,等.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染风险预测评分模型的建立与评价[J].护理研究,2017,31(17):2076-2080.[27] Desai D, Desai N, Nightingale P, et al. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is associated with an increased risk of infection after liver transplantation.Liver Transpl. 2003,9(7):754-759.[28] Hashimoto M,Sugawara Y,Tamura S,et al.Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection after living-donor liver transplantation in adults.Transpl Infect Dis.2008;10(2):110-116.[29] Avkan-Oguz V,Ozkardesler S,Unek T,et al.Risk factors for early bacterial infections in liver transplantation.Transplant Proc.2013; 45(3):993-997.[30] 谢秀华,姜英俊,解曼,等.肝移植后早期受者发生感染的危险因素及病原学分析[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2017,38(4):200-205.[31] Shi SH,Kong HS,Jia CK,et al.Risk factors for pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli among liver recipients. Clin Transplant.2010;24(6):758-765.[32] 浦燕萍,顾燕,杨富,等.肝移植患者术后多重耐药鲍曼不动杆菌感染影响因素[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2016,5(3):158-162.[33] Zhong L,Men TY, Li H,et al.Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections after liver transplantation - spectrum and risk factors.J Infect.2012;64(3):299-310.[34] Alonso JC.Pleural effusion in liver disease.Semin Respir Crit Care Med.2010;31(6):698-705.[35] 聂深钰,时宇,高普均.难治性肝性胸水的治疗[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(11):3171-3173.[36] Machicao VI,Balakrishnan M,Fallon MB.Pulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. Hepatology.2014;59(4):1627-1637.[37] Singh A,Bajwa A,Shujaat A.Evidence-based review of the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Respiration. 2013;86(2): 155-173.[38] 杨富.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染风险预测模型的构建[D].上海:上海交通大学,2015. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。
文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。.jpg) 文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。
文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。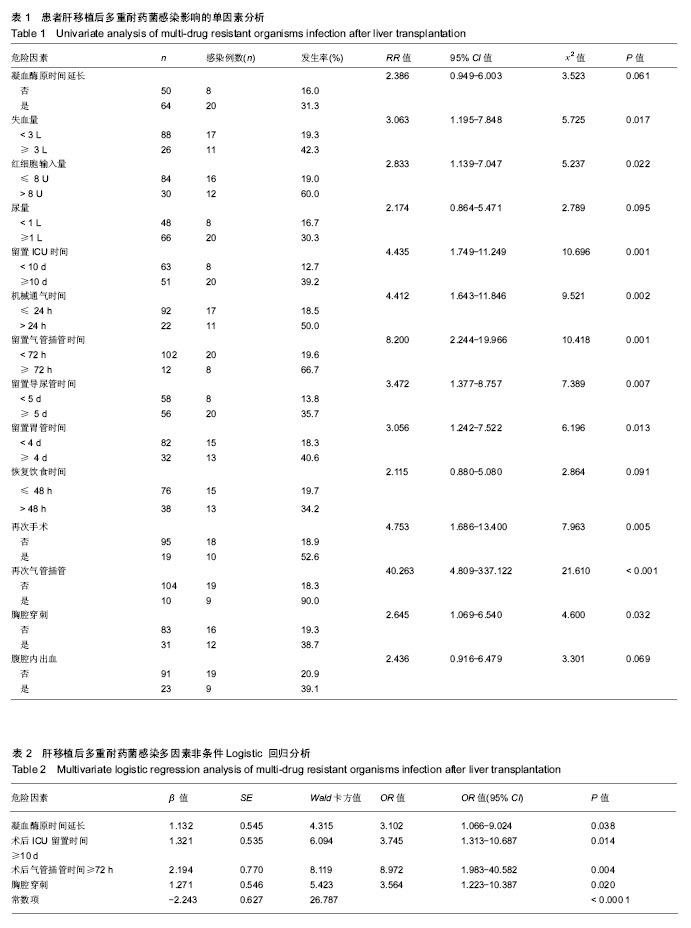
.jpg) 文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。
文题释义:
肝移植(Liver Transplantation):肝移植是指经手术切取一健康肝脏或者部分肝脏,来取代已患不可逆性功能衰竭的终末病肝,以恢复肝脏功能,挽救生命。
多重耐药菌(multi-drug resistance bacteria,MDRO):2015年由中国感染杂志和专家共同发起和制定的《多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识》将多重耐药菌定义为对通常敏感的常用的3类或3类以上抗菌药物同时呈现耐药的细菌。