| [1] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[2] Visweswaran M, Pohl S, Arfuso F, et al. Multi-lineage differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells - To Wnt, or not Wnt. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;68:139-147.[3] Cho DI, Kang WS, Hong MH, et al. The optimization of cell therapy by combinational application with apicidin-treated mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Oncotarget. 2017;8(27):44281-44294.[4] Zang L, Hao H, Liu J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9:36.[5] Satoh A, Brace CS, Ben-Josef G, et al. SIRT1 promotes the central adaptive response to diet restriction through activation of the dorsomedial and lateral nuclei of the hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 2010;30(30):10220-10232.[6] Correia M, Perestrelo T, Rodrigues AS, et al. Sirtuins in metabolism, stemness and differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1861(1 Pt A):3444-3455.[7] Rahman S, Islam R. Mammalian Sirt1: insights on its biological functions. Cell Commun Signal. 2011;9:11.[8] Yuan HF, Zhai C, Yan XL, et al. SIRT1 is required for long-term growth of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012;90(4):389-400.[9] Chen H, Liu X, Chen H, et al. Role of SIRT1 and AMPK in mesenchymal stem cells differentiation. Ageing Res Rev. 2014;13:55-64.[10] Yoon DS, Choi Y, Lee JW. Cellular localization of NRF2 determines the self-renewal and osteogenic differentiation potential of human MSCs via the P53-SIRT1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2093.[11] Buhrmann C, Busch F, Shayan P, et al. Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) is required for promoting chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(32): 22048-22062.[12] Joe IS, Jeong SG, Cho GW. Resveratrol-induced SIRT1 activation promotes neuronal differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Neurosci Lett. 2015;584: 97-102.[13] Agathocleous M, Harris WA. Metabolism in physiological cell proliferation and differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 2013; 23(10):484-492.[14] Bhaskar B, Mekala NK, Baadhe RR, et al. Role of signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;9(6):508-12.[15] Etheridge SL, Spencer GJ, Heath DJ, et al. Expression profiling and functional analysis of wnt signaling mechanisms in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004; 22(5):849-860. [16] Yu SJ, Kim HJ, Lee ES, et al. β-Catenin Accumulation Is Associated With Increased Expression of Nanog Protein and Predicts Maintenance of MSC Self-Renewal. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(2):365-377.[17] Dong YF, Soung do Y, Schwarz EM, et al. Wnt induction of chondrocyte hypertrophy through the Runx2 transcription factor. J Cell Physiol. 2006;208(1):77-86.[18] Quarto N, Behr B, Longaker MT. Opposite spectrum of activity of canonical Wnt signaling in the osteogenic context of undifferentiated and differentiated mesenchymal cells: implications for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(10):3185-3197.[19] Maruyama T, Mirando AJ, Deng CX, et al. The balance of WNT and FGF signaling influences mesenchymal stem cell fate during skeletal development. Sci Signal. 2010;3(123): ra40.[20] He X, Wang H, Jin T, et al. TLR4 Activation Promotes Bone Marrow MSC Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation via Wnt3a and Wnt5a Signaling. PLoS One. 2016;11(3): e0149876.[21] Luo S, Shi Q, Zha Z, et al. Inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human adipose-derived stem cells is necessary for chondrogenic differentiation and maintenance. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013;67(8):819-824.[22] Bermeo S, Al-Saedi A, Kassem M, et al. The Role of the Nuclear Envelope Protein MAN1 in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(12):4425-4435.[23] Brunt KR, Zhang Y, Mihic A, et al. Role of WNT/β-catenin signaling in rejuvenating myogenic differentiation of aged mesenchymal stem cells from cardiac patients. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(6):2067-2078.[24] He Z, Li H, Zuo S, et al. Transduction of Wnt11 promotes mesenchymal stem cell transdifferentiation into cardiac phenotypes. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(10):1771-1778.[25] Belema Bedada F, Technau A, Ebelt H, et al. Activation of myogenic differentiation pathways in adult bone marrow-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(21): 9509-9519.[26] Yu Q, Liu L, Duan Y, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;439(2):297-302.[27] Watabe T, Miyazono K. Roles of TGF-beta family signaling in stem cell renewal and differentiation. Cell Res. 2009;19(1): 103-115.[28] Alfaro MP, Vincent A, Saraswati S, et al. sFRP2 suppression of bone morphogenic protein (BMP) and Wnt signaling mediates mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) self-renewal promoting engraftment and myocardial repair.J Biol Chem. 2010;285(46):35645-35653.[29] Ng F, Boucher S, Koh S, et al. PDGF, TGF-beta, and FGF signaling is important for differentiation and growth of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): transcriptional profiling can identify markers and signaling pathways important in differentiation of MSCs into adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic lineages. Blood. 2008;112(2):295-307.[30] Casado-Díaz A, Anter J, Müller S, et al. Transcriptomic Analyses of Adipocyte Differentiation From Human Mesenchymal Stromal-Cells (MSC). J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232(4):771-784.[31] Grafe I, Alexander S, Peterson JR, et al. TGF-β Family Signaling in Mesenchymal Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 May 15. pii: a022202. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022202. [Epub ahead of print][32] Tseng YH, Kokkotou E, Schulz TJ, et al. New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature. 2008;454(7207):1000-1004.[33] Liao J, Wei Q, Zou Y, et al. Notch Signaling Augments BMP9-Induced Bone Formation by Promoting the Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling Process in Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(5):1905-1923.[34] Song BQ, Chi Y, Li X, et al. Inhibition of Notch Signaling Promotes the Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Autophagy Activation and PTEN-PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):1991-2002.[35] Augello A, De Bari C. The regulation of differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2010;21(10): 1226-1238. [36] Armiñán A, Gandía C, Bartual M, et al. Cardiac differentiation is driven by NKX2.5 and GATA4 nuclear translocation in tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(6):907-918. [37] Lin TH, Gibon E, Loi F, et al. Decreased osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells derived from the aged mouse is associated with enhanced NF-κB activity. J Orthop Res. 2017; 35(2):281-288.[38] Meng X, Cui J, Wang Y, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 interacts with microRNA-34a to promote chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(4):1774-1782.[39] Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2005; 122(6):947-956.[40] Yoon DS, Choi Y, Jang Y, et al. SIRT1 directly regulates SOX2 to maintain self-renewal and multipotency in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(12):3219-3231.[41] Simic P, Zainabadi K, Bell E, et al. SIRT1 regulates differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by deacetylating β-catenin. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(3):430-440.[42] Yoon DS, Choi Y, Choi SM, et al. Different effects of resveratrol on early and late passage mesenchymal stem cells through β-catenin regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;467(4):1026-1032.[43] Zhou H, Shang L, Li X, et al. Resveratrol augments the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in promoting osteoblastic differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(17):2953-2962.[44] Huang XZ, Wen D, Zhang M, et al. Sirt1 activation ameliorates renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(5):996-1005.[45] Kume S, Haneda M, Kanasaki K, et al. SIRT1 inhibits transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells via Smad7 deacetylation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(1):151-158.[46] Xu Y, Wang S, Tang C, et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA HIF 1α-anti-sense 1 induced by transforming growth factor-β-mediated targeting of sirtuin 1 promotes osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(5):7233-7238.[47] Bäckesjö CM, Li Y, Lindgren U, et al. Activation of Sirt1 decreases adipocyte formation during osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(7):993-1002.[48] Said RS, El-Demerdash E, Nada AS, et al. Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory signaling implicated in ionizing radiation-induced premature ovarian failure through antagonistic crosstalk between silencing information regulator 1 (SIRT1) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1). Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;103:140-150. [49] Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J, et al. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell Signal. 2013;25 (10):1939-1948. |
.jpg)

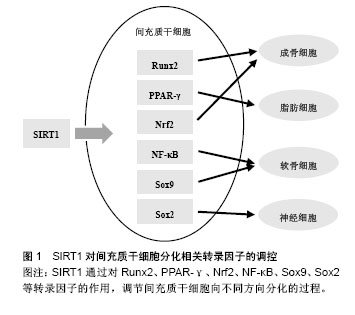
.jpg)