中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5097-5103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0548
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
普伐他汀能否降低早期兔激素诱导性股骨头坏死发生的风险
王小龙1,韩超前1,赵晓娜2,赵建民3,刘 玉3
- 1内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院手足显微外科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010030;内蒙古医科大学附属医院,2儿科,3骨科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010050
Can pravastatin reduce the risk of early stage of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head?
Wang Xiao-long1, Han Chao-qian1, Zhao Xiao-na2, Zhao Jian-min3, Liu Yu3
- 1Department of Hand and Foot Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Pediatrics, 3Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
.jpg) 文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。摘要
背景:研究表明脂质代谢和凝血紊乱以及细胞凋亡与激素性股骨头坏死的发病机制密切相关,而部分研究显示普伐他汀具有降脂、抗凝以及干预骨细胞凋亡的作用。
目的:探讨普伐他汀能否降低早期兔激素诱导性股骨头坏死发生的风险,是否可作为兔激素诱导性股骨头坏死的早期靶向干预药物。
方法:将60只新西兰雄性兔随机分为3组,模型组和干预组各24只,对照组12只。模型组采用激素联合马血清的方法准备激素性股骨头坏死模型,干预组在模型组的基础上给予普伐他汀治疗,对照组注射等量生理盐水,分别于造模第2、4、6周行血脂、凝血指标检测以及MRI检查,随后处死动物,在光镜下观察组织病理学改变,并计算空骨陷窝率,应用TUNEL法检测骨细胞凋亡,并计算凋亡指数。
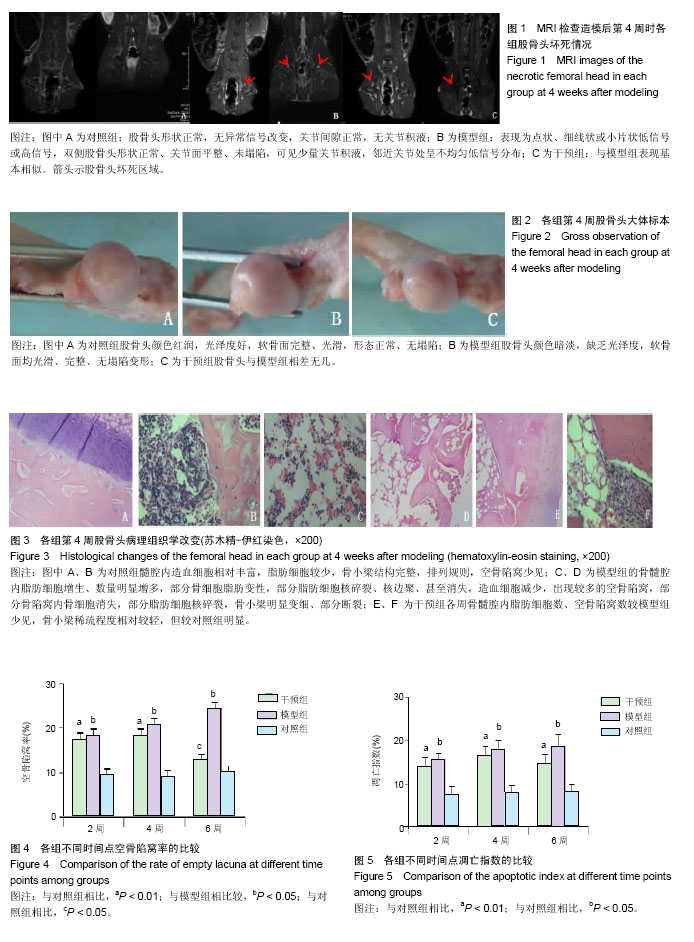
结果与结论:①干预组的大体标本和MRI表现与模型组相比,各周坏死程度相仿,无明显差别;②干预组在第2,4周的胆固醇、三酰甘油及低密度脂蛋白水平高于对照组(P < 0.05),干预组在第6周的胆固醇、三酰甘油及低密度脂蛋白水平明显低于模型组(P < 0.05),但与对照组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05);③各组间不同时间点凝血酶原时间及组织纤维溶酶原激活物水平均无显著性差异(P > 0.05);④病理组织学显示,干预组骨髓腔内脂肪细胞数、空骨陷窝数较模型组少,骨小梁稀疏程度相对较轻。干预组第2,4周的空骨陷窝率高于对照组(P < 0.05),在第6周时,与对照组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),但显著低于模型组(P < 0.05);⑤干预组各时间点的凋亡指数显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),但与模型组相比,无显著差异(P > 0.05);⑥结果显示,普伐他汀不能降低早期兔激素诱导性股骨头坏死发生的风险,尚不能作为兔激素诱导性股骨头坏死早期的有效靶向干预药物。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9376-4653(王小龙)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
文题释义:
普伐他汀:是他汀类中惟一具有亲水性的药物,其不仅具有调节脂肪代谢和促进成骨的作用,而且还有血浆半衰期短、全身不良反应少、蛋白结合率低等优点,可与多种蛋白结合率高的药物联合应用,是临床上应用最广泛的药物。
激素诱导性股骨头坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变。激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。