| [1] Zeldenrust S, Gertz M, Uemichi T, et al. Orthotopic liver transplantation for hereditary fibrinogen amyloidosis. Transplantation. 2003;75(4):560-561.[2] Rhim JA, Sandgren EP, Palmiter RD, et al. Complete reconstitution of mouse liver with xenogeneic hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(11):4942-4946.[3] Pietrosi G, Vizzini GB, Gruttadauria S, et al. Clinical applications of hepatocyte transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(17):2074-2077.[4] Ishii T, Yasuchika K, Machimoto T, et al. Transplantation of embryonic stem cell-derived endodermal cells into mice with induced lethal liver damage. Stem Cells. 2007;25(12): 3252-3260. [5] Yap KK, Dingle AM, Palmer JA, et al. Enhanced liver progenitor cell survival and differentiation in vivo by spheroid implantation in a vascularized tissue engineering chamber. Biomaterials. 2013;34(16):3992-4001. [6] Franco OE, Shaw AK, Strand DW, et al. Cancer associated fibroblasts in cancer pathogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21(1):33-39.[7] Folkman J, Kalluri R. Cancer without disease.Nature. 2004; 427(6977):787.[8] Gordillo M, Evans T, Gouon-Evans V. Orchestrating liver development. Development. 2015;142(12):2094-2108. [9] Suzuki K, Tanaka M, Watanabe N, et al. p75 Neurotrophin receptor is a marker for precursors of stellate cells and portal fibroblasts in mouse fetal liver. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1): 270-281.e3.[10] Tanimizu N, Saito H, Mostov K, et al. Long-term culture of hepatic progenitors derived from mouse Dlk+ hepatoblasts. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 26):6425-6434.[11] Cheng K, Benten D, Bhargava K, et al. Hepatic targeting and biodistribution of human fetal liver stem/progenitor cells and adult hepatocytes in mice. Hepatology. 2009;50(4):1194-1203.[12] Chen L, Davis GJ, Crabb DW, et al. Intrasplenic transplantation of isolated periportal and perivenous hepatocytes as a long-term system for study of liver-specific gene expression. Hepatology. 1994;19(4):989-998.[13] Martins PN, Theruvath TP, Neuhaus P. Rodent models of partial hepatectomies. Liver Int. 2008;28(1):3-11.[14] Sancho-Bru P, Najimi M, Caruso M, et al. Stem and progenitor cells for liver repopulation: can we standardise the process from bench to bedside. Gut. 2009;58(4):594-603.[15] Duncan AW, Dorrell C, Grompe M. Stem cells and liver regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(2):466-481.[16] Zhang W, Tucker-Kellogg L, Narmada BC, et al. Cell-delivery therapeutics for liver regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010; 62(7-8):814-826.[17] Kalinichenko VV, Bhattacharyya D, Zhou Y, et al. Foxf1 +/- mice exhibit defective stellate cell activation and abnormal liver regeneration following CCl4 injury. Hepatology. 2003; 37(1): 107-117.[18] Onitsuka I, Tanaka M, Miyajima A. Characterization and functional analyses of hepatic mesothelial cells in mouse liver development. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(4):1525-1535.[19] Yasui O, Miura N, Terada K, et al. Isolation of oval cells from Long-Evans Cinnamon rats and their transformation into hepatocytes in vivo in the rat liver. Hepatology. 1997;25(2): 329-334.[20] Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med. 2011;17(11): 1359-1370. [21] Liu D, Xiao H, Du C, et al. The effect of fibroblast activation on vascularization in transplanted pancreatic islets. J Surg Res. 2013;183(1):450-456.[22] Cai J, Ito M, Nagata H, et al. Treatment of liver failure in rats with end-stage cirrhosis by transplantation of immortalized hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2002;36(2):386-394.[23] Gupta S, Vemuru RP, Lee CD, et al. Hepatocytes exhibit superior transgene expression after transplantation into liver and spleen compared with peritoneal cavity or dorsal fat pad: implications for hepatic gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1994;5(8):959-967.[24] Ahmad TA. Study of the survival of hepatocytes transplanted to the spleen in rats. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58 (107-108): 892-895.[25] 万真,张晓刚,郑幸龙,等. 异种肝前体细胞移植治疗急性肝损伤大鼠[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(53): 9132-9138.[26] Pintilie DG, Shupe TD, Oh SH, et al. Hepatic stellate cells' involvement in progenitor-mediated liver regeneration. Lab Invest. 2010;90(8):1199-1208.[27] Clotman F, Jacquemin P, Plumb-Rudewiez N, et al. Control of liver cell fate decision by a gradient of TGF beta signaling modulated by Onecut transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2005; 19(16):1849-1854.[28] Zong Y, Stanger BZ. Molecular mechanisms of bile duct development. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43(2):257-264.[29] Suzuki A, Iwama A, Miyashita H, et al. Role for growth factors and extracellular matrix in controlling differentiation of prospectively isolated hepatic stem cells. Development. 2003; 130(11):2513-2524.[30] Iwama A, Osawa M, Hirasawa R, et al. Reciprocal roles for CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) and PU.1 transcription factors in Langerhans cell commitment. J Exp Med. 2002;195(5):547-558. |
.jpg)
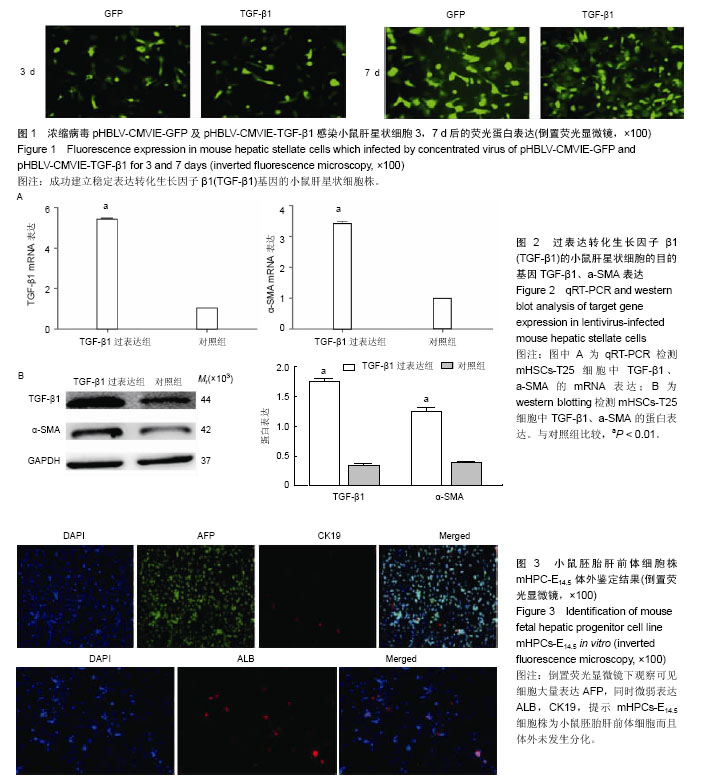
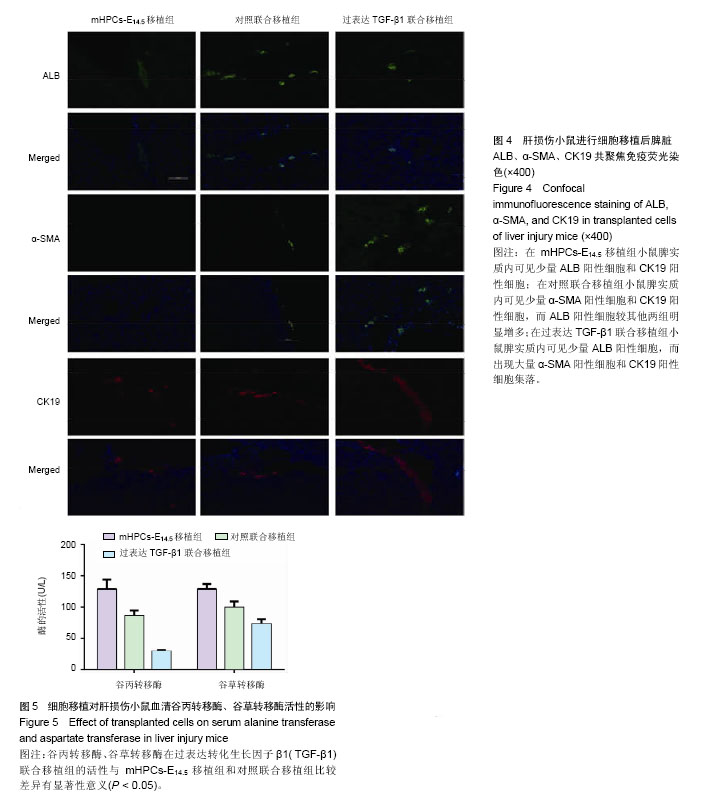
.jpg)
.jpg)