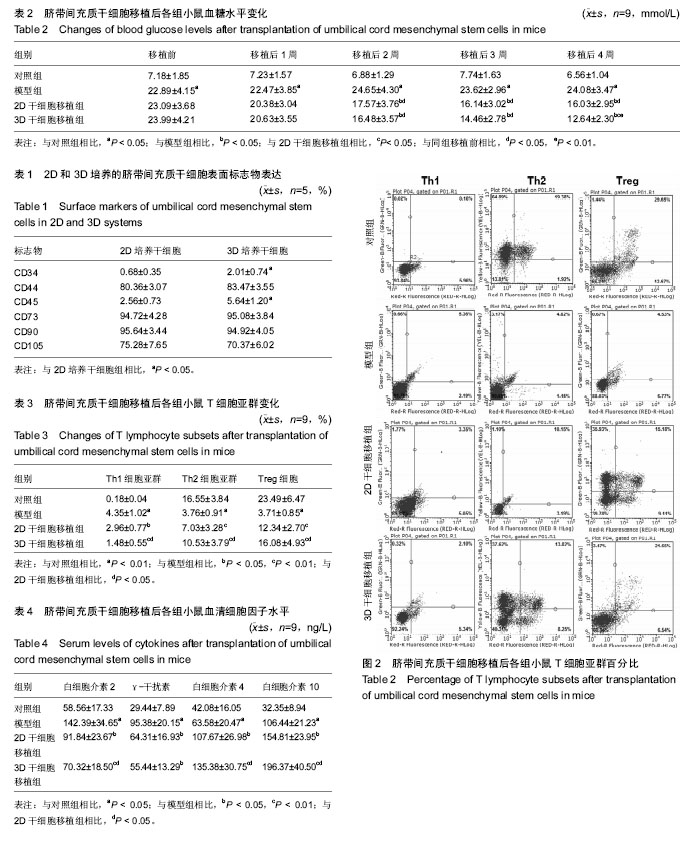
| [1] Handorf AM, Sollinger HW, Alam T. Insulin gene therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Transplant. 2015;13 Suppl 1:37-45.[2] Morgan E, Halliday SR, Campbell GR, et al. Vaccinations and childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetologia. 2016;59(2):237-243.[3] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2004;27 Suppl 1:S5-S10.[4] 郝永蕾,朱旅云,王更银,等.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞实验研究[J].临床误诊误治,2010,23(9):804-807.[5] 申义,王意忠,时瀚,等.人脐带间充质干细胞分化胰岛样细胞过程中胰岛素和巢蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(50): 7500-7506.[6] Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Bonner-Weir S. Stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6(3):139-148.[7] Hu J, Yu X, Wang Z, et al. Long term effects of the implantation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord for newly-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J. 2013;60(3):347-357.[8] 贾晓蕾,沈山梅,李莉蓉,等. 异体间充质干细胞移植治疗酮症起病1型糖尿病的临床疗效[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2015, 7(7):425-430.[9] He B, Li X, Yu H, et al. Therapeutic potential of umbilical cord blood cells for type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes. 2015;7(6): 762-773.[10] Liu S, Yuan M, Hou K, et al. Immune characterization of mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and derived cartilage cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;278(1-2):35-44. [11] Yang H, Sun J, Li Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress proliferation of PHA-activated lymphocytes in vitro by inducing CD4(+)CD25(high)CD45RA(+) regulatory T cell production and modulating cytokine secretion. Cell Immunol. 2016;302:26-31. [12] Vellasamy S, Sandrasaigaran P, Vidyadaran S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells of human placenta and umbilical cord suppress T-cell proliferation at G0 phase of cell cycle. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(3):250-256.[13] Braghirolli DI, Zamboni F, Acasigua GA, et al. Association of electrospinning with electrospraying: a strategy to produce 3D scaffolds with incorporated stem cells for use in tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:5159-5169.[14] González S, Mei H, Nakatsu MN, et al. A 3D culture system enhances the ability of human bone marrow stromal cells to support the growth of limbal stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res. 2016;16(2):358-364.[15] Rath SN, Nooeaid P, Arkudas A, et al. Adipose- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells display different osteogenic differentiation patterns in 3D bioactive glass-based scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E497-E509.[16] Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(3):211-224.[17] Ferlin KM, Prendergast ME, Miller ML, et al. Influence of 3D printed porous architecture on mesenchymal stem cell enrichment and differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2016;32:161-169.[18] Li SL, Liu Y, Hui L. Construction of engineering adipose-like tissue in vivo utilizing human insulin gene-modified umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(12):E267-275.[19] Qin Y, He YH, Hou N, et al. Sonic hedgehog improves ischemia-induced neovascularization by enhancing endothelial progenitor cell function in type 1 diabetes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;423:30-39.[20] Colomeu TC, Figueiredo D, Cazarin CB, et al. Antioxidant and anti-diabetic potential of Passiflora alata Curtis aqueous leaves extract in type 1 diabetes mellitus (NOD-mice). Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;18(1):106-115.[21] Grisé KN, Olver TD, McDonald MW, et al. High Intensity Aerobic Exercise Training Improves Deficits of Cardiovascular Autonomic Function in a Rat Model of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus with Moderate Hyperglycemia. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016: 8164518. [22] 付清松, 夏玉军, 张明, 等. 三维球体间充质干细胞移植对大鼠缺血再灌注损伤脑组织TNF-α及凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响[J].第二军医大学学报, 2015,36(8):845-850.[23] Antebi B, Zhang Z, Wang Y, et al. Stromal-cell-derived extracellular matrix promotes the proliferation and retains the osteogenic differentiation capacity of mesenchymal stem cells on three-dimensional scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(2):171-181. [24] Occhetta P, Centola M, Tonnarelli B, et al. High-Throughput Microfluidic Platform for 3D Cultures of Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Towards Engineering Developmental Processes. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10288.[25] Papadimitropoulos A, Piccinini E, Brachat S, et al. Expansion of human mesenchymal stromal cells from fresh bone marrow in a 3D scaffold-based system under direct perfusion. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102359.[26] Caron I, Rossi F, Papa S, et al. A new three dimensional biomimetic hydrogel to deliver factors secreted by human mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2016;75:135-147.[27] Li Y, Guo G, Li L, et al. Three-dimensional spheroid culture of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promotes cell yield and stemness maintenance. Cell Tissue Res. 2015; 360(2):297-307.[28] Rodina AV, Tenchurin TK, Saprykin VP, et al. Migration and Proliferative Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in 3D Polylactide Scaffolds Depends on Cell Seeding Technique and Collagen Modification. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2016;162(1):120-126. [29] Zheng Z, Shen W, Le H, et al. Three-dimensional parallel collagen scaffold promotes tendon extracellular matrix formation. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;45(2):120-125.[30] Shami A, Gonçalves I, Hultgårdh-Nilsson A. Collagen and related extracellular matrix proteins in atherosclerotic plaque development. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014;25(5):394-399.[31] 刘锐,刘畅,殷甜甜. 三维培养下化学方法诱导肌源性干细胞向胰岛素分泌细胞分化的研究[J]. 辽宁医学学报, 2016,37(1):4-7.[32] Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W, et al. TH1/TH2 cell differentiation and molecular signals. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;841:15-44.[33] Perez-Mazliah D, Langhorne J. CD4 T-cell subsets in malaria: TH1/TH2 revisited. Front Immunol. 2015;5:671.[34] Matsuzaki J, Tsuji T, Imazeki I, et al. Immunosteroid as a regulator for Th1/Th2 balance: its possible role in autoimmune diseases.Autoimmunity. 2005;38(5):369-375.[35] Raz I, Eldor R, Naparstek Y. et al. Immune modulation for prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus.Trends Biotechnol. 2005;23(3):128-134.[36] Heurtier AH, Boitard C.T-cell regulation in murine and human autoimmune diabetes: the role of TH1 and TH2 cells. Diabetes Metab. 1997;23(5):377-385.[37] Haritha C, Shankar V, Trivedi HL, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation with Non-myeloablative Conditioning for Type I Diabetes Mellitus : Lab to Clinic. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2009; 75(3) :S486-S487.[38] Masteller EL, Tang Q, Bluestone JA. Antigen-specific regulatory T cells--ex vivo expansion and therapeutic potential. Semin Immunol. 2006;18(2):103-110.[39] Tan T, Xiang Y, Chang C, et al. Alteration of regulatory T cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014;47(2):234-243.[40] Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL, et al. Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(46):17438-17443. |
.jpg)

.jpg)