| [1] Holzapfel BM, Pilge H, Toepfer A, et al. Proximal tibial replacement and alloplastic reconstruction of the extensor mechanism after bone tumor resection. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24(3):247-262. [2] Papagelopoulos PJ, Savvidou OD, Koutsouradis P, et al. three-dimensional technologies in orthopedics. Orthopedics. 2018;41(1):12-20. [3] Lee SW, Kim HG, Ham MJ, et al. Custom implant for reconstruction of mandibular continuity defect. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(6):1370-1376. [4] Mohan Raj R, Priya P, Raj V. Gentam-loaded ceramic-biopolymer dual layer coatings on the Ti with improved bioactive and corrosion resistance properties for orthopedic applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;82:299-309. [5] Heller M, Bauer HK, Goetze E, et al. Applications of patient- specific 3D printing in medicine. Int J Comput Dent. 2016;19(4): 323-339. [6] Gross BC, Erkal JL, Lockwood SY, et al. Evaluation of 3D printing and its potential impact on biotechnology and the chemical sciences. Anal Chem. 2014;86(7):3240-3253. [7] Derby B. Printing and prototyping of tissues and scaffolds. Science. 2012;338(6109):921-926. [8] Farzadi A, Waran V, Solati-Hashjin M, et al. Effect of layer printing delay on mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of 3D printed porous prototypes in bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int. 2015;41(7):8320-8330. [9] Le Cann S, Galland A, Rosa B, et al. Does surface roughness influence the primary stability of acetabular cups? A numerical and experimental biomechanical evaluation. Med Eng Phys. 2014; 36(9):1185-1190. [10] Chikarakara E, Fitzpatrick P, Moore E, et al. In vitro fibroblast and pre-osteoblastic cellular responses on laser surface modified Ti-6Al-4V. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(1):015007. [11] Chang B, Song W, Han TX, et al. Influence of pore size of porous titanium fabricated by vacuum diffusion bonding of titanium meshes on cell penetration and bone ingrowth. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:311-321. [12] Han Q, Qin YG, Zou Y, et al. Novel exploration of 3D printed wrist arthroplasty to solve the severe and complicated bone defect of wrist. Rapid Prototyping J. 2017;23(3):465-473. [13] Luo W, Huang L, Liu H, et al. Customized knee prosthesis in treatment of giant cell tumors of the proximal tibia: application of 3-dimensional printing technology in surgical design. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1691-1700. [14] Variola F, Brunski JB, Orsini G, et al. Nanoscale surface modifications of medically relevant metals: state-of-the art and perspectives. Nanoscale. 2011;3(2):335-353. [15] Fahmy-Garcia S, van Driel M, Witte-Buoma J, et al. NELL-1, HMGB1, and CCN2 enhance migration and vasculogenesis, but not osteogenic differentiation compared to BMP2. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2018;24(3-4):207-218. [16] Boriani F, Fazio N, Fotia C, et al. A novel technique for decellularization of allogenic nerves and in vivo study of their use for peripheral nerve reconstruction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(8):2228-2240. [17] Prosthesi Campana V, Milano G, Pagano E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(10):2445-2461. [18] Hosny HAH, El-Bakoury A, Fekry H, et al. Mid-term results of graft augmentations ii cage and impacted allograft bone in revision hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1487-1493. [19] Waern JM, Yuan Q, Rudrich U, et al. Ectopic expression of murine CD47 minimizes macrophage rejection of human hepatocyte xenografts in immunodeficient mice. Hepatology. 2012;56(4): 1479-1488. [20] Li H, Qu X, Mao Y, et al. Custom Acetabular cages offer stable fixation and improved hip scores for revision tha with severe bone defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(3):731-740. [21] Li HW, Wang L, Mao YQ, et al. Revision of complex acetabular defects using cages with the aid of rapid prototyping. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(10):1770-1775. [22] Berasi CC, Berend KR, Adams JB, et al. Are custom triflange acetabular components effective for reconstruction of catastrophic bone loss? Clin Orthop Relat R. 2015;473(2):528-535. [23] Stoffelen DV, Eraly K, Debeer P. The use of 3D printing technology in reconstruction of a severe glenoid defect: a case report with 2.5 years of follow-up. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2015; 24(8):E218-E222. [24] Fan HB, Fu J, Li XD, et al. Implantation of customized 3-D printed titanium prosthesis in limb salvage surgery: a case series and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:308. [25] Xu N, Wei F, Liu X, et al. Reconstruction of the upper cervical spine using a personalized 3d-printed vertebral body in an adolescent with ewing sarcoma. Spine. 2016;41(1):E50-E54. [26] Phan K, Sgro A, Maharaj MM, et al. Application of a 3D custom printed patient specific spinal implant for C1/2 arthrodesis. J Spine Surg. 2016;2(4):314-318. [27] Choy WJ, Mobbs RJ, Wilcox B, et al. Reconstruction of the thoracic spine using a personalized 3D-printed vertebral body in an adolescent with a T9 primary bone tumour: case report. World Neurosurg. 2017;105:1032. e13-1032. e17. [28] Jaiswal PK, Aston WJS, Grimer RJ, et al. Peri-acetabular resection and endoprosthetic reconstruction for tumours of the acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90B(9):1222-1227. [29] Zoccali C, Skoch J, Patel A, et al. The surgical neurovascular anatomy relating to partial and complete sacral and sacroiliac resections: a cadaveric, anatomic study. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(5):1109-1113. [30] Puchner SE, Funovics PT, Bohler C, et al. Oncological and surgical outcome after treatment of pelvic sarcomas. Plos One. 2017;12(2):e0172203. [31] Kim D, Lim JY, Shim KW, et al. Sacral Reconstruction with a 3D-Printed Implant after Hemisacrectomy in a Patient with Sacral Osteosarcoma: 1-Year Follow-Up Result. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58(2):453-457. [32] Wei R, Guo W, Ji T, et al. One-step reconstruction with a 3D-printed, custom-made prosthesis after total en bloc sacrectomy: a technical note. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(7):1902-1909. [33] Yamamoto K, Yamaguchi S, Matsushita T, et al. Histologic evaluation of bone regeneration using titanium mesh prepared by selective laser melting technique. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2017;26(3): 257-260. [34] Mishra S, Tate MLK. Effect of lacunocanalicular architecture on hydraulic conductance in bone tissue: Implications for bone health and evolution. Anat Rec Part A. 2003;273A(2):752-762. [35] Kujala S, Ryhanen J, Danilov A, et al. Effect of porosity on the osteointegration and bone ingrowth of a weight-bearing nickel-titanium bone graft substitute. Biomaterials. 2003;24(25): 4691-4697. [36] Li GY, Wang L, Pan W, et al. In vitro and in vivo study of additive manufactured porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds for repairing bone defects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34072. [37] Pobloth AM, Checa S, Razi H, et al. Mechanobiologically optimized 3D titanium-mesh scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in critical segmental defects in sheep. Sci Transl Med. 2018; 10(423). pii: eaam8828. [38] Luo DM, Rong QG, Chen Q. Finite-element design and optimization of a three-dimensional tetrahedral porous titanium scaffold for the reconstruction of mandibular defects. Med Eng Phys. 2017;47:176-183. [39] Zhao SF, Wen F, He FM, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the osteogenic ability of implant surfaces with a local delivery of simvastatin. Int J Oral Max Impl. 2014;29(1):211-220. [40] Tan J, Yang N, Fu X, et al. Single-dose local simvastatin injection improves implant fixation via increased angiogenesis and bone formation in an ovariectomized rat model. Med Sci Monitor. 2015; 21:1428-1439. [41] Liu H, Wang C, Li C, et al. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Advances. 2018;8(14):7533-7549. [42] Liu H, Li W, Liu C, et al. Incorporating simvastatin/poloxamer 407 hydrogel into 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds for the promotion of angiogenesis, osseointegration and bone ingrowth. Biofabrication. 2016;8(4):045012. [43] Yin B, Xue BJ, Wu ZH, et al. A novel hybrid 3D-printed titanium scaffold for osteogenesis in a rabbit calvarial defect model. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(2):474-482. [44] Kumar A, Nune KC, Misra RDK. Design and biological functionality of a novel hybrid Ti-6Al-4V/hydrogel system for reconstruction of bone defects. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(4):1133-1144. [45] Kondiah PJ, Choonara YE, Kondiah PP, et al. A review of injectable polymeric hydrogel systems for application in bone tissue engineering. Molecules. 2016;21(11):E1580. [46] Sui BD, Hu CH, Liu AQ, et al. Stem cell-based bone regeneration in diseased microenvironments: Challenges and solutions. Biomaterials. 2017. [47] Cotts KG, Cifu AS. Treatment of osteoporosis. JAMA. 2018; 319(10):1040-1041.[48] Fujiwara S, Zhao X, Teoh C, et al. Disease burden of fractures among patients with osteoporosis in Japan: health-related quality of life, work productivity and activity impairment, healthcare resource utilization, and economic costs. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018. [49] Cheng N, Dai J, Cheng XR, et al. Porous CaP/silk composite scaffolds to repair femur defects in an osteoporotic model. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(8):1963-1975. [50] Kwon BJ, Seon GM, Lee MH, et al. Locally delivered ethyl-2, 5-dihydroxybenzoate using 3d printed bone implant for promotion of bone regeneration in a osteoporotic animal model. Eur Cells Mater. 2018;35:1-12. [51] Ray S, Thormann U, Eichelroth M, et al. Strontium and bisphosphonate coated iron foam scaffolds for osteoporotic fracture defect healing. Biomaterials. 2018;157:1-16.[52] Khadra M. The effect of low level laser irradiation on implant-tissue interaction. In vivo and in vitro studies. Swed Dent J Suppl. 2005;(172):1-63. [53] Fukuhara E, Goto T, Matayoshi T, et al. Optimal low-energy laser irradiation causes temporal G2/M arrest on rat calvarial osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;79(6):443-450. [54] Boldrini C, de Almeida JM, Fernandes LA, et al. Biomechanical effect of one session of low-level laser on the bone-titanium implant interface. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28(1):349-352. [55] de Vasconcellos LMR, Barbara MAM, Rovai ED, et al. Titanium scaffold osteogenesis in healthy and osteoporotic rats is improved by the use of low-level laser therapy (GaAlAs). Lasers Med Sci. 2016;31(5):899-905. [56] Ormianer Z, Block J, Matalon S, et al. The effect of moderately controlled type 2 diabetes on dental implant survival and peri-implant bone loss: a long-term retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(2):389-394. [57] Hu XF, Feng YF, Xiang G, et al. Lactic acid of PLGA coating promotes angiogenesis on the interface between porous titanium and diabetic bone. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(15):2274-2288. [58] Weber DR, Schwartz G. Epidemiology of skeletal health in type 1 diabetes. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016;14(6):327-336. [59] Zhai MM, Jing D, Tong SC, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote in vitro osteoblastogenesis through a Wnt/-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics. 2016; 37(3):152-162. [60] Jing D, Shen GH, Huang JH, et al. Circadian rhythm affects the preventive role of pulsed electromagnetic fields on ovariectomy- induced osteoporosis in rats. Bone. 2010;46(2):487-495. [61] Jing D, Zhai MM, Tong SC, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis and osseointegration of porous titanium implants in bone defect repair through a Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32045. [62] Cai J, Li W, Sun T, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields preserve bone architecture and mechanical properties and stimulate porous implant osseointegration by promoting bone anabolism in type 1 diabetic rabbits. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(5):1177-1191. [63] Jing D, Yan ZD, Cai J, et al. Low-1 level mechanical vibration improves bone microstructure, tissue mechanical properties and porous titanium implant osseointegration by promoting anabolic response in type 1 diabetic rabbits. Bone. 2018, 106:11-21. [64] Stolzing A, Jones E, McGonagle D, et al. Age-related changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: consequences for cell therapies. Mech Ageing Dev. 2008;129(3): 163-173. [65] Schacht VJ, Neumann LV, Sandhi SK, et al. Effects of silver nanoparticles on microbial growth dynamics. J Appl Microbiol. 2013;114(1):25-35. [66] Devlin-Mullin A, Todd NM, Golrokhi Z, et al. Atomic layer deposition of a silver nanolayer on advanced titanium orthopedic implants inhibits bacterial colonization and supports vascularized de novo bone ingrowth. Advanced Healthcare Materials. 2017. [67] Geng H, Poologasundarampillai G, Todd N, et al. Biotransformation of silver released from nanoparticle coated titanium implants revealed in regenerating bone. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9(25):21169-21180. |
.jpg)
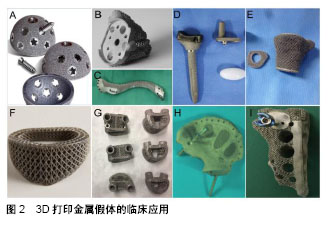
.jpg)
.jpg)