| [1] Yang JF, Cao HC, Pan QL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord ameliorate fulminant hepatic failure and increase survival in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14(2):186-193.[2] Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.[3] Hong SH, Gang EJ, Jeong JA, et al. In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330(4):1153-1161.[4] Campard D, Lysy PA, Najimi M, et al. Native umbilical cord matrix stem cells express hepatic markers and differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(3):833-848.[5] Zhang L, Zhao YH, Guan Z, et al. Application potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly in liver tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl): 137-143.[6] An SY, Han J, Lim HJ, et al. Valproic acid promotes differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells from whole human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Cell. 2014;46(2):127-135.[7] Zhang YN, Lie PC, Wei X. Differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly into hepatocyte-like cells. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):548-558.[8] Anzalone R, Lo Iacono M, Corrao S, et al. New emerging potentials for human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells: immunological features and hepatocyte-like differentiative capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):423-438.[9] Cui L, Zhou X, Li J, et al. Dynamic microRNA profiles of hepatic differentiated human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44737.[10] Liang XJ, Chen XJ, Yang DH, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells by hTERT gene transfection in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(2): 215-221.[11] Cui L, Shi Y, Zhou X, et al. A set of microRNAs mediate direct conversion of human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e918.[12] Xue G, Han X, Ma X, et al. Effect of Microenvironment on Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Hepatocytes In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8916534.[13] Herencia C, Martínez-Moreno JM, Herrera C, et al. Nuclear translocation of β-catenin during mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into hepatocytes is associated with a tumoral phenotype. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34656.[14] García-Castro MI, Marcelle C, Bronner-Fraser M. Ectodermal Wnt function as a neural crest inducer. Science. 2002;297(5582): 848-851.[15] Fagotto F. Looking beyond the Wnt pathway for the deep nature of β-catenin. EMBO Rep. 2013;14(5):422-433.[16] Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky-Shapiro II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381-390.[17] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[18] He H, Nagamura-Inoue T, Takahashi A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Int J Hematol. 2015;102(3): 368-378.[19] Zahari W, Hashim SN, Yusof MF, et al. Immunomodulatory Effect of Cytokines in the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(3):197-206.[20] Doan CC, Le TL, Hoang NS, et al. Differentiation of umbilical cord lining membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells into endothelial-like cells. Iran Biomed J. 2014;18(2):67-75.[21] Robinson AP, Foraker JE, Ylostalo J, et al. Human stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow enhance glial differentiation of rat neural stem cells: a role for transforming growth factor β and Notch signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(2): 289-300.[22] Pattabhi SR, Lehaf AM, Schlenoff JB, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell osteoblast differentiation, ECM deposition, and biomineralization on PAH/PAA polyelectrolyte multilayers. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(5):1818-1827.[23] Qian SW, Li X, Zhang YY, et al. Characterization of adipocyte differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow. BMC Dev Biol. 2010;10:47.[24] Esmaeli S, Allameh A, Adelipour M, et al. The impact of oxidative DNA changes and ATM expression on morphological and functional activities on hepatocytes obtained from mesenchymal stem cells. Biologicals. 2017;47:52-58.[25] Haegele L, Ingold B, Naumann H, et al. Wnt signalling inhibits neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells by controlling bone morphogenetic protein expression. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003; 24(3):696-708.[26] Aubert J, Dunstan H, Chambers I, et al. Functional gene screening in embryonic stem cells implicates Wnt antagonism in neural differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20(12):1240-1245.[27] Ke Z, Zhou F, Wang L, et al. Down-regulation of Wnt signaling could promote bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(2):342-348.[28] Yoshida Y, Shimomura T, Sakabe T, et al. A role of Wnt/beta-catenin signals in hepatic fate specification of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;293(5):G1089-1098.[29] Ren S, Johnson BG, Kida Y,et al. LRP-6 is a coreceptor for multiple fibrogenic signaling pathways in pericytes and myofibroblasts that are inhibited by DKK-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(47):E7643-E7644.[30] Yamamoto H, Sakane H, Yamamoto H, et al. Wnt3a and Dkk1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell. 2008;15(1):37-48. |
.jpg)
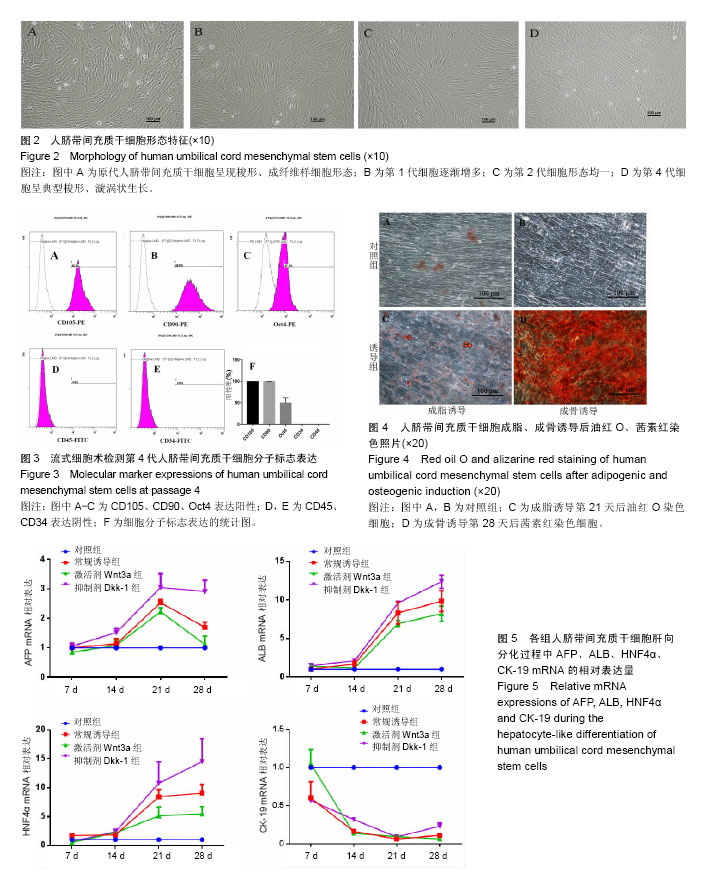
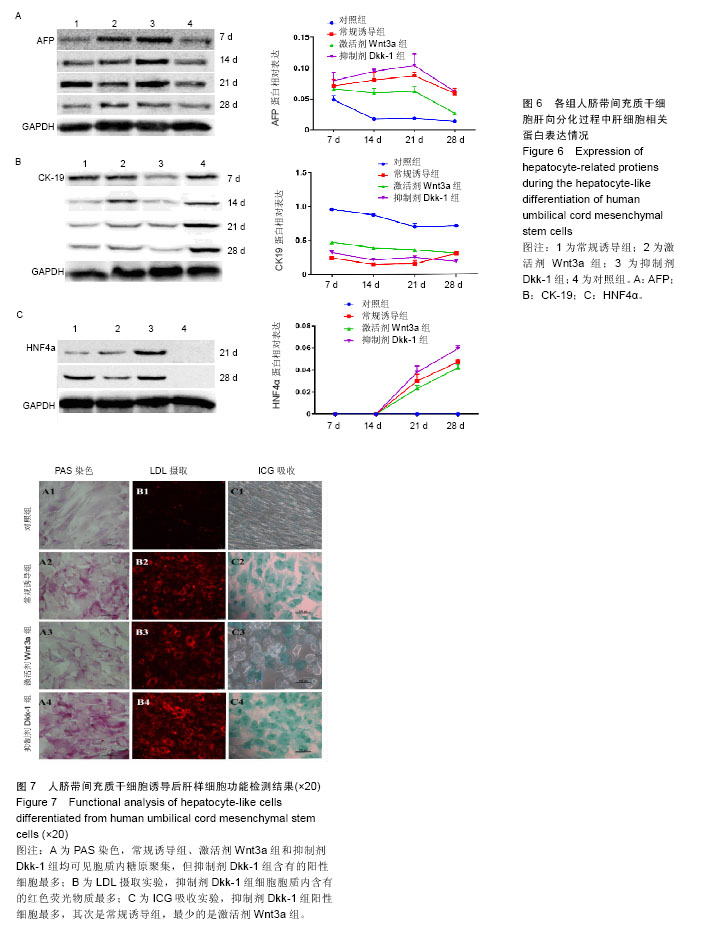
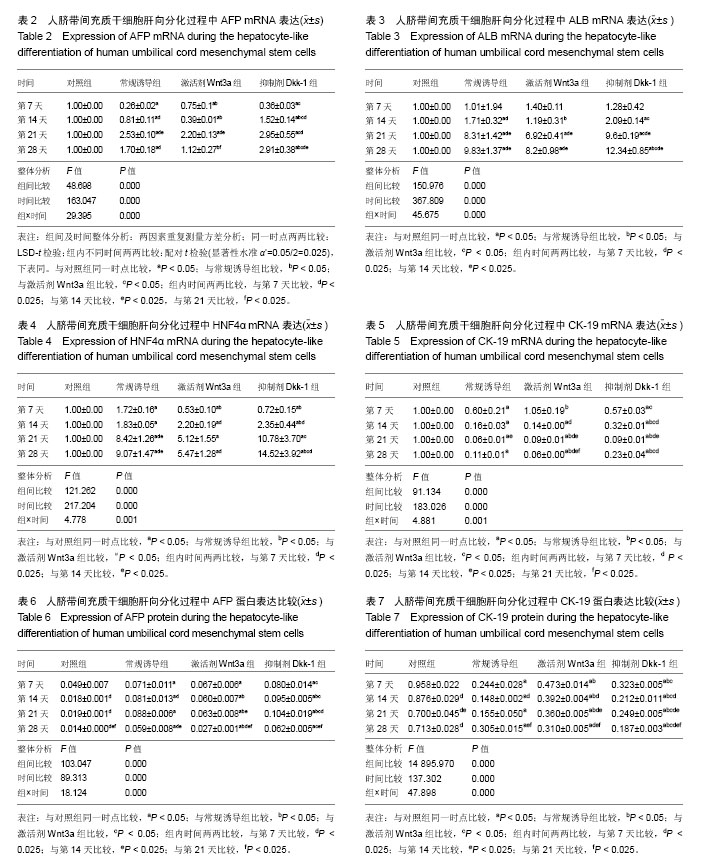
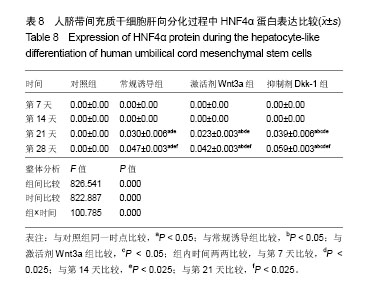
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)