| [1] Schindeler A, McDonald MM, Bokko P, et al. Bone remodeling during fracture repair: The cellular picture. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008;19(5): 459-466.[2] Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 200;407(6801):249-257.[3] Lee SH, Coger RN, Clemens MG. Antioxidant functionality in hepatocytes using the enhanced collagen extracellular matrix under different oxygen tensions. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(10):2825-2834.[4] Kneser U, Stangenberg L, Ohnolz J, et al. Evaluation of processed bovine cancellous bone matrix seeded with syngenic osteoblasts in a critical size calvarial defect rat model. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(3): 695-707.[5] Zelzer E, Olsen BR. Multiple roles of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;65:169-187.[6] Unger RE, Sartoris A, Peters K, et al. Tissue-like self-assembly in cocultures of endothelial cells and osteoblasts and the formation of microcapillary-like structures on three-dimensional porous biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2007;28(27):3965-3976.[7] 李彪.VEGF 165基因修饰HUVECs复合BMSCs促组织工程骨血管生成的体外实验研究[D].泸州:四川医科大学,2015:1-59.[8] Kubota Y, Kishi K, Satoh H, et al. Transplanted endothelial progenitor cells augment the survival areas of rat dorsal flaps. Cell Transplant. 2003;12(6):647-657.[9] Devine SM. Mesenchymal stem cells: will they have a role in the clinic. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2002;38:73-9.[10] Minguell JJ, Conget P, Erices A. Biology and clinical utilization of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000;33(8): 881-887.[11] 冯祥生,潘银根,谭家驹,等.异种(猪)脱细胞真皮与自体表皮复合移植研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2000,16(1):41-43,69.[12] Ryan JW, Ryan US. Endothelial surface enzymes and the dynamic processing of plasma substrates. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1984;26:1-43.[13] Grellier M, Ferreira-Tojais N, Bourget C, et al. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the communication between human osteoprogenitors and endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(3): 390-398.[14] Guillotin B, Bareille R, Bourget C, et al. Interaction between human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human osteoprogenitors triggers pleiotropic effect that may support osteoblastic function. Bone. 2008; 42(6):1080-1091.[15] Li H, Daculsi R, Grellier M, et al. Role of neural-cadherin in early osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells cocultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;299(2):C422-430.[16] Villars F, Bordenave L, Bareille R, et al. Effect of human endothelial cells on human bone marrow stromal cell phenotype: role of VEGF. J Cell Biochem. 2000;79(4):672-685.[17] Grellier M, Bordenave L, Amédée J. Cell-to-cell communication between osteogenic and endothelial lineages: implications for tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2009;27(10):562-571.[18] Grellier M, Granja PL, Fricain JC, et al. The effect of the co-immobilization of human osteoprogenitors and endothelial cells within alginate microspheres on mineralization in a bone defect. Biomaterials. 2009;30(19):3271-3278.[19] Kaigler D, Krebsbach PH, Polverini PJ, et al. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone marrow stromal cell modulation of endothelial cells. Tissue Eng. 2003;9(1):95-103.[20] Kaigler D, Krebsbach PH, West ER, et al. Endothelial cell modulation of bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic potential. FASEB J. 2005; 19(6):665-667.[21] Xu J, Liu X, Chen J, et al. Cell-cell interaction promotes rat marrow stromal cell differentiation into endothelial cell via activation of TACE/TNF-alpha signaling. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(1):43-53. |
.jpg)
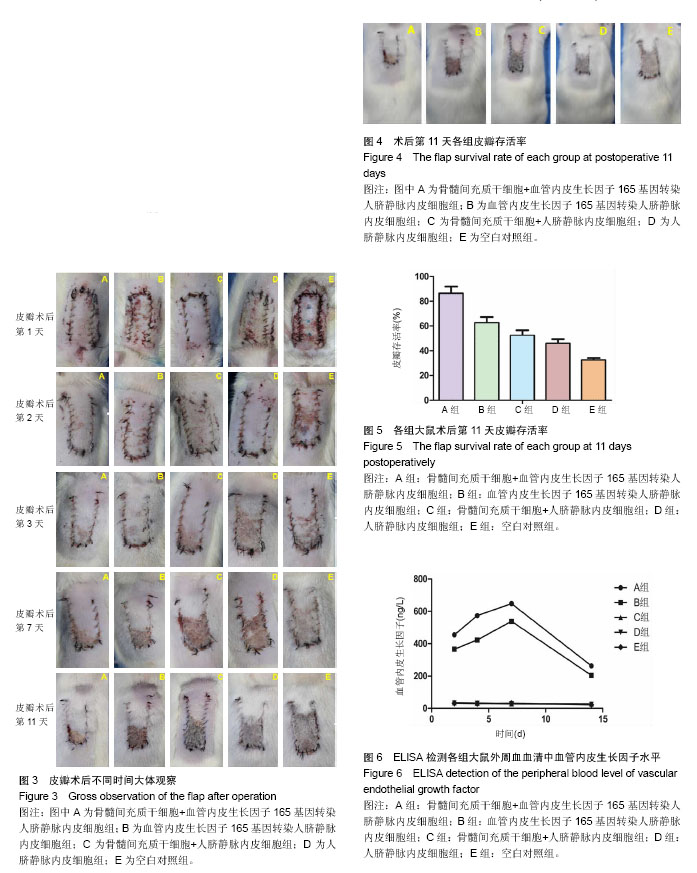
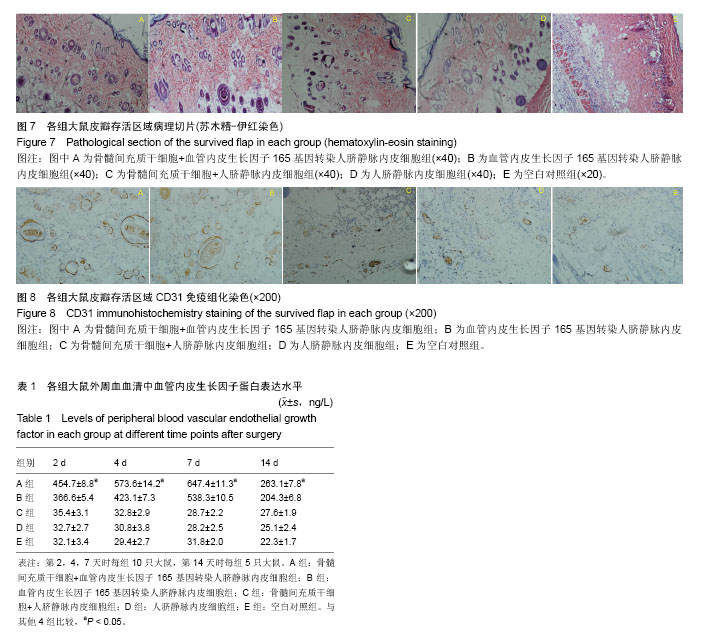
.jpg)
.jpg)