| [1] GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117-171.[2] Wang W, Jiang B, Sun H, et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China: Results from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey of 480 687 Adults. Circulation. 2017;135(8):759-771.[3] Ning M, Sarracino DA, Buonanno FS, et al. Proteomic Protease Substrate Profiling of tPA Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Step Toward Individualizing Thrombolytic Therapy at the Bedside. Transl Stroke Res. 2010;1(4):268-275.[4] Cramer SC, Stradling D, Brown DM, et al. Organization of a United States county system for comprehensive acute stroke care. Stroke. 2012;43(4):1089-1093.[5] van Velthoven CT, Dzietko M, Wendland MF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate MRI-identifiable injury, protect white matter, and improve long-term functional outcomes after neonatal focal stroke in rats. J Neurosci Res. 2017;95(5):1225-1236.[6] Oh SH, Choi C, Chang DJ, et al. Early neuroprotective effect with lack of long-term cell replacement effect on experimental stroke after intra-arterial transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(8):1090-1103.[7] Liao W, Xie J, Zhong J, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat model of stroke. Transplantation. 2009;87(3):350-359.[8] 朱尧,汪青松,黄海丽,等.脐带血间充质干细胞改善兔脑梗死神经生长因子和神经元凋亡的研究[J].中华老年心血管病杂志,2013,15(12): 1316-1320.[9] 中华医学会第四次脑血管病学术会议组:各类脑血管疾病诊断要点[J].中华神经科杂志,1996,29(6):379-380.[10] Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(5):541-553.[11] Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005;57(6): 874-882.[12] Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1099-1106.[13] 孟宪国,朱士文,高华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死:6个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(32):6374-6378.[14] 陈文斗,李江涛,张效北,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死临床分析[J].吉林医学,2012,33(21):4522.[15] 何振东.骨髓间充质干细胞移植改善脑梗死患者神经功能机制研究[J].亚太传统医药,2012,8(12):126-127.[16] 胡晴,曹梦莹,李瑞芳,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的安全性与有效性[J].武汉大学学报医学版,2013,34(1):57-60.[17] 冯?,田国萍,李莉,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的临床疗效研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2014,22(1):28-30.[18] 谢旭芳,刘诗英,金光华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床分析[J].检验医学与临床,2014,11(21): 2955-2957.[19] 刘定华,韩伯军,洪珊珊,等.自体骨髓间充质神经干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(6):425-428.[20] 沈大鹏.脐带间充质干细胞早期单次移植治疗对急性脑梗死的神经功能恢复[J].中国伤残医学,2015,23(2):26-28.[21] Packham DK, Fraser IR, Kerr PG, et al. Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells (MPC) in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Dose Escalation Study. EBioMedicine. 2016; 12:263-269.[22] Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388 (10051):1281-1290.[23] Qin HL, Zhu XH, Zhang B, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation After Angioplasty for Diabetic Foot. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2016;124(8):497-503.[24] Bai L, Li D, Li J, et al. Bioactive molecules derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Histochem. 2016;118(8): 761-769.[25] Vu Q, Xie K, Eckert M, et al. Meta-analysis of preclinical studies of mesenchymal stromal cells for ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2014;82(14):1277-1286.[26] 刘超,吴海琴,严璞,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗缺血性卒中疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2015,15(6): 659-663.[27] Jeong H, Yim HW, Cho YS, et al. Efficacy and safety of stem cell therapies for patients with stroke: a systematic review and single arm meta-analysis. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2):63-69. |
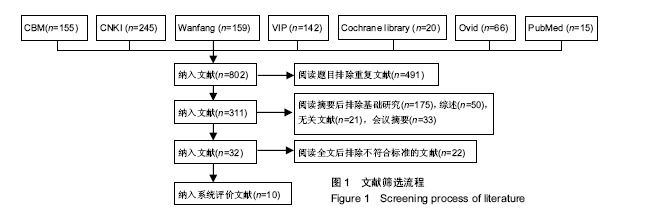
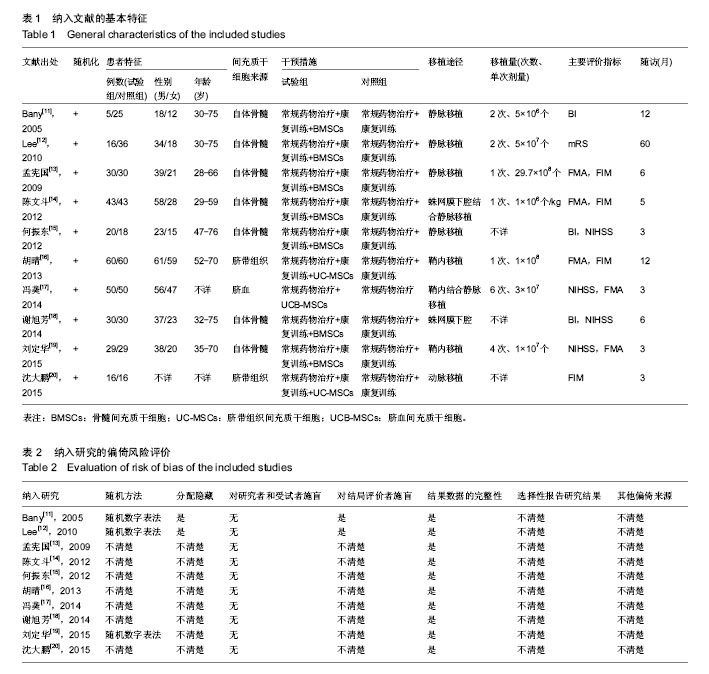
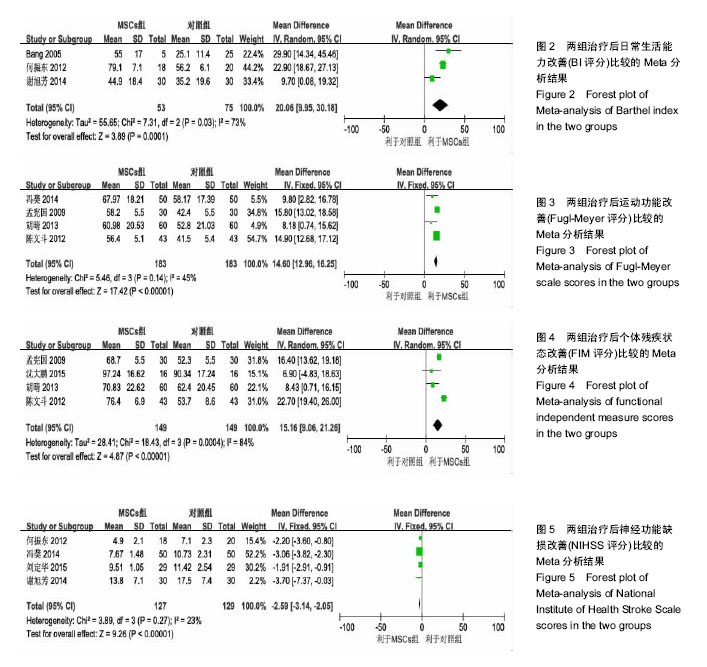
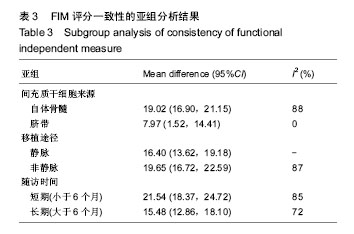
.jpg)
.jpg)